|
|
The conditional expressions allow developers to make decisions and manipulate data within queries, templates, and Python code, making it easier to create complex and dynamic web applications. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of conditional expressions in Django and explore how they can be used to enhance your web development projects. Setting up the ProjectInstallation: To install Django follow these steps. Creating the Project Create the project by using the command Django-admin startproject projectdemo
cd projectdemo
Create an application named ‘gfg’ by using the command: python3 manage.py startapp gfg
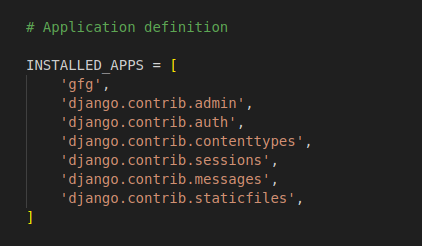
Now add this app to the ‘INSTALLED_APPS’ in the settings file.
Structuring Our ProjectOrganize your project directory with a clear file structure. model.py The model has three fields: “name” (a character field with a maximum length of 100 characters), “quantity” (an integer field), and “price” (a decimal field with a maximum of 10 digits and 2 decimal places). Python3
forms.py This code defines a Django form called ‘ProductForm’ in a file named forms.py within a Django app called ‘products’. The form is used to create and update instances of the Product model. Python3
views.py The code handles product listing and addition. The ‘product_list’ view annotates products to determine their stock status, while the ‘add_product’ view handles the submission of a form to add new products to the database. The HTML templates ‘myapp/index2.html’ and ‘myapp/index.html’ likely contain the presentation and form rendering for these views. Python3
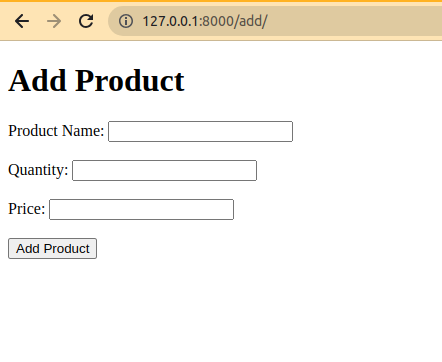
product_form.html This HTML code represents a simple web page for adding a product. HTML
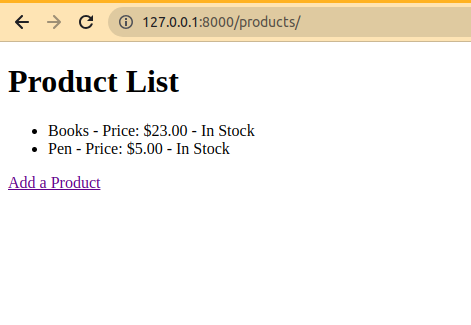
product_list.html This HTML template is used to display a list of products in a Django web application. It iterates through the “products” list, displaying each product’s name, price, and stock status (in stock or out of stock). Additionally, it includes a link for users to add new products to the list. HTML
app/urls.py This code defines URL patterns for a Django web application in the “pdfapp” module. It uses the Django urls.py file to map URLs to views in the application. Python3
urls.py This code defines URL patterns for a Django web application of the project. Python3
Deployement of the ProjectRun these commands to apply the migrations: python3 manage.py makemigrations
python3 manage.py migrate
Run the server with the help of following command: python3 manage.py runserver
Output
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Geeks Premier League |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |