
|
|
Jupyter Notebook is an open-source framework that comes under Anaconda software. It is a free cloud-based interactive platform used for computing in different types of languages. It is used for data analysis, visualizations, numerical calculations and simulations, equations, executing codes, machine learning, and sharing data easily. So, while performing any of such tasks, you may have encountered some errors at some point in time. One such error is the kernel error in Jupyter Notebook. This issue can be frustrating, especially when you are working on an important project and have to deal with some critical datasets. In this article, we will be reading about the basic concepts of kernels and their various causes for errors. Also, we will see some of the specific scenarios that arise due to kernel errors, along with their diagnostic ways and troubleshooting techniques or steps that can be taken to identify and remove such errors. Moreover, we will also deal with working with alternative kernels. What is a kernel?Generally, the term “kernel” has several meanings depending on the context. Conceptually, a “kernel” often refers to a core component of an operating system (eg: Windows, Linux, MacOS) or a foundational part of certain software computing systems. It serves as an intermediary or a bridge between hardware and software, manages all the system resources, and provides essential services for running the processes. Coming to its relation with the Jupyter Notebook, acts as an engine that does all the computations for the codes written in the cells in specific programming languages such as Python, R, Perl, etc. It interprets the results and then, communicates it back to the notebook interface. What is a kernel Error?While working with the kernel on any platform, it’s very obvious that we may sometimes encounter some errors. These errors are called kernel errors. A kernel error is an error that occurs when the kernel of your program crashes or becomes unresponsive while executing any code due to an error. Why Does a Kernel Error Happen?There are several reasons why a kernel error may occur. Here are some of the most common causes:
If you encounter such issues and errors. then no need to panic. Because if there is a problem, there has to be a solution for it. How to Fix Kernel Error in Jupyter Notebook?Below are some of the steps which you may take to diagnose the problems related to kernel. 1. Update AnacondaSince we all know that Jupyter Notebook is a framework of Anaconda software, so, first step is to deal with Anaconda. You can update Anaconda by opening the Anaconda Navigator and clicking on the “Update” button next to the Anaconda distribution, or you can use the following command in your terminal: conda update anaconda
2. Update JupyterNotebookNext, you may need to update your Jupyter Notebook to the latest version. To update Jupyter Notebook, use the “pip install –upgrade jupyter” command in the terminal. This will install the latest version of Jupyter Notebook and fix any issues with the installation. pip install –upgrade jupyter
3. Restart the KernelThe next step which you may take is to restarting your Jupyter Notebook’s kernel. You may do this by choosing the “Restart Kernel” option under the “Kernel” menu from the notebook toolbar.
4. Reinstall the kernelThe next step is to reinstall the kernel. To do this, go to the “Kernel” menu in the notebook and click on “Restart & Clear Output”. Next, go to the “Kernel” menu again and click on “Change kernel”. Finally, select the kernel you want to use and click on “Set Kernel“.
5. Check for any of the conflicting Packages or SoftwareConflicts with other packages can occasionally result in kernel faults. Use the “pip list” command in the terminal to view all the installed packages and their versions and to check for conflicts. Look for any incompatible or out-of-date packages that require updating.
There are certain factors which leads to such conflicts. For example, dependency issues which may arise due to any latest updates or any software installation. But, it can be addressed with the help of some package management tools like ‘apt’, ‘yum’ or ‘dnf’ to check for any broken dependencies. And, afterwards, this may lead to upgrading or downgrading the specific packages to their compatible versions. Moreover, if one has installed any third party drivers for hardware components such as graphics card or wifi, they need to check their compatibility too with the system’s kernel. Uninstalling or disabling problematic drivers or checking the hardware manufacturer’s website for updated drivers may help in resolving the conflicts between them. Also, some of the kernel errors are related to conflicts between loaded kernel modules. One can investigate loaded modules using the lsmod command.
On the other hand, if one has multiple versions of Python or packages installed on its system, then, this may also lead to kernel crash or errors. So, to deal with this, one can create a new virtual environment using virtual environment managers like Anaconda or Virtualenv on its system, which will isolate Python and the packages from other versions installed on the computer. 6. Check for any Errors in CodeThe next step is to check the code for faults if restarting the kernel does not resolve the issue. Check for syntax errors, missing parenthesis, and other typical coding issues. To test if the error still occurs, you may also try executing the code in a different environment. 7. Check Memory UsageMemory problems are another frequent reason for kernel faults. Too much memory usage by your code can result in a kernel crash. Use the Python “psutil” module to view the memory use. You can use this package to keep track of the system’s memory utilization and determine whether your code is using too much memory.
Apart from this, one can also manually check for any kernel errors on their Windows operating system by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc under the Task Manager, while on macOS, one can open the Activity Monitor by searching for it in the Spotlight. Kernel errors due to memory-related issues may occur due to various reasons. For example, memory leaks, which can lead to kernel errors over a period of time. One can keep a check on this using tools like ‘Valgrind’ which helps in analyzing the application’s memory leaks. Inspecting system logs for any memory-related errors or updating or restarting any suspectible application to a more stable version, can also help in managing memory usage. Also, certain monitor swap usage tools like ‘free’, ‘top’, or ‘htop’ used for optimizing space swapping, can also result to be advantageous to this. Along with this, if one finds the memory usage to be too high, they can adapt closing any unnecessary programs or browser or application which are not in use to free-up the memory, also, reducing the size of the large datasets while working with them, may also lessen the memory usage. However, if one is frequently encountering memory-related issues, they may need to upgrade their computer’s memory. 8. Ask For HelpApart from these, you may also explore several communities such as Stack Overflow, by posting your queries with all the relevant proofs and wait for someone to come and help you out. Specific Kernel Errors ScenariosSpecific kernel error scenarios are situations or instances in an operating system when some errors or defects occurs in the operating system. These scenarios varies from system to system and leads to several malfunctioning in the OS. Some of the specific kernel error scenarios are described below:
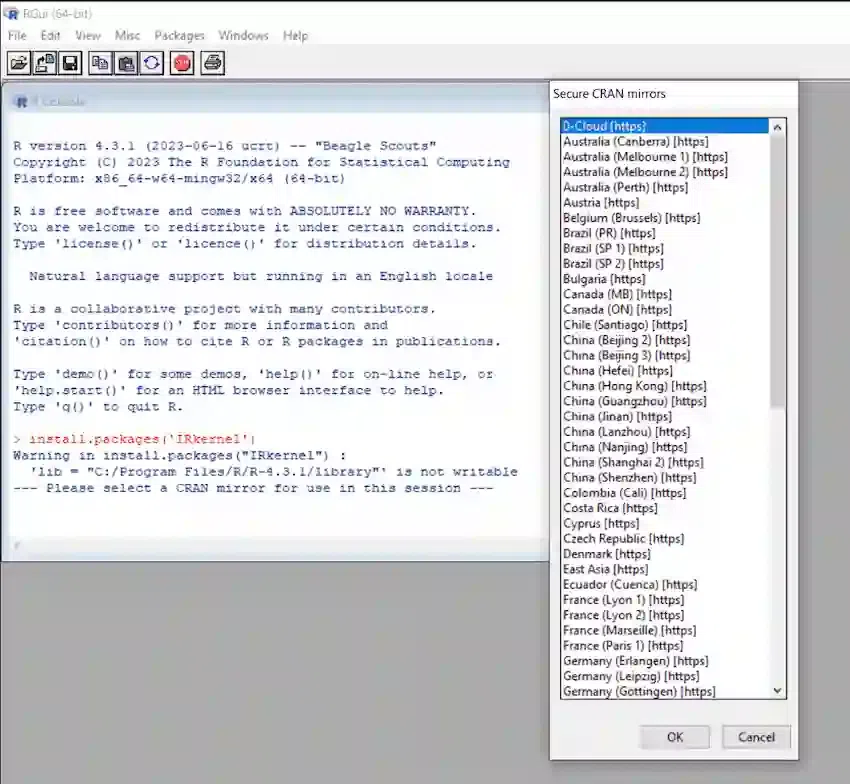
However, to understand these errors more precisely, some more depth knowledge of various types of systems is required. But, their early diagnostic steps to resolve and to stop them from becoming more serious, has to be implemented consciously. Working with Alternative KernelsWorking with alternative or multiple kernels, basically in the context of Jupyter Notebook, is the ability to use multiple programming languages within the same single jupyter notebook. It encompasses flexibility, portability and ability to handle specific use cases without reinstallation of another operating system multiple times. One system can have multiple kernels for its various uses according to its requirements and needs. Through this process, you will be installing and removing kernels from your operating system, also, with the help of this, you will be able to see the lists of all types of kernels which your system is carrying with it. Similarly, if you want to add or work with multiple alternative kernels such as Python, R, Julia, etc. in Jupyter Notebook, you can do it very easily. Since, here R programming language is used, following steps can be taken for adding an alternative Julia kernel in Jupyter Notebook. Step 1: Install RFirst of all, you need to install R in your system. For this, you can use the link https://cran.rstudio.com/ in your web browser and, then after install it as per your system type. Step 2: Install the IRKERNEL package in RNow, open R terminal in your system and type the following commands to install the ‘IRkernel‘ package in R. install.packages('IRkernel')
After downloading the ‘IRkernel’ Kernel, run this command to add the kernel: IRkernel::installspec(user = FALSE) The user = FALSE argument installs the kernel system-wide, making it available for all users on the system. If you want to install it only for your user, set user = TRUE.
This will add R kernel to your Jupyter Notebook. Step 4: Select a Kernel to your notebookWhen you create a new notebook or open an existing one, you can select the kernel you want to use from the “Kernel” menu. The available kernels will be listed, and you can choose the one you installed earlier.
Step 5: Run code in Different languagesOnce you’ve selected a kernel, you can write and execute code in the chosen language within your Jupyter Notebook cells. Each cell in the notebook can have a different kernel, allowing you to mix and match languages as needed. Note: If you want to work with more languages or environments, you can install additional kernels following the same process as described previously. Common Kernel ErrorsSome of the common kernel errors which you may have experienced or can experience in future, are shown and described below:
Diagnosing Kernel ErrorsThe primary objective or goal behind diagnosing kernel errors is to identify and understand the root cause for the occurrence of the problem. It is typically the very first step taken in case of kernel errors. This process involves investigating the error codes, examining system logs, analyzing error messages, and using diagnostic tools to gather information about what caused the kernel error. And as an outcome of this, we have a clear understanding about why these errors occurred. Some of the common diagnostic processes are:
Troubleshooting ErrorsThe primary goal or objective of troubleshooting is to fix or resolve the kernel error based on the diagnosis made. This includes more practical steps to be taken for resolving and eliminating the problem after the diagnosis has been made. Taking precise steps to address the underlying problems found during diagnosis is known as troubleshooting. This could involve installing or upgrading drivers, configuring hardware, applying software updates, or changing other aspects of the system configuration. The outcome of this results in the resolution of the kernel error, if the troubleshooting process is successful. Some of the basic troubleshooting steps are describes below:
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Geeks Premier League |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |


.webp)