|
|
Division in maths is a way of sharing or grouping numbers into equal parts. It helps us understand how many times one number can fit into another. It is a mathematical operation that involves splitting something into equal parts. It is also one of the four basic arithmetic operations, along with addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Division is the mathematical operation opposite to multiplication. It involves distributing a number into equal portions or sets. When we perform division, we decompose a larger number into smaller units, ensuring that they reconstruct the original number when these units are multiplied together. For instance, dividing 4 by 2 yields 2, because splitting 4 into 2 equal parts results in each part being 2. In this article, we will learn the division method, its symbol, examples, how to perform division, properties, and applications in detail.
Table of Content
What is Division in Math?The division operation in mathematics is used for finding the smaller group into which a large group of numbers. It is used to the larger group into smaller groups. Suppose we have 32 chapatis and 8 children to feed then one child gets how many chapatis is found out using division operation as,
Thus, each child gets four chapatis, the division in maths is very useful for finding the smaller groups of the number and for simplifying the arithmetic problems. Also, it holds significance for class 2 divide as well. 
Division Meaning
Suppose we have to find the division of 16 by 4 then 4 is subtracted from 16 four times, 16 – 4 – 4 – 4 – 4 = 0. Thus, the dividing math’s is referred to as repetitive subtraction and 16/4 = 4. Division by Zero
Division SymbolThe symbol used to denote the division is ÷ (obelus) and / (backslash). These symbols are used for division, suppose we have to divide 24 by 6 then this is represented as,
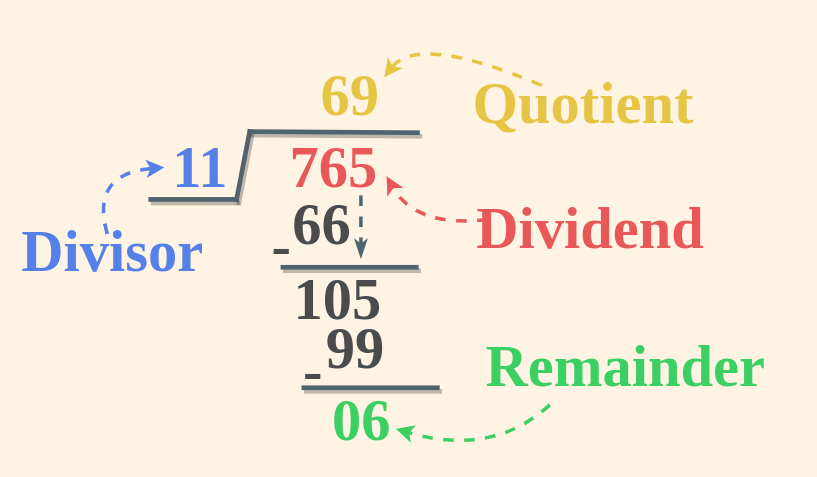
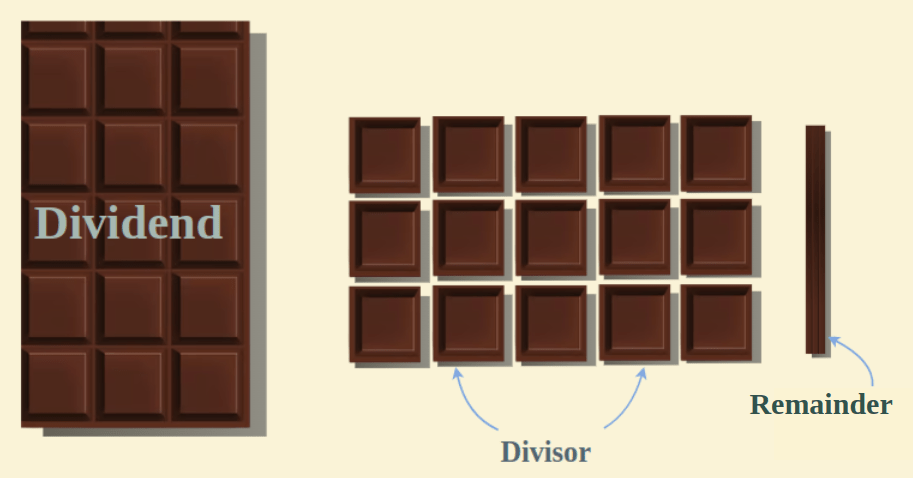
Parts of DivisionThere are four parts to the division that includes,
Division FormulaThe equation or the technique used to find the division of the number is called the division formula sometimes also known as division algorithm. The division algorithm or the division in math formula is,
This algorithm is used to verify the results of the division process, the division of two numbers yields a quotient and the remainder which when used verified the results of the division. This can be understood using the following example of division, Example: Divide math 22 by 3.
How To Do Division – RuleThe division of one digit number can be directly performed using the tables of various numbers, such as suppose we have to find the division of 24 by 4 then we know that by the table of 4,
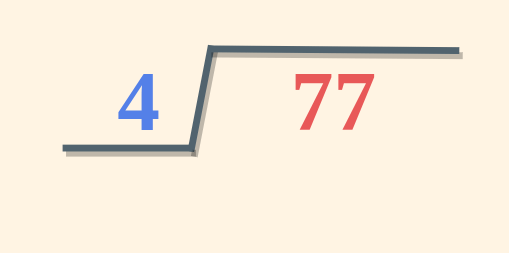
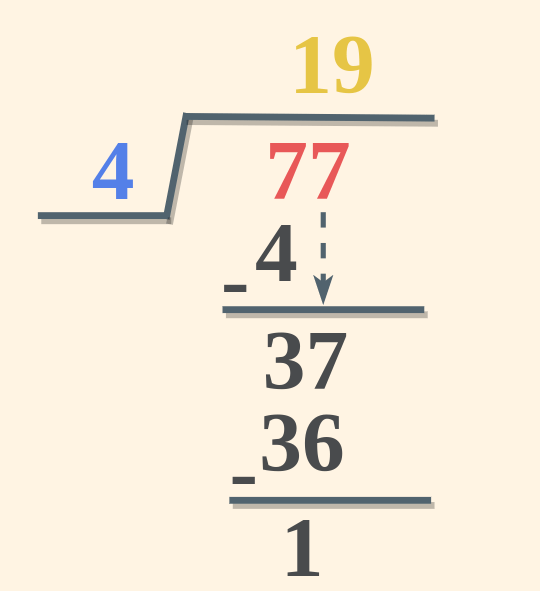
For two-digit or three-digit numbers division is performed using the steps discussed below, here we use the example of division, 77 divided by 4 to get the steps of division. Step-by-Step Guide to DivisionHere is a stepwise method of doing division in math’s. Step 1: Using the symbol ⟌ write the divisor (here 4) on its left side and the dividend (here 77) enclosed under the division symbol(⟌).
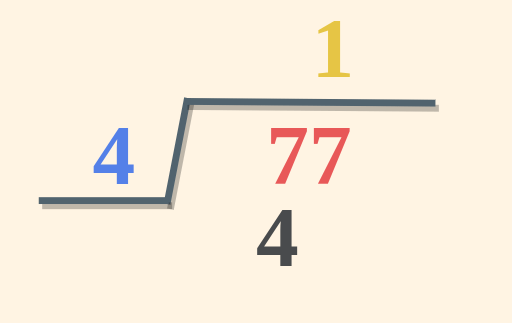
Step 2: Starting from the left-hand side take one digit of the dividend at a time and check whether it is smaller or greater than the divisor. If the digit is smaller, then take two digits at a time. (here, 7 is greater than 4). Step 3: Take the multiple of the divisor that is equal to or less than the digits in step 2. (here 4×1 = 4, i.e. less than 7). Write the number in the Quotient.
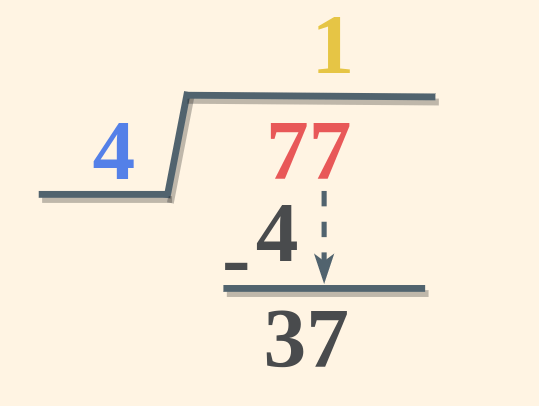
Step 4: Subtract the multiple of the divisor from the digits in Step 2 and write the remainder and then carry the next digit from the dividend. If the number is less than the divisor adds zero in the quotient and bring the next digit down, repeat this process till the divisor is greater than the number. (here 7 – 4 = 3)
Step 5: Now again find the suitable multiple of the quotient and repeat the above process till the remainder so obtained is less than the divisor.
Step 6: When the remainder obtained is less than the divisor the Quotient and the remainder so obtained are the result of the division. Division with RemaindersThe number left at the end of the division process is called the remainder of the division and it is not always zero. But it is always less than the divisor. This can be understood by the example discussed below, Example: 14 ÷ 2
Example: 15 ÷ 2
Division of FractionsFractions can also be easily divided and the divisibility rules for dividing the fractions are different from dividing natural numbers. If we in math divide a fraction from another fraction, then the latter is multiplied with the former by taking its reciprocal. This can be understood as,
For example, Divide 2/5 by 4/3
Division PropertiesSome of the most important + properties of the math division operation are, Property of Division by 1: If we divide any number by 1 then the quotient is the number itself. This can be understood by the example, 23 divided by 1 then the result is 23, thus,
Property of Division by 0: If we divide maths any number by 0 then the quotient is undefined as the division of zero is not possible. This can be understood by the example, 23 divided by 0 then the result is undefined, thus, If Divisor = 0, then Quotient = Undefined (Division is not possible), i.e.
Property of Division by Itself: If we divide any number by itself then the quotient is the 1. This can be understood by the example, 23 divided by 23 then the result is 1, thus,
Property of Division of 0 by Any Number: If we divide the sums any number by 0 then the quotient is always 0. This can be understood by the example, 0 divided by 23 then the result is 0, thus,
Property of Division by 10: If we divide any number by 10 then the quotient is the number itself without the one’s digit and the remainder is one’s digit. This can be understood by the example, 237 divided by 10 then the result is 23, and 7 is the remainder, thus,
Property of Division by a Power of 10: If we divide any number by the Power of 10 then the quotient is the number obtained by removing the digits (from the right-hand side) from the number as there are a number of zeroes or exponent in the divisor. This can be understood by the example, 2376 divided by 100 now here there are two zeroes in the divisor then the result is 23, and 76 is the remainder, thus,
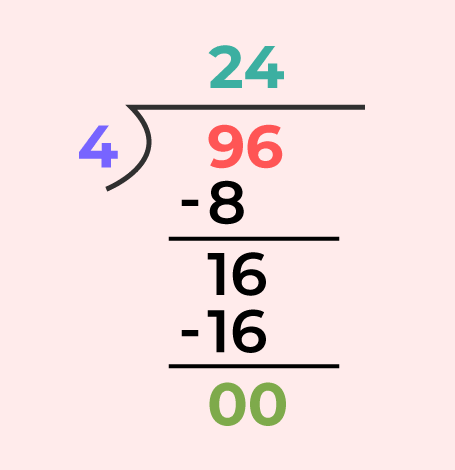
Division of 2 Digit NumberIn division 2 digits we study how to divide a two digit number by one digit number. The same can be studied by the examples added below, Example: Divide 96 by 4 Using Division Algorithm,
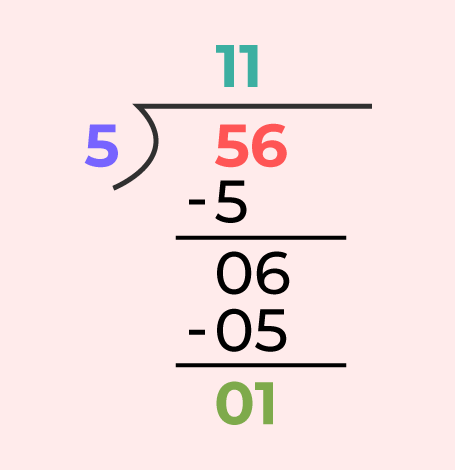
Example: Divide 56 by 5. Using Division Algorithm
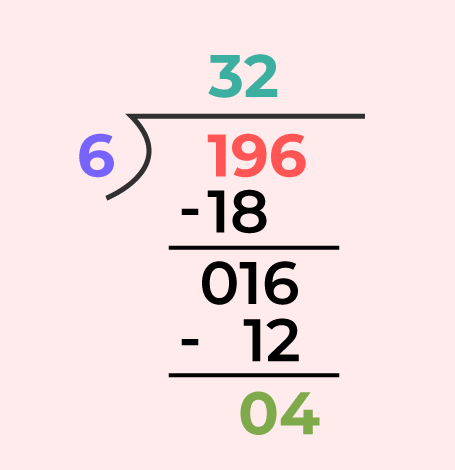
Division of 3 Digit NumberIn division 3 digits we study how to divide a three digit number by one digit number. The same can be studied by the examples added below, Example: Divide 196 by 6 Using Division Algorithm
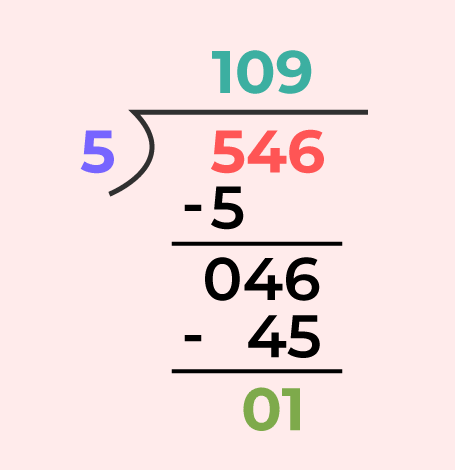
Example: Divide 546 by 5 Using Division Algorithm
Division SumDivision sum contains the sums, or the problems related to the division. Some example problems of division sums are, Division Sum Problem 1. If we have to distribute 20 mangoes among 5 boys then each boys gets how many mangoes? Solution:
Division Sum Problem 2. Krisha has 45 sweets to distribute in his class if there are 15 students in his class then how many sweets each student of the class gets? Solution:
Long Division in Math’s
It is called “long division” because it often involves writing out the division problem with multiple steps and carrying out the division process one digit at a time, working from left to right. Division Tricks and Divisibility CheckIf a number can be divided by a single-digit number without any remainder, it is considered divisible. There are quick methods to determine divisibility without performing the actual division. Some of the most important tricks of the math division operation, including divisibility, shortcuts of division, and tricks of division, are:
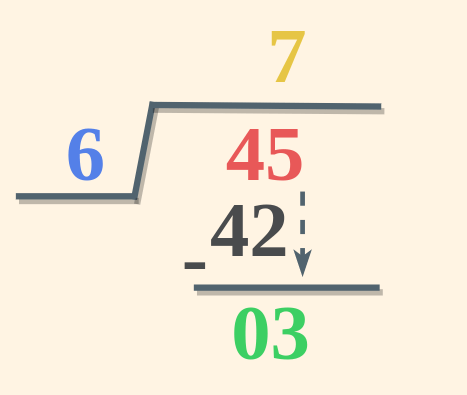
Division Solved ExamplesHere are some solved examples on Division for you help. Example 1: Divide 45 by 6 and verify using Division Algorithm. Solution:
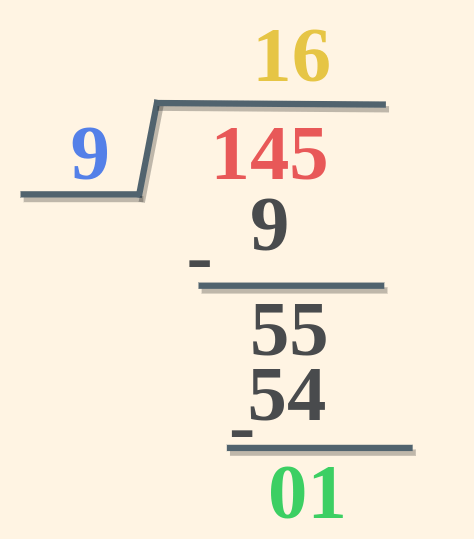
Example 2: Divide 145 by 9 and verify using Division Algorithm. Solution:
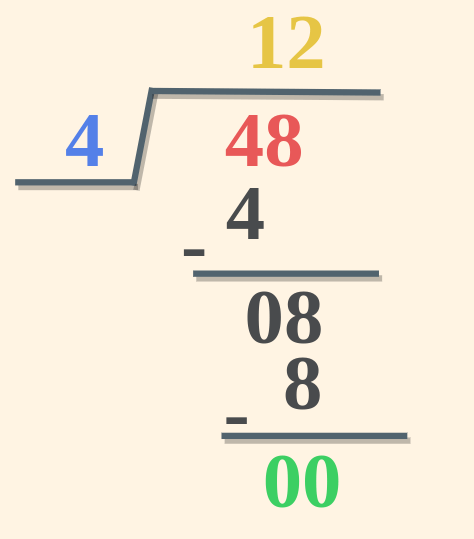
Example 3: Divide 48 by 4 and verify using Division Algorithm. Solution:
Division Worksheet Class 2 and 3Here are some practice problems on Division in Math’s for you to solve. Problem 1. If we divide 25 pencils among 5 students. How many pencils will each student receive? Problem 2. If a farmer has has harvested 368 apples, and he distributes them in 4 baskets. How many apples will be in each basket? Problem 3. A bakery bakes 72 breads and needs to distribute it among 12 different persons. How many bread each person gets? Problem 4. In a garden there are 45 different flowers equally distributed in 5 rows then each row has how many flowers?
Conclusion of Division in Math’sDivision, the inverse of multiplication, is essential in both education and daily life. It helps distribute quantities into equal parts, aiding in problem-solving and analysis. From simple arithmetic to complex calculations involving fractions and percentages, division is crucial for understanding patterns and managing resources. Its practical applications in personal finance and business underscore its importance in developing mathematical literacy and problem-solving skills, preparing individuals to handle real-world quantitative challenges. Division In Math’s – FAQsWhat is Division in Maths?
What are the parts of Division?
What is the Division Symbol?
What is the Division Algorithm Formula?
What are types of Division?
What is the remainder formula?
What is the value of a number when divided by 0?
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Mathematics |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |