|
|
The cardiac cycle is a sequential event in the heart that is cyclically repeated. The cardiac cycle diagram shows the cardiac cycle phases consisting of systole and diastole of both the atria and ventricles. The cardiac cycle class 11 is an important concept that is also studied in higher classes. It is regulated by electrical signals from the sinoatrial (SA) node and atrioventricular (AV) node, which ensures the circulation of oxygenated blood throughout the body. The heart beats 72 times per minute, that is many cardiac cycles are performed per minute. In this article, we will cover the cardiac cycle – steps, diagram, and physiology of the cardiac cycle. Table of Content Cardiac Cycle Definition
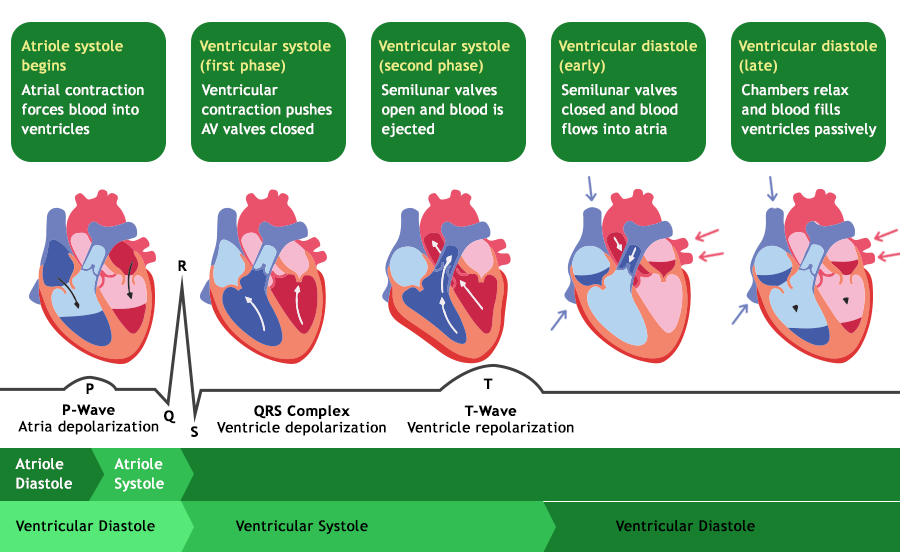
What is the Cardiac Cycle?The cardiac cycle represents the series of events that occur to complete a heartbeat. The electrical impulse is started by the SA node, which causes the atria and ventricles to contract and relax. During this process, the heart muscles undergo changes, involuntarily pumping blood through the circulatory system. During a cardiac cycle, each ventricle pumps out approximately 70 mL of blood which is called the stroke volume. The stroke volume multiplied by the heart rate gives the cardiac output. Therefore, the cardiac output can be defined as the volume of blood pumped out by each ventricle per minute and averages 5000 mL or 5 litres in a healthy individual. Each cardiac cycle consists of a complete contraction and relaxation of both the atria and ventricles and each cardiac cycle lasts approximately 0.8 seconds. In the cardiac cycle, the heart contracts during systole, expelling blood, and relaxes during diastole, filling with blood. When the atria contract, they push blood into the ventricles through the valves, creating the “lubb” sound when the valves close. Then, the ventricles force blood into the pulmonary and systemic arteries, producing the “dubb” sound as these arteries’ valves close. Cardiac Cycle DiagramThe cardiac cycle diagram class 11 is an important concept that we study in our biology syllabus and even in higher studies. Different phases of the cardiac cycle are represented in the diagram below:
Physiology of the Cardiac CycleThe human heart is a muscular organ with four chambers. These chambers are divided into left and right halves in which the top chambers are the atrium and the lower chambers are the ventricles. The right atrium receives the deoxygenated blood from the body and then passes it on to the right ventricle which pumps the blood towards the lungs through the pulmonary artery. On the other hand, the left atrium receives the oxygenated blood from the lungs and then passes it on to the left ventricle which then pumps the blood towards the body through the aorta. Cardiac Cycle PhasesCardiac cycle phases ensure that the heart efficiently pumps blood and maintain the circulation of oxygenated blood throughout the body. Systole of the cardiac cycle refers to the contraction of heart muscles that result in the pumping of the blood. Diastole refers to the relaxation of the heart muscles that result in the relaxing and filling of the chambers of the heart. Both the atrium and ventricles of the heart undergo systole and diastole simultaneously.
Atrial Relaxation (Atrial Diastole)
Atrial Contraction (Atrial Systole)
Isovolumetric Contraction (Ventricular Systole)
Ventricular Ejection
Isovolumetric Relaxation
Passive Ventricular Filling (Early Diastole)
 Cardiac Cycle Phases Duration of the Cardiac CycleThe heart rate per minute determines the length of a cardiac cycle. The length of the cardiac cycle and heart rate are inversely related. As a result, if the heart rate is increased to 120 beats per minute, the cardiac cycle will be completed in around 0.5 seconds.
A normal person’s heartbeat is 72 beats per minute. As a result, the length of one cardiac cycle may be estimated as follows:
Each cardiac cycle will last 0.8 seconds at a heart rate of 72 beats per minute. The following table shows the duration of the various phases of the cardiac cycle:  Duration of Cardiac Cycle
Conclusion – Cardiac CycleIn conclusion, the cardiac cycle is an important process in the heart. The cardiac cycle consits of systole and diastole phases that ensure blood circulation. This cycle will be covered in various calsses as it forms an important part of biology syllabus. Cardiac cycle is regulated by electrical signals, maintaining a heart rate of 72 beats per minute. Understanding its phases and physiology helps in learning about heart function and overall health.
FAQs on Cardiac CycleWhat are the Different Phases of the Cardiac Cycle?
What is Cardiac Cycle Length?
What Happens During Systole?
What are the Major Symptoms of Diastolic Dysfunction?
What Exactly is the Cardiac Cycle?
What is Diastole?
What are the 4 Stages of the Cardiac Cycle?
How do you Calculate your Cardiac Cycle?
What is the Cardiac Cycle of Blood Flow?
What are the Major Symptoms of Diastolic Dysfunction?
What Happens During Systole?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Biology MAQ |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |