
|
|
Argparse is a Python library used to parse command-line arguments in a user-friendly manner. It makes it easy to write user-friendly command-line interfaces, and it is widely used in Python applications. In this tutorial, we will discuss how to pass a list as a command-line argument using the Argparse library in Python. Passing a List as a Command Line Argument with ArgparseTo pass a Python list as a command-line argument with the Argparse library, we will use the “nargs” argument in the add_argument() method. The “nargs” stands for “number of arguments”, and it tells the argparse how many arguments a specific option should expect. Steps to pass a List as Command Line Argument with ArgparseLet us see the steps involved in passing lists as command line arguments with Argparse Library in Python. Step 1: Import the required module To use the argparse, you need to import the argparse module. You can do this by adding the following line at the beginning of your Python script: import argparse Step 2: Create an argument parser Next, create an argument parser object by calling the ArgumentParser() method: parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() Step 3: Add an argument Add the argument to the argument parser using the add_argument() method. Use the type parameter to specify the data type of the argument, The list can be of any type, a string, an integer, etc. parser.add_argument("--numbers", type=int) Step 4: Parse the arguments Finally, parse the command-line arguments by calling the parse_args() method on the argument parser object. This will return an object that contains the parsed arguments. args = parser.parse_args() Step 5: Access the list You can access the list of integers passed as the “–numbers” argument using the “numbers” attribute of the args object. print(args.numbers) Passing a list of StringsIn this example, the list_of_strings function takes a string as input and returns a list of strings. The type parameter of add_argument is set to list_of_strings, so when parse_args is called, the string value of –str-list is converted into a list of strings. Python3
Output: You can run this script with the following command. Here ‘script.py’ refers to the name of the saved Python file. python script.py --str-list foo,bar,baz  Passing a list of strings as command line arguments Note: Make sure that there is no space between the items of the list, else it can generate an error. We will see how we can resolve this error in the upcoming examples. Passing a list of IntegersIn this example, the list_of_ints function takes a string as input and returns a list of Python integers. The type parameter of add_argument is set to list_of_ints, so when parse_args is called, the string value of –int-list is converted into a list of integers. Python3
Output: You can run this script with the following command: python script.py --int-list 1,2,3,4,5,6  Passing a list of integers Pass a List as a Command-Line ArgumentLet us see a few examples for Python passing a list as an argument: Example 1: Passing one or more values using nargs=’+’ In this example, we add an argument called “my_list” using the “add_argument” method. The “metavar” parameter is used to specify the argument’s name in the usage message. The “type” parameter is set to “str” since we want the list to be a list of strings. The “nargs” parameter is set to “+” to indicate that the argument can take one or more values. Python3
Output: Passing only one argument: python my_script.py horje 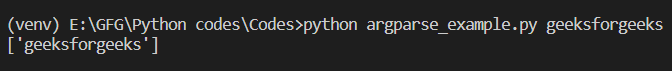 Passing only one value using nargs=’+’ Passing more than one argument: python my_script.py geeks for geeks  Passing more than one value using nargs=’+’ Example 2: Passing zero or more values using nargs=’*’ In this example, the ‘nargs’ parameter is set to ‘*’ to indicate that the argument can take zero or more values. Here, we are in Python passing a list as an argument. Python3
Output: Passing zero arguments: python my_script.py 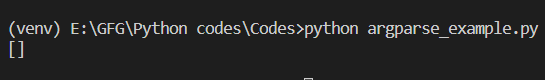 Passing zero value using nargs=’*’ Passing more than zero arguments or Python passing a list as an argument: python my_script.py geeks for geeks  Passing more than zero values using nargs=’*’ Example 3: Passing Optional Arguments In this example, we provided two arguments, one is compulsory and the other is optional. We set the ‘required’ parameter to ‘True’ which means it is a compulsory one. In the second argument, we did not define the required parameter, which means it is an optional argument. Python3
Output: When both arguments are defined: python my_script.py --string1 Hello --string2 world  Passing optional arguments as command line argument When the optional parameter is not defined: python my_script.py --string1 Hello 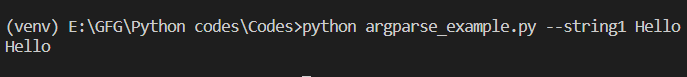 Without passing optional arguments as command line argument |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Python |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |