
|
|
Java Collection Framework was introduced in JDK 1.2 which contains all the collection classes and interfaces. Java Collection is a framework that provides a mechanism to store and manipulate the collection of objects. It allows developers to access prepackaged data structures and algorithms for manipulating data. Here, we’ve covered the 50+ Java Collections Interview Questions and Answers tailored for both Fresher and experienced professionals, which cover everything from basic to advanced Java collection concepts such as navigation collection, WeakHashMap, streams Lambdas, etc.  Java Collections Interview Questions Whether you are a fresher or an experienced Java developer, these Java Collections Interview Questions give you all the confidence you need to ace your next Java interview. Table of Content We have divided the 50 questions into two parts: Experienced and Freshers. Let’s begin with the questions for Freshers. Java Collection Interview Questions For Freshers1. What is Collection in Java?The term collection refers to a group of objects represented as one unit. Classes in the Java collection class hierarchy are divided into two “root” interfaces: Collection (java.util.Collection) and Map (java.util.Map). Terms that you will encounter while learning about the collection in Java:
2. What is a Framework in Java?Frameworks are sets of classes and interfaces that provide a ready-made architecture. It is not necessary to define a framework in order to implement new features or classes. As a result, an optimal object-oriented design includes a framework containing a collection of classes that all perform similar tasks. The framework can be used in a variety of ways, such as by calling its methods, extending it, and supplying “callbacks”, listeners, and other implementations. Some of the popular frameworks in java are:
3. What is the difference between Array and Collection in Java?Arrays are a collection of similar-typed variables with a common name in Java. There are some differences between arrays in Java and C/C++. On the other hand, Collections are groups of individual objects that form a single entity known as the collection of objects.
4. What are the various interfaces used in Java Collections Framework?The collection is known as the root of the collection hierarchy. Collections represent groups of objects known as elements. The java platform does not provide any direct implementation of this interface but the Collection interface is being implemented by List and Set classes.
5. Explain the hierarchy of the Collection framework in Java.All classes and interfaces required by the collection framework are contained in the utility package (java. util). Collection frameworks have an interface called an iterable interface, which allows the iterator to iterate over all collections. In addition to this interface, the main collection interface acts as a root for the collection framework. All the collections extend this collection interface thereby extending the properties of the iterator and the methods of this interface. The following figure illustrates the hierarchy of the collection framework. 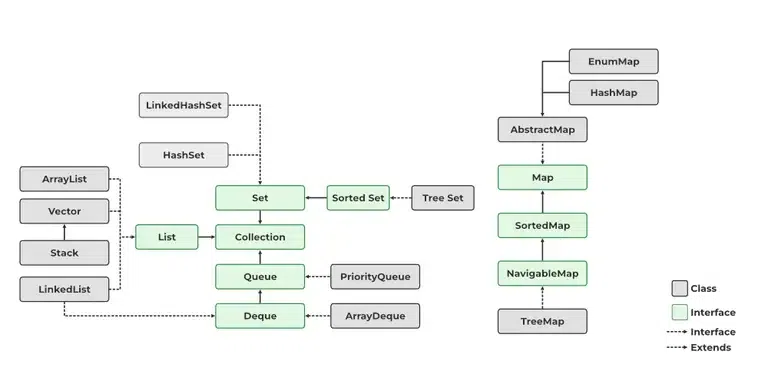 Java Collection Hierarchy 6. What are the advantages of the collection Framework?Advantages of the Collection Framework: Since the lack of a collection framework gave rise to the above set of disadvantages, the following are the advantages of the collection framework.
7. What is ArrayList in Java?ArrayList is a part of the Java collection framework and it is a class of java.util package. It provides us with dynamic arrays in Java. The main advantages of ArrayList are, if we declare an array then it’s needed to mention the size but in ArrayList, it is not needed to mention the size of ArrayList if you want to mention the size then you can do it.  Image of Array List
8. What is the difference between Collection and Collections?
9. Difference between ArrayList and LinkedList in the java collection framework? ArrayList and LinkedList
10. What is an iterator?Java’s Collection framework uses iterators to retrieve elements one by one. This iterator is universal since it can be used with any type of Collection object. Using Iterator, we can perform both reading and removing operations. This is an improved version of Enumeration with the addition of removing elements. When enumerating elements in all Collection framework implemented interfaces, such as Set, List, Queue, Deque, and all implemented classes of Map, an Iterator must be used. The only cursor available for the entire collection framework is the iterator. Using the iterator() method in the Collection interface, you can create an iterator object. Syntax: Iterator itr = c.iterator(); Note: Here “c” is any Collection object. itr is of type Iterator interface and refers to “c”.
11. What is the difference between an Iterator and an Enumeration?A major difference between iterator and enumeration is that iterators have a remove() method while enumerations do not. Thus, using Iterator we can manipulate objects by adding and removing them from collections. Since enumeration can only traverse objects and fetch them, it behaves like a read-only interface.
12. What is the difference between List and Set in JavaA major difference between a List and a Set is that a List can contain duplicate elements while a set contains only unique elements. The list is Ordered and maintains the order of the object to which they are added. The set is unordered.
13. What are the best practices for Java Collections Framework?Following are some of the best practices while using Java Collections:
14. What is a priority queue in Java?PriorityQueues are used to process objects according to their priority. Queues follow the First-In-First-Out algorithm, but sometimes the elements of the queue need to be processed according to their priority, which is where PriorityQueue comes into play. Priority queues are based on priority heaps. The elements of the priority queue are ordered according to the natural ordering, or by a Comparator provided at queue construction time, depending on which constructor is used.  Priority Queues in Java Declaration: public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements Serializable The class implements Serializable, Iterable<E>, Collection<E>, and Queue<E> interfaces. 15. What is the difference between List, set, and map in java?
16. What is the difference between Queue and Stack?
17. What is BlockingQueue in Java?The BlockingQueue interface in Java is added in Java 1.5 along with various other concurrent Utility classes like ConcurrentHashMap, Counting Semaphore, CopyOnWriteArrrayList, etc. The BlockingQueue interface supports flow control (in addition to queue) by introducing blocking if either BlockingQueue is full or empty. A thread trying to enqueue an element in a full queue is blocked until some other thread makes space in the queue, either by dequeuing one or more elements or clearing the queue completely. Similarly, it blocks a thread trying to delete from an empty queue until some other threads insert an item. BlockingQueue does not accept a null value. If we try to enqueue the null item, then it throws NullPointerException. Usage of BlockingQueue  Blocking Queue in Java The Hierarchy of BlockingQueue  Hierarchy of Blocking Queue in Java Declaration: public interface BlockingQueue<E> extends Queue<E> Here, E is the type of elements stored in the Collection.
18. What is the hashCode()? Image to demonstrate Java Hash Code hashCode() method returns the hashcode value as an Integer. It is defined in the Java Object class which computes the hash values of given input objects. Hashcode value is mostly used in hashing-based collections like HashMap, HashSet, HashTable….etc. This method must be overridden in every class which overrides the equals() method. Syntax : public int hashCode()
19. Distinguish between ArrayList and Vector in the Java Collection Framework.In collection interviews, this question is frequently asked; however, Vector is synchronized whereas ArrayList is not. ArrayList is faster than Vector. ArrayList’s Array size is increased by 50% when needed, while Vector’s capacity is doubled whenever it is needed.  Array List vs Vector in java
20. Differentiate between Iterator and ListIterator.
21. What is the difference between an Iterator and an Enumeration?Iterator: It is a universal iterator as we can apply it to any Collection object. By using an Iterator, we can perform both read and remove operations. Syntax: // Here "c" is any Collection object. itr is of Enumeration: Enumeration (or enum) is a user-defined data type. It is mainly used to assign names to integral constants, the names make a program easy to read and maintain. Syntax: // A simple enum example where enum is declared
22. What are the features of Java Hashmap?HashMap is similar to HashTable, but it is unsynchronized. It allows us to store the null keys as well, but there should be only one null key object and there can be any number of null values. This class makes no guarantees as to the order of the map. To use this class and its methods, you need to import java.util. HashMap package or its superclass. 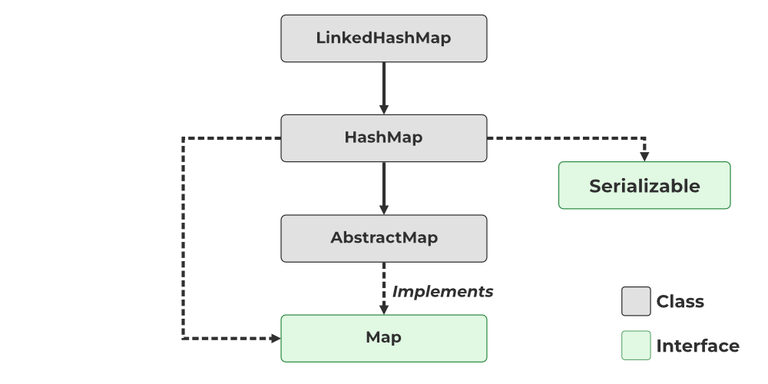 HashMap in Java Syntax: public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable Parameters: It takes two parameters namely as follows:
23. What are Collection Interfaces?The Collection interface is a member of the Java Collections Framework. It is a part of java.util package. It is one of the root interfaces of the Collection Hierarchy. The Collection interface is not directly implemented by any class. However, it is implemented indirectly via its subtypes or subinterfaces like List, Queue, and Set. For Example, the HashSet class implements the Set interface which is a subinterface of the Collection interface. If a collection implementation doesn’t implement a particular operation, it should define the corresponding method to throw UnsupportedOperationException. The Hierarchy of Collection:  Collection Interface in Java 24. Explain the list interface.In Java, the List interface allows the user to store an ordered collection of objects. The list is the child interface of Collection. In Collection, a list is an ordered collection of objects which can have duplicate values. Since List preserves the insertion order, it allows positional access and insertion, which also allows duplicate values. 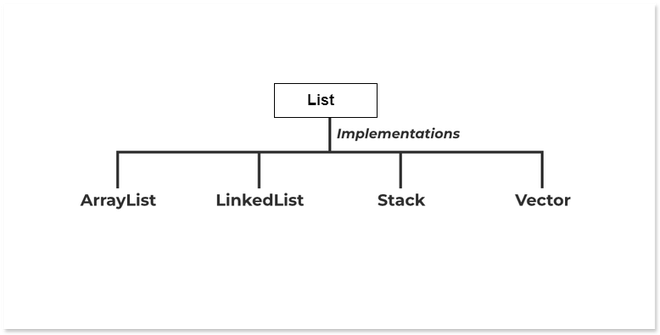 Syntax: public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> ; This list interface is implemented by various classes like ArrayList, Vector, Stack, etc. Since all the subclasses implement the list, we can instantiate a list object with any of these classes. Example:
 Array List in Java The classes which implement the List interface are as follows:
25. Write a program to convert a given array into a collection with the asList() method.To convert array-based data into Collection based we can use java.util.Arrays class. This class provides a static method asList(T… a) that converts the array into a Collection. Output Array input: [Kamlesh, Abhay, Abhishek, Shivansh] Converted elements: [Kamlesh, Abhay, Abhishek, Shivansh] 26. Differentiate between HashSet and HashMap
27. Differentiate between HashSet and HashTable.
28. What is the default size of the load factor in the hashing-based collection?As the Load Factor increases, the capacity increases so that the operational complexity of the HashMap remains O(1) if the ratio of the current element to the initial capacity crosses the threshold. The meaning of operational complexity of O(1) means the retrieval and insertion operations take constant time. The default load factor size is 0.75. The default capacity is calculated by multiplying the initial capacity by the load factor.
Java Collection Interview Questions For Experienced29. What is the difference between Comparable and Comparator in Java?Java provides two interfaces to sort objects using data members of the class:
30. What is the difference between fail-fast and failsafe?Iterators in Java are used to iterate over the Collection objects. Fail-Fast iterators immediately throw ConcurrentModificationException if there is a structural modification of the collection. Structural modification means adding, or removing any element from a collection while a thread is iterating over that collection. Iterator on ArrayList and HashMap classes are some examples of fail-fast Iterator.
31. Write a program to iterate the list using the lambda expression.Iteration can be done using a lambda expression. Syntax: list_name.forEach(variable->{//block of code}) Output Geeks for Geeks For more information, refer to the article – Iterate through List in Java 32. What is IdentityHashMap?The IdentityHashMap implements the Map interface using Hashtable, comparing keys (and values) using reference equality instead of object equality. This class implements the Map interface, but it intentionally breaks Map’s general contract, which demands that objects are compared using the equals() method. This class is used when the user allows objects to be compared using references. It belongs to java.util package. For more information, refer to the article – IdentityHashMap class in Java 33. Write a program in Java to display the contents of a HashTable using enumeration.The hashtable class implements a hash table, which maps keys to values. Any non-null object can be used as a key or as a value. To successfully store and retrieve objects from a hashtable, the objects used as keys must implement the hashCode method and the equals method. Below is the program to display the contents of a HashTable using enumeration: Output Geeks for Geeks 34. Write a program in java to get the collection view of the values present in a HashMap.Java’s HashMap class has the java.util.HashMap.values() method for creating collections out of HashMap values. It basically returns a Collection view of HashMap values. Output Initial Mappings are: {0=Welcome, 1=to, 2=Geeks, 3=4, 4=Geeks}
The collection is: [Welcome, to, Geeks, 4, Geeks]
For more information, refer to the article – HashMap values() Method in Java 35. Write a program to join two ArrayList into one single ArrayList.Given two ArrayLists in Java, our task is to join these ArrayLists. Output ArrayList 1: [Geeks, For, ForGeeks] ArrayList 2: [GeeksForGeeks, A computer portal] Joined ArrayLists: [Geeks, For, ForGeeks, GeeksForGeeks, A computer portal] For more information, refer to the article – Join two ArrayLists in Java 36. How can you synchronize an ArrayList in Java?Using the Collections.synchronizedList() method, we can synchronize our collections in Java. SynchronizedList() returns a synchronized (thread-safe) list backed by a selection. Output Eat Coffee Code Sleep Repeat 37. What is a Properties Class in Java?The properties class is a subclass of Hashtable. The properties class stores a list of values whose key is a string and whose value is also a string. Properties can define other properties class lists, but the default is properties. Features of Properties class:
38. What will happen if you use HashMap in a multithreaded Java application?In a multi-threaded environment, if multiple threads alter the map structurally, such as adding, removing, or modifying mappings, the internal data structure of HashMap may become corrupted and there may be some missing links, incorrect entries, and the map itself may become completely useless. Thus, you should not use HashMap in a concurrent application; instead, use ConcurrentHashMap or Hashtable which is thread-safe. The ConcurrentHashMap includes all the Hashtable’s methods as well as full concurrency of retrievals and updates. How did ThreadSafeConcurrentHashMap become thread-safe?
39. What will happen if two different keys of HashMap return the same hashcode()?When two different keys of HashMap return the same hash code, they will end up in the same bucket; therefore, collisions will occur. n case of collision, i.e. index of two or more nodes is the same, nodes are joined by a link list i.e. the second node is referenced by the first node and the third by the second, and so on.
40. What is WeakHashMap?WeakHashMap implements the Map interface. Unlike HashMap, WeakHashMap allows garbage collection even if the object specified as the key doesn’t contain any references despite being associated with WeakHashMap. In other words, Garbage Collector is better than WeakHashMap.
41. What is UnsupportedOperationException?In the context of APIs or list implementations, the UnsupportedOperationException is a common exception. The exception is thrown when the requested operation cannot be performed. This class is a member of the Java Collections Framework. Syntax: public class UnsupportedOperationException
42. How to make a Collection Read-Only in Java?Creating a Read-Only Collection involves restricting the object to only fetching the data and not adding or removing data. Java has different methods for different Collection types like unmodifiableCollection(), unmodifiableMap(), ununmodifiableSet(), etc. java.util.The collections class defines all methods. The unmodifiableCollection() method creates a Read-Only collection. It requires a reference to the Collection class. If we have an object of Set Interface, we can use ununmodifiableSet() to make Read-Only.
43. Difference between PriorityQueue and TreeSet in Java?
44. What is the diamond operator in Java?Diamond operators are used for simplifying the use of generics when creating objects while avoiding unchecked warnings in a program. When the Diamond operator was introduced in Java 7, we can create the object without mentioning the generic type on the right side of the expression as shown below. Syntax: List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
45. How TreeMap works in Java?TreeMap stores the key-value pairs, but TreeMap sorts the keys ascending rather than descending like HashMap. Depending on which constructor is used, TreeMap will be sorted either based on its keys, or by a Comparator. In TreeMap, the elements are sorted based on a Red-Black tree. A red-black tree is a self-balancing binary search tree where each node has an extra bit, and that bit is often interpreted as the color (red or black). These colors are used to ensure that the tree remains balanced during insertions and deletions.  Structure of a Node in Java
46. List down ways to iterate over Map in java?The HashMap class provides Java’s Map interface by storing data in (Key, Value) pairs and accessing them by an index of another type. To use this class it is necessary to import java.util.HashMap package or its superclass. There are numerous ways to iterate over HashMap of which 5 are listed below:
47. What is CopyOnWriteArrayList in Java? CopyOnWriteArrayList in Java JDK 1.5 introduced an enhanced version of ArrayList called CopyOnWriteArrayList, where all modifications (add, set, remove, etc) are implemented by a new copy. It can be found in java.util.concurrent. It is a data structure created to be used in a concurrent environment. In a Thread-based environment, the CopyOnWriteArrayList is intended for frequent reading and infrequent updating. CopyOnWriteArrayList is a thread-safe version of ArrayList.
48. What is EnumMap in Java?EnumMap is an implementation of the Map interface specific to enumeration types. EnumMap class is a member of the Java Collections Framework & is not synchronized. It extends AbstractMap and implements the Map interface in java. EnumMap belongs to java.util package. Syntax:
Parameters:
 EnumMap in Java
49. How does Hashmap internally Works?HashMap works on the principle of Hashing. HashMap contains an array of Node and Node can represent a class having the following objects:
The internal workings of HashMap:
50. Why iterator in hashmap is considered fail-fast?fail-fast iterators immediately throw concurrent modification exceptions if any thread from outside attempts to modify the collection on which they are iterating. The fail-fast feature ensures that the iterator fails immediately if it detects that any modification of the collection will lead to anomalous behavior in the future.
Example: Output: [1, 3, 4, 5] ConclusionJava Collections is important to understand for Java developers or programmers because Java is widely used in various industries. It’s important for developers to have a solid understanding of core concepts of Java Collections. Java is one of the most widely used languages in top companies such as Uber, Airbnb, Google, Netflix, Instagram, Spotify, Amazon, etc. To get into these companies or any other IT companies, you need to master these mostly asked Java Collections interview questions in order to crack their Java-based online assessment and technical interview.
Java Collections Interview Questions – FAQsWhat are collections in Java interview questions?
What are the 4 collection classes in Java?
Can HashMap have duplicate keys?
Why array is not a collection?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Interview Questions |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |