
|
|
Timetables are a type of tables in MATLAB that store a timestamp corresponding to each row. Similar to tables, timetables can store column-oriented data under a variable name (column name), where every variable has same number of rows. All the functions of a table work with timetables as well along with some timetable-specific functions that are used to align, combine and perform various calculations with other timetables. Let us see various ways of creating timetables. Method 1:Using timetable()A timetable can be created with the timetable function. This function takes a time vector and different vector variables. Syntax:
Here, all var1…var n must have the same number if rows. See the following example for better understanding. Example 1: Matlab
Output: 
This will create a table of 3×2 and not 3×3 because the time stamp is not considered a column vector. Method 2: Using table2timetable()Converting a table into timetable by the table2timetable function. This function creates a timetable from a function that already has a time vector as one of its column vectors. See the following example to understand its working. Example 2: Matlab
Output: 
Method 3: Using istimetable()The istimetable() function returns a Boolean value. True if the given table is a timetable else false. See the following example Example 3: Matlab
Output: 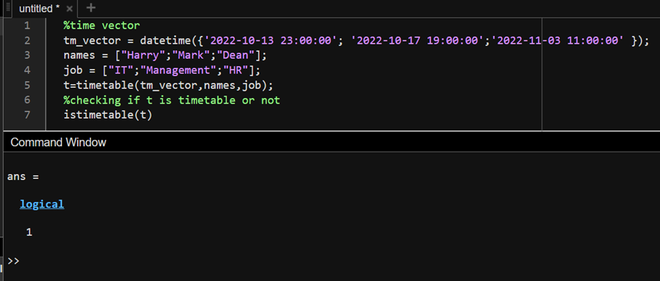
Accessing Elements:You can access the elements of a timetable in the same manner as ordinary tables by any of the following methods:
Refer to this GfG article for further explanation of accessing tables in MATLAB. Conclusion:This article discussed various methods of creating timetables in MATLAB and also briefly explained how to access the elements of a table in MATLAB. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| MATLAB |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |