|
|
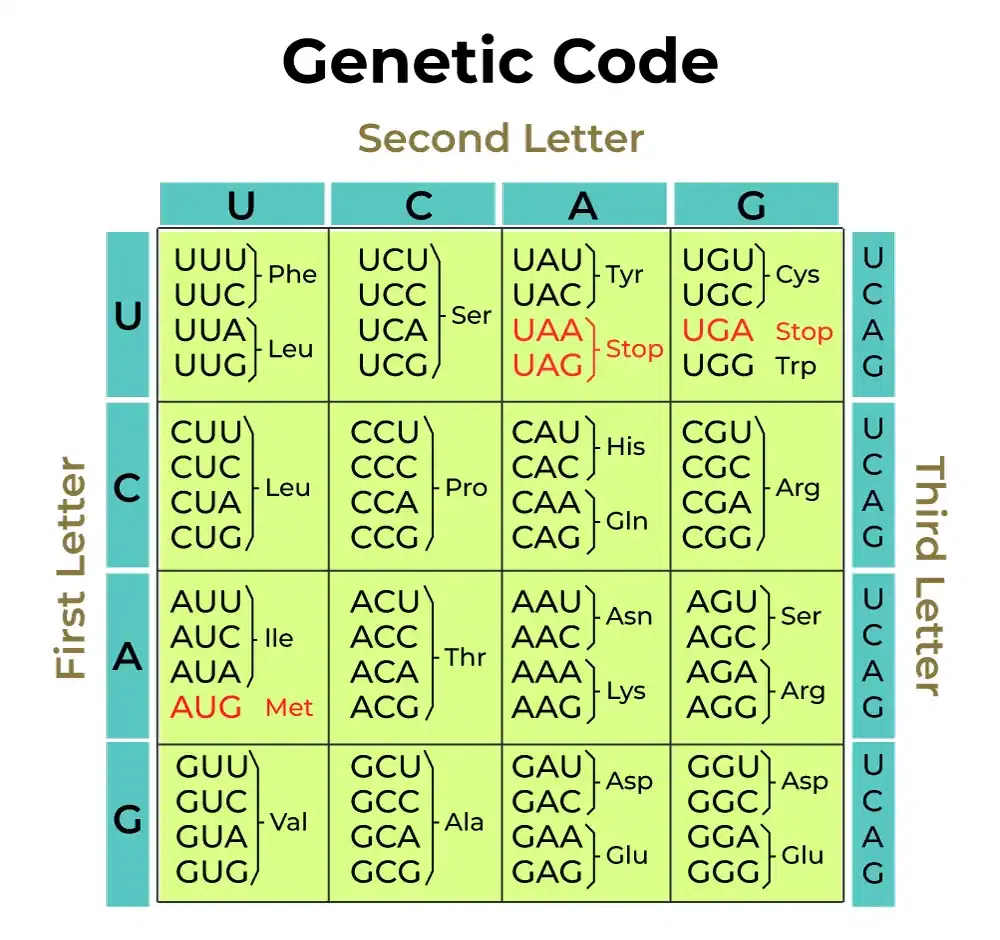
CBSE Class12- Molecular Basis Of Inheritance- Genetic Code: The sequence of nucleotides in deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid which determines the amino acids sequence of proteins is known as Genetic code. DNA consists of information for protein sequences. RNA consists of four nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U). The genetic code is made up of three nitrogen bases which are known as the triplet code. What is Genetic Code
A nucleic acid was copied to form another nucleic acid during the process of replication and transcription. The process of translation needs to transfer genetic information from the polymer of nucleotide to the polymer of amino acids. Some evidences were there to support the notion that changes in nucleic acids were responsible for the change in amino acids of the proteins which led to the preposition of genetic code that direct the sequence of amino acids during the synthesis of proteins. George Gamow, a physicist said that there are only 4 bases, and if they code for 20 amino acids then the code should consist of the combination of bases. Further, he suggested that to code for all 20 amino acids the code should be made up of 3 nucleotides. This was the bold preposition because of the permutation combination 43(4*4*4). Salient features of the genetic code are
What is Genetic Table?The set of relationships between amino acids and codons is known as genetic code. When a genetic code is summarized in a table it is known as a Genetic code Table. Amino acids represent in the table by more than one codon. Example – In total, there are 6 ways to write leucine in mRNA language. Properties of Genetic Code
Exceptions of Genetic CodeDue to similar codons being seen in all organisms, the genetic code is universal along with the same START and STOP signals in the genes of microorganisms and plants. Therefore there are few exceptions which include one or two STOP codons of an amino acid. Though GUG is meant for valine both the codons GUG and AUG code for methionine as starting codons which breaks the property of non-ambiguousness. Therefore, few codes are different from universal code or non-ambiguous code. FAQs on Genetic CodeQ1: What do you mean by Genetic code?Answer:
Q2: State why the genetic code degenerates.Answer:
Q3: Discuss why the codon is a triplet.Answer:
Q4: Write some features of the genetic code.Answer:
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Class 12 |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |