|
|
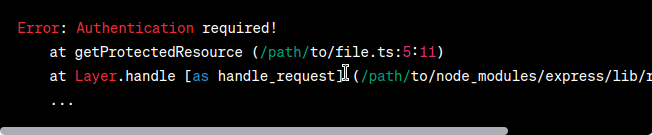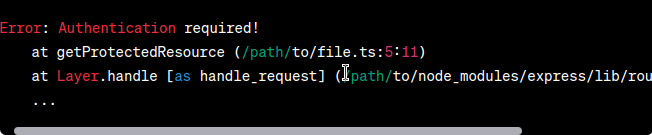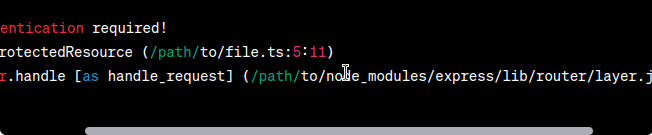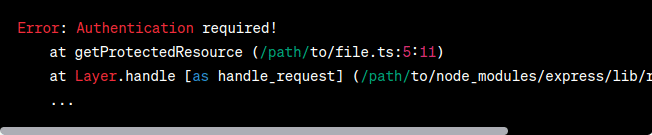
In this article, we will explore the importance of using custom error handling in TypeScript for RESTful APIs. We will begin by highlighting the problem statement, followed by demonstrating the problem with code examples and error outputs. Finally, we will present a solution approach using custom error classes and showcase the desired output. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of how to implement custom errors to improve error handling in your TypeScript-based RESTful APIs. 1. Problem StatementWhen developing RESTful APIs in TypeScript, error handling plays a crucial role in providing meaningful feedback to clients and aiding in debugging. However, relying solely on default error classes like Display the ErrorLet’s examine a scenario where a user attempts to access a resource that requires authentication. We’ll demonstrate the problem by using default error classes and observing the resulting error message. Javascript
When an unauthenticated user makes a request to this route, the server throws a generic Output (Error):  Output Solution ApproachTo address the problem, we can implement custom error classes in TypeScript. These classes allow us to define specific error types that extend the base Let’s create a custom error class called Javascript
Now, we can modify our route handler to throw an instance of Javascript
By using a custom error class, we provide more specific information about the encountered issue, making it easier to understand and handle the error. Output (Desired): 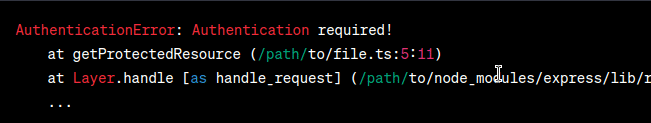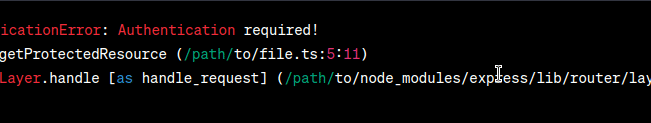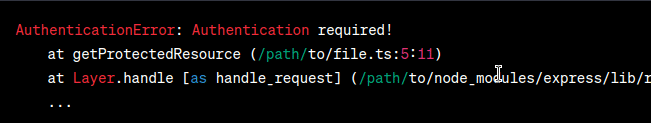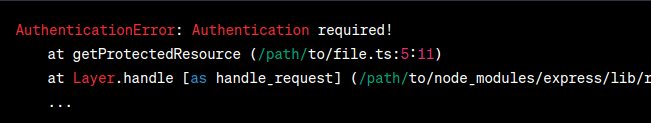 Output In the desired output, the error message now includes the name of the custom error class ( 2. Problem StatementIn this scenario, we have an API endpoint that fetches user data based on their ID. However, there may be cases where the requested user ID does not exist in the database. We want to handle this situation with a custom error class to provide a clear and meaningful error message. Display the ErrorLet’s consider the following code snippet: Javascript
In this code, we have an API endpoint Output (Error): 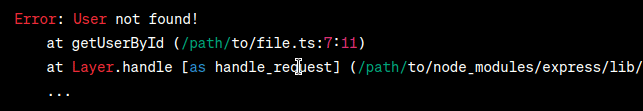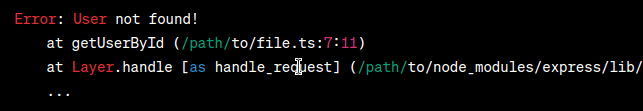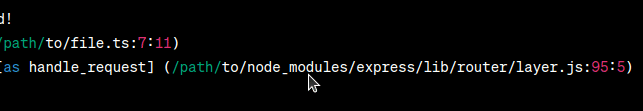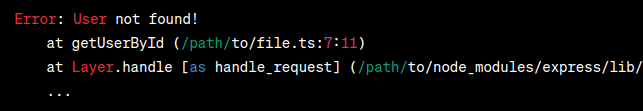 Output The error message in this case is generic and does not provide specific information about the encountered issue, which makes it challenging to determine whether the user ID was invalid or if there was an issue with the database. Solution ApproachTo improve error handling, we can create a custom error class called Let’s define the Javascript
In this code snippet, we define the Next, we modify our code to throw an instance of Javascript
Now, when a user with an invalid ID is requested, the server throws an instance of Output (Desired): 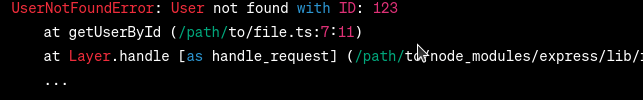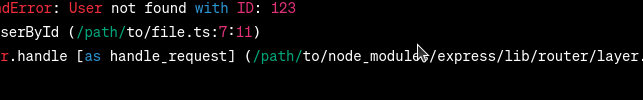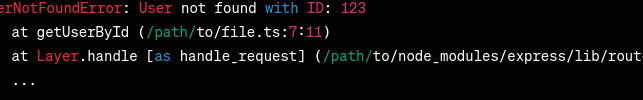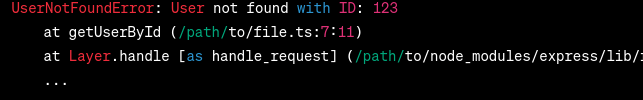 Output In the desired output, the error message indicates the specific error type ( ConclusionIn this article, we explored the significance of using custom error handling in TypeScript for RESTful APIs. By implementing custom error classes, we can provide more specific and informative error messages. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| JavaScript |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |