
|
|
A Resistor acts as a main electronic component in regulating or limiting the flow of an electric current in an electrical circuit. It is mainly used in electronic circuits because it acts as a current controller, it controls high and low voltage and it protects the components. The resistor mainly helps in regulating the flow of electricity in a circuit and it achieves the desired circuit behavior. Resistors are mainly used in electronic networks and electrical circuits to prevent the excess flow of current and to set the voltage levels in the circuit. Table of Content What is a Resistor?The resistor can be defined as a passive electronic component with two terminals that produce electrical resistance to the flow of current in a circuit. It is measured in ohm(Ω). The Dimensional formula for a resistor is given as [Tex]ML^2A^{-2}T^{(-3)}[/Tex]. It can control limit or divide the electric current provided in the circuit, and its value can be determined by its resistance rating. A Resistor contains four bands as shown in the below image:
Symbol of ResistorThe Symbol Resistor can be represented as :  Symbol of Resistor The Resistor can be denoted by its Value and name like R1 , R2 .The terminals of the resistor are represented by each lines which are extending from the squiggle or rectangle. The resistance value, typically expressed in ohms, is fundamental for circuit analysis and construction. Different Types of ResistorsThere are different types of resistors, which are mainly classified into
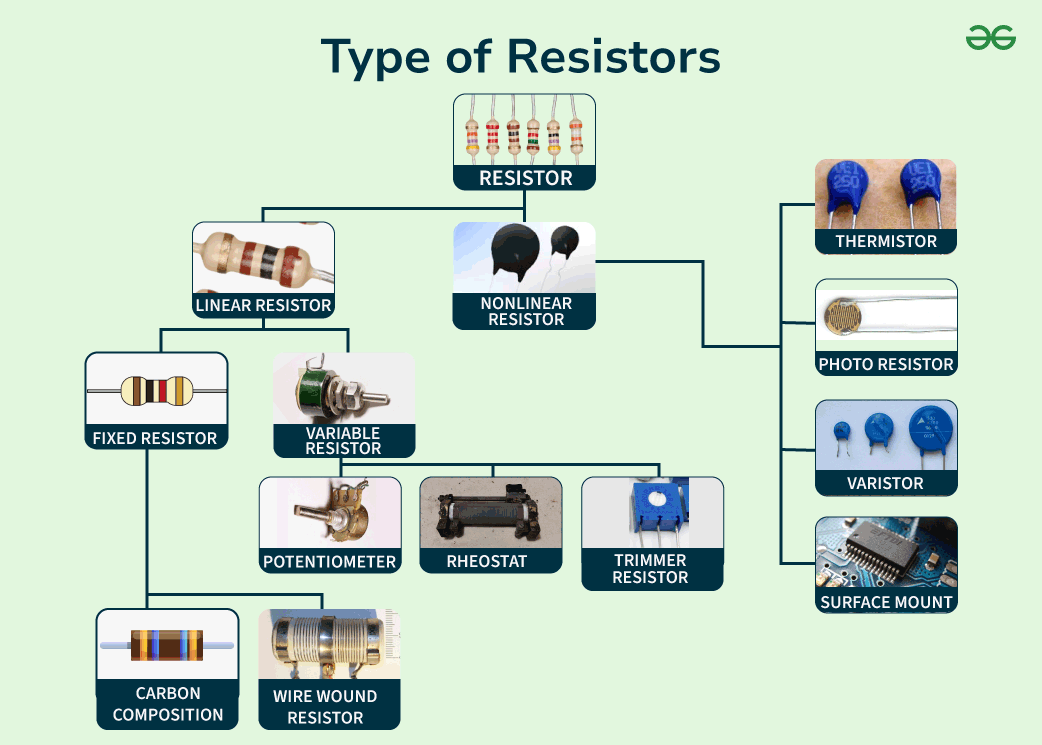 Types of Resistor Linear ResistorsIn Linear Resistors, the value of resistance changes based on the applied temperature and voltage. These Linear Resistors are again classified into Fixed and Variable Resistors. 1. Fixed Resistors: In Fixed Resistors, the value of resistance is fixed and cannot be changed. These are mostly used in fixed circuits because the resistance value is fixed. Fixed Resistors are mainly used in electronic circuits where a stable or fixed resistance is required, For example: in voltage dividers or current limiters. Fixed Resistor follows Ohm’s law, which states, that voltage (V) is directly proportional to current (I) and resistance (R). There are different types of Fixed Resistors:
2. Variable Resistors: In Variable Resistors, the value is not specific and can be changed and can manually adjust the value of resistance by using the dial, knob of a screw. It is also known as potentiometer having two connecting wires instead of three. Variable Resistors are mainly used in applications where resistance needs to be variable, for example: in volume controls or sensor applications or radio receiver. There are the different types of Variable Resistors:
Non-Linear ResistorsIn non-linear resistors, the value of resistance changes significantly with changes in voltage or current in an electrical circuit. This indicates the relationship between voltage and current is not proportional and it do not follow Ohm’s law. The resistor values change according to the temperature and voltage applied in the circuit. Non-linear resistors are mainly used in applications where resistance needs to be change based on the applied voltage or current. Non-linear resistors are mainly used in applications like voltage regulation or precise control. There are different types of Non-Linear Resistors:
Resistor Color CodeThe value of resistance offered by a resistor is marked using a color code called Resistor Color Code. The resistors we use are very tiny and the printing of the value of resistance in the resistor is not feasible. Thus, to find the value of the resistor we use various color bands(mainly four color bands) that help to determine the value of the resistance. These color bands on the resistor are called the Resistor Color Codes. 1. Mnemonic of Resistor Color Code: Learning the Resistor Color Coding is very important and the mnemonic used to find the value of the resistor is:
Combination of ResistorsResistors are used in various combinations. There are two methods of arranging the resistors in different combinations: Equivalent Resistance: The equivalent resistance of combinations of resistors in series is equal to the sum of their individual resistances in the circuit. 1. Resistors in Series CombinationTwo or more resistances are said to be connected in series when they are connected end to end and the same current flows through each of them in turn. In this case, the equivalent or the total resistance equals the sum of the number of individual resistances present in the series combination. Mathematically, the equivalent resistance of any number of resistances (R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, ……..) connected in series is given as:
2. Resistors in Parallel CombinationTwo or more resistances are said to be connected in parallel connected when they are connected between two points and each has a different current direction. The current is branched out and recombined as the branches intersect at a common point in such circuits. Mathematically, the equivalent resistance of any number of resistances (R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, ……..) connected in parallel is given as:
Power Dissipated in a ResistorThe Formula for the power Dissipation in the resistor can be given as [Tex]P=I^2R=VI=V^2[/Tex] The following equation is derived from Joule’s law and Ohm’s law. Working Principle of ResistorResistor is an passive electronic component which limits the flow of electric current in an electric circuit. It works on the principle of electrical resistance. It works mainly on resistance of an electrical circuit. Resistance has a property to opposes the flow of electric current. Resistance is measured in ohms(Ω).The more and the higher the resistance value of a resistor, the more it can restricts the flow of current passing through it. By using Ohm’s Law: Resistor working principle can be explained using Ohm’s Law, which states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across it and it is inversely proportional to its resistance (R). Mathematically, Ohm’s Law is represented as follows : V = I * R Where,
Calculate the Resistance Value
Difference between Resistor and ResistanceGiven below is the difference between resistor and resistance
Applications of Resistor
Advantages of ResistorsThe main advantages of using resistor in a electrical circuit are:
Disadvantages of Resistors
ConclusionIn conclusion, Resistors are main and fundamental components in an electrical components. They can help many electrical circuits to control current, voltage, and resistance with correct precision and reliability. Resistors has many applications in daily life. These are mainly used in electrical circuits. There are many different types of resistors. these each type of resistor is used in different types of circuits according their use. Resistors can help to control the flow of current, voltage and resistance. Resistors – FAQsCan we use resistors to generate the heat intentionally?
Why Carbon composition resistors are less common these days?
What is meant by “Chip Resistors” or “Surface Mount Resistors”?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Electronics Engineering |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |