|
|
The ecosystem term was first coined by an ecologist Arthur Tansley in 1935. The ecosystem is a balance or equilibrium between living and non-living factors of the ecosystem where they tend to interact with each other. All living things, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, depend on non-living substances to survive and maintain the equilibrium of the natural environment. This relationship between the living and nonliving elements is studied by the study of ecosystems. In this article, we will discuss ecosystem structure, function, and types of ecosystems. Table of Content What is an Ecosystem?
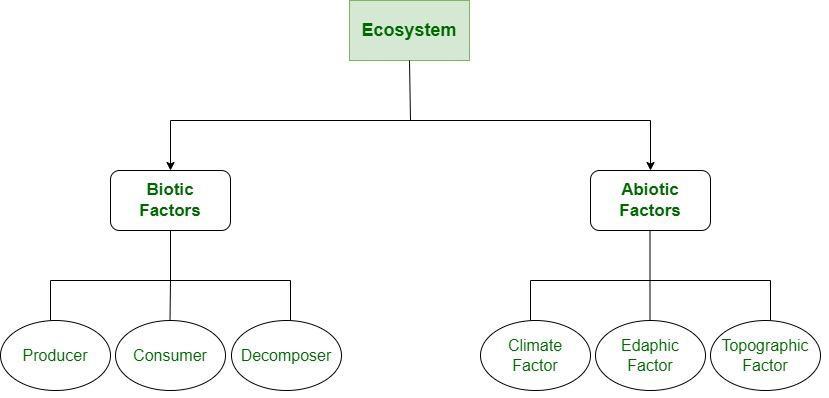
In the word “ecosystem”, “eco” means environment, and “system,” refers to connected processes or elements. Ecosystems are made up of both biotic (or alive) and abiotic (or nonliving) components. It is a biological community where living and non-living components of the planet interact with each other. Ecosystem varies in the size and number of organisms they consist of. When the ecosystem is land-based it is called a terrestrial ecosystem and when it is water-based it is called an aquatic ecosystem. Structure of EcosystemThe structure of an ecosystem is made of two main components: biotic and abiotic components. The biotic component interacts with the abiotic components to maintain the flow of energy. The energy is distributed in the environment. The ecosystem includes 2 main components for a working ecosystem:
Also Read: Ecosystem and Its Component
Biotic ComponentsPlants, animals, microorganisms, aquatic plants, and all other living creatures are the biotic components of the ecosystem. These biotic components can be classified into:
Abiotic ComponentsIt involves all the non-living things present in the environment. Some of the abiotic components are sun, soil, water, minerals, climate, rocks, temperature, and humidity. These components’ functioning together enables the ecosystem’s energy and nutrition cycles. The sun’s rays are the primary energy source. An ecosystem’s temperature changes have an impact on the types of plants that may flourish there. The availability of nutrients and soil nature determines the type and abundance of vegetation in an area. All the abiotic factors are essential factors that determine the number and type of organisms present in a region. Functions of EcosystemFollowing are some of the functions of the ecosystem;
Types of EcosystemAn ecosystem can be small or large. There are 2 types of ecosystem:
Aquatic EcosystemOceans, rivers, seas, lakes, springs, and other water bodies are aquatic biomes. The bulk of the earth’s surface is covered by the water. Two-thirds of the earth’s surface is made up of oceans, seas, the intertidal zone, reefs, the seabed, and rock pools. This ecosystem includes plants, fishes, amphibians, coral reefs, huge sea creatures, and insects.
There are 2 types of aquatic ecosystem:
Freshwater EcosystemsA freshwater ecosystem has low salinity levels, providing a good environment for a variety of plants and animals. The sizes of freshwater resources range from small ponds to very large rivers. Freshwater resources vary from one another in terms of how they travel. While some freshwater bodies are constantly moving, like rivers, others remain still, like ponds. Freshwater Ecosystem Types: Based on the region, the three main categories of the freshwater environment are the lotic, lentic, and wetland freshwater ecosystems.
Living creatures that live in Freshwater Ecosystems: Fishes, amphibians, reptiles, mosquitoes, dragonflies, bees, wasps, water spiders, ducks, geese, etc. Marine EcosystemsAquatic environments with high levels of dissolved salt are marine ecosystems. These comprise the deep ocean, the open ocean, and the coastal marine ecosystems. Each of these has unique biological and physical properties. The ecosystem’s exposure to the sun, the amount of oxygen and nutrients that are dissolved in the water, the distance from land, the depth, and the temperature are all significant abiotic factors. Marine ecosystems have unique biotic and abiotic characteristics. Terrestrial EcosystemA terrestrial ecosystem refers to an ecosystem of diverse land surfaces. Forests, deserts, grasslands, tundra, and coastal regions are all examples of terrestrial ecosystems. These terrestrial ecosystems are climate-dependent.
Functional Units of EcosystemThe ecosystem’s function is to maintain its various parts working together. It is a natural process of a transfer of energy in different biotic and abiotic elements of the world. Ecosystems maintain all the important ecological processes, including nutrient cycling. Ecosystems have different functional units those are:
Ecosystem DiversityEcosystem diversity refers to the variety of different habitats and communities found in a particular area, along with the various interactions between them. These ecosystems include forests, grasslands, deserts, rivers, and oceans, each supporting a unique array of plants, animals, and microorganisms. The diverse range of ecosystems contributes to the overall health and stability of the environment, providing essential services like air and water purification, soil fertility, and climate regulation. Ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining biodiversity, as it ensures the survival of a wide range of species and helps ecosystems adapt to environmental changes. Protecting and conserving ecosystem diversity is essential for preserving the delicate balance of nature and ensuring the well-being of both wildlife and humans. Concepts of EcosystemThese are the important concepts under the ecosystem. Those are: Food Chain and Food WebsThe cycle of energy starts with solar energy. The chain of energy transfer from one level to the topmost level is known as the food chain. Plants absorb solar energy and synthesize their food. Later on, herbivores feed on the plants for energy. Similarly, carnivores and omnivores feed on them for energy.
The interconnected food chain is known as the food web. In nature mostly food webs are common instead of the food chain. Also Read: Difference Btetween Food Webs and Food Chain
Ecological PyramidsThese are the graphical representations of the number, energy, and biomass of the trophic level of an ecosystem. Charles Elton postulated the ecological pyramid in 1927. The base of the ecological pyramid denotes the producers of that particular ecosystem. Then it is followed by the consumers and the top decomposers.
Energy Flow in EcosystemThe flow of energy in the ecosystem is always in one direction or unidirectional. Even though producers tend to absorb 100% sun’s light energy in their capacity, they only pass on 10% of that energy to the next trophic level and then only 10% of that energy is passed into the next level. Biogeochemical CycleIt is also known as the nutrient cycle and includes all the phenomena that ensure that all the basic elements of nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus that are absorbed by living organisms from the environment are returned to the environment. This process involves the transfer of nutrients between abiotic and biotic factors and vice-versa. It includes the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, water cycle, phosphorus cycle, etc. Conclusion – EcosystemEcosystems are the complex webs of life that includes all living organisms and their physical surroundings, working together in harmony. They provide essential services like clean air, water, and food, supporting life on Earth. Understanding and protecting ecosystems is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the well-being of both wildlife and humans. By conserving ecosystems and practicing sustainable living, we can preserve the delicate balance of nature and secure a healthy environment for future generations to thrive in.
FAQs on EcosystemWhat is the Ecosystem?
What are the Major Ecosystems?
What are the main functions of the Ecosystem?
What is the Structure of the Ecosystem?
Which is the Largest Ecosystem in the world?
What are the Functional Components of an Ecosystem?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Class 12 |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |



