
|
|
Geospatial data analysis involves working with data that has a geographic or spatial component. It allows us to analyze and visualize data in the context of its location on the Earth’s surface. R Programming Language is a popular open-source programming language, that offers a wide range of packages and tools for geospatial data analysis. fundamental concepts of Geospatial data1. Spatial Data TypesVector Data: Geospatial vector data represent discrete geographical features as points, lines, and polygons. Points can be used for locations, lines for linear features like roads, and polygons for areas such as administrative boundaries. Raster Data: Raster data represents geographic features as a grid of cells, where each cell has a value. This type of data is suitable for continuous or gridded data, such as satellite imagery and elevation data. 2. Coordinate Reference Systems (CRS):Geospatial data relies on coordinate reference systems to define locations on the Earth’s surface. Common CRS include WGS84 (GPS coordinates) and UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator). You must understand CRS to work with geospatial data effectively. 3. Geospatial Packages:R offers several packages for geospatial data analysis, including:
Example 1: Importing and Plotting Spatial Data (Vector)R
Output:  Introduction to Geospatial Data Analysis with R we load the sf package and read a shapefile containing polygon data representing North Carolina counties. We then plot the spatial data using the plot() function. Example 2: Raster Data AnalysisR
Output: test In this example, we use the raster package to read a raster dataset containing elevation data. We then compute summary statistics, such as minimum, maximum, and mean elevation, using the summary() function. The result, elev_summary, provides information about the elevation dataset. Plot the graph for Geospatial Data in RR
Output: 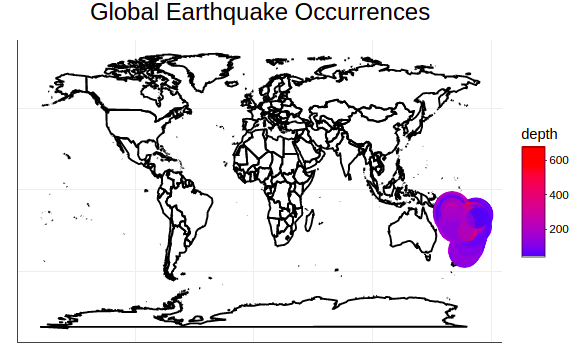 Introduction to Geospatial Data Analysis with R
Example 3 using rgdal (Reading and Plotting Spatial Data)R
Output:  Introduction to Geospatial Data Analysis with R In this example, we use the rgdal package to read a shapefile containing polygon data representing countries of the world. We use the readOGR() function to read the shapefile, and then we use the plot() function to visualize the spatial data. We specify the col argument to set the fill color for the polygons and add a title to the plot. Example 4 using sp (Spatial Data Manipulation and Visualization)R
Output:  Introduction to Geospatial Data Analysis with R In this example, we use the sp package to create a simple SpatialPointsDataFrame. We define coordinates (x and y) for three points, create a data frame for attribute data, and then combine them into a SpatialPointsDataFrame. Finally, we use the plot() function to visualize the points. We specify the pch argument to set the point type, the col argument to set the point color, and add a title to the plot. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| AI ML DS |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |