
|
|
In general, Inheritance is a mechanism by which a subordinate or child class acquires the traits and qualities of a superordinate class or other derived classes. It also allows extra features like taking child class properties and using them in other derived classes. The syntax of classes is used to implement inheritance in Objective-C. A class also referred to as a superclass or parent class, can inherit the attributes and functions of other classes. The term “subclass” or “child class” refers to the class that inherits these attributes and methods. The syntax for defining Subclass:
A subclass inherits all of the instance variables, attributes, and methods of the superclass when it is defined. The subclass can also provide its own implementation of a method by overriding one from the superclass. Sample Program: ObjectiveC
Output: 
Types of InheritancesIn Objective-c there are two types of inheritances. They are:
Single inheritanceIn Objective-C, single inheritance is the type that is most frequently employed. A subclass inherits the methods and attributes of a single superclass under single inheritance. The subclass has the ability to replace any of the methods from the superclass as well as add new attributes and methods of its own. Because multiple inheritance is not supported by Objective-C, inheritance hierarchies can only be implemented in Objective-C using single inheritance. Example Program: ObjectiveC
Output: 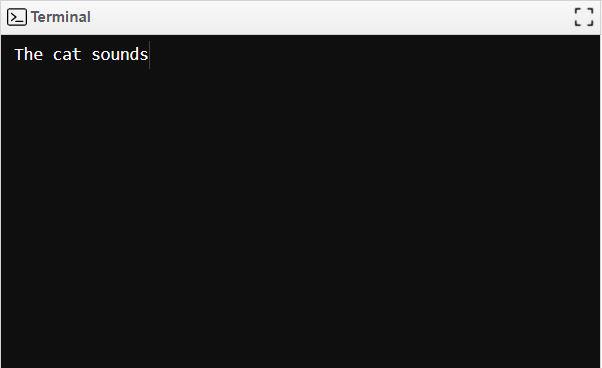
Multiple InheritanceObjective C does not directly enable multiple inheritances. However, it is possible because of a notion known as protocols. A class can implement a protocol’s set of methods. A class can inherit the methods specified in a protocol by implementing the protocol. Since a class can implement numerous protocols, it can inherit methods from various sources. Example Program: ObjectiveC
Output: 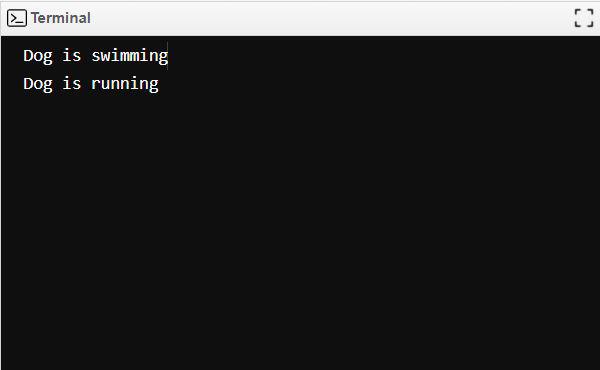
The class “Animal” is next, and it adopts both the “swimming” and “running” procedures. We define a property name and put the methods from the “Swimming” and “Running” protocols into the “Animal” protocol. We create a new instance of the “Animal” class in the main.m, change its name property to “Dog,” and then call the “swim” and “run” methods. “Dog is swimming”, followed by “Dog is running,” since “Animal” accepts both the “Swimming” and “Running” procedures. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Objective C |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |