|
Constitutional Rights in India: Articles 12-35 of the Indian Constitution are the all about fundamental rights which are essential human rights granted to every citizen of India. The fundamental rights in the Indian Constitution prevent discrimination based on race, religion, gender, and more. The Fundamental Rights in Indian constitution include important rights like the Right to Equality, Right to Freedom, Right to Education, and Freedom of Religion.
Fundamental Rights Latest News Update
In October 2023, Supreme Court of India ruled that same-sex marriage and civil unions are not covered as fundamental rights under the Indian Constitution. Five-judge panel Bench unanimously decided not to recognize same-sex marriages or ‘civil unions’ in India.
The term “Fundamental Rights” finds its roots in two fundamental principles:
- Constitution as Guarantor: These rights find their sanctuary in the Constitution itself, with an unequivocal guarantee of protection.
- Court-Backed Enforcement: In the event of a breach, individuals possess the power to seek legal recourse, turning to the courts for redressal.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at Articles 12-35 and understand why these rights are so important in building a fair and equal society.
Current Affairs on Fundamental Rights 2023
- Supreme Court Ruling on Article 19: On January 5, 2023, the Supreme Court of India made a significant ruling in a case involving the fundamental right to freedom of speech. In a 4-1 majority decision, the Constitution Bench of the court stated that an individual can seek enforcement of this right.
- Supreme Court Verdict on Same-Sex Marriage: In October 2023, a five-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court unanimously declined to recognize same-sex marriages. The Bench also declined to permit ‘civil unions’ for same-sex couples. All the judges of the Bench, although in favor of civil unions, ruled that there is no fundamental right to marry under the Indian Constitution
What are Fundamental Rights?
Fundamental rights refer to the basic human rights which are enshrined in the Indian Constitution which came to guaranteed for all citizens and were applied without any discrimination on the basis of race, gender, religion etc. and significantly, the fundamental rights are enforceable by the courts, subject to certain conditions.
Why are they called Fundamental Rights?
The Fundamental rights are called so because:
- They are enshrined in the Constitution which guarantees them.
- They are justifiable and in case of any violation, a person can approach a court of law.
How many Fundamental Rights are there in the Indian Constitution?
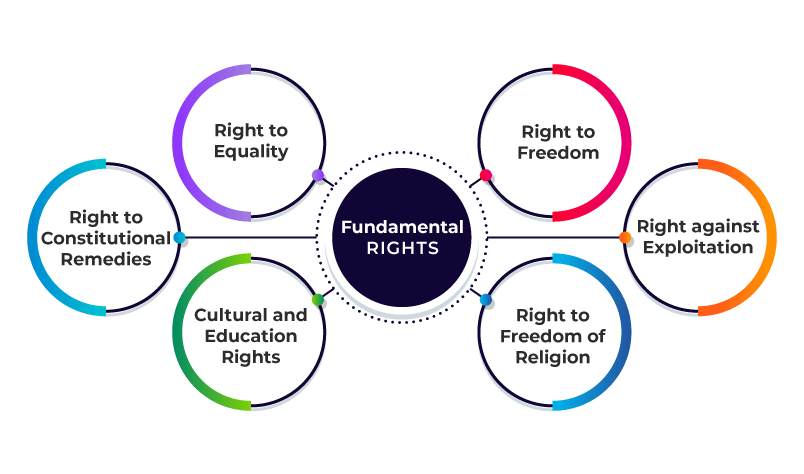
There are six fundamental rights in the Indian Constitution are:
- Right to Equality (Article 14-18)
- Right to Freedom ( Article 19-22)
- Right against Exploitation
- Right to Freedom of Religion (Article 25-28)
- Cultural and Educational Rights (Article 29-30)
- Right to Constitutional Remedies ( Article 32)
Why Right to Property is not a Fundamental Right?
Right to Property was also a fundamental right for Indian Constitution. This right was removed from the list of fundamental rights by the 44th Constitutional Amendment. This happened because this right came to be hindrance towards attainment of the goal for socialism and also redistribution of wealth, equitably among the various people.
Is Right to property a constitutional right or legal right?
Right to Propery is now a legal right and not a fundamental right.
Also Check:
6 Fundamental Rights of India
Fundamental rights are essential for everyone’s moral and intellectual growth. Fundamental rights are essential for an individual’s growth. India’s post-independence era has resulted in the addition of some extremely important fundamental rights in the Indian constitution. Every citizen of India is given certain rights by law. It’s vital to know what they are so that no one’s rights get infringed upon. The Indian Constitution Overview Indian Constitution states the following six fundamental rights for an Indian citizen:
- Right to Equality
- Right to Freedom
- Right against Exploitation
- Right to Freedom of Religion
- Cultural and Educational Rights
- Right to Constitutional Remedies
The Indian constitution originally had seven essential rights, one of which was the right to property (Article 31), which was subsequently turned into a legal right by the “44 amendments” to the Indian constitution in 1978.
Right to Equality
Equal legal rights for all citizens are completely safeguarded by the right to equality. Inequality based on caste, creed, religion, place of birth, race, or sex strictly is prohibited by the Right to Equality. It also guarantees equal opportunity in government employment and prevents the government from discriminating against anybody in the workplace merely based on religion, caste, race, gender, descent, place of birth, place of residence, or any of these considerations. Articles 14 to 18 provide for equality before the law. Equality before the law is guaranteed by the Constitution, which assures that all people are treated equally before the law. The state cannot discriminate against citizens based on their religion, caste, race, gender, or place of birth. To attain equality, this is necessary.
Example for the Right to Equality:
- Women are entitled to the same salary as men because there should be not any discrimination based on gender as per law.
- In the eyes of the law, every person in India is equal, regardless of their status, wealth, etc.
Right to Freedom
It can also be called as Right to Liberty. Every person’s most treasured desire is for them to be free. Freedom of speech, expression of freedom, freedom of assembly without arms, freedom of movement throughout our country’s territory, freedom of association, freedom to pursue any profession, and freedom to reside in any region of the country are just a few of the rights granted by the right to freedom. These rights, however, are subject to several restrictions.
Example for Right to Freedom:
- Any person is entitled to say anything he/she wants freely unless it is deemed to be derogatory or defaming against another person/community/organization.
- Indian citizens can freely relocate to any place in India.
Right Against Exploitation
Historically, the Indian society has been based hierarchically, which has resulted in all sorts of exploitation. It’s important to realize that being exploited is the same as, if not worse than mistreated. This is a crucial Fundamental Right that ensures that no citizen is subjected to any form of forced labor. No one may be forced to labor against their will, even if money is provided. The Indian constitution prohibits any form of forced labor. If a lower-than-minimum wage is paid, it is considered forced labor. In addition, the article declares human trafficking to be unconstitutional. As a result, buying and selling men and women for unlawful and immoral purposes is prohibited. In addition, this article declares this ‘bound labor’ unconstitutional.
Examples of Rights Against Exploitation:
- Any Employer is expected to at least pay the minimum wage to his/her workers and provide rightful working conditions to his or her workers.
- Employers are not permitted to engage in the practice of employing underage or minor labor.
Cultural and Educational Rights
Cultural and educational rights give all members of society the right to preserve their cultural script or language. The image of Indian society that springs to mind is one of diversity. Our Constitution thinks that variety is our strength in such a diverse society. As a result, one of the fundamental rights of minorities is the right to preserve their culture. Minorities are ethnic or religious groups that share a common language or religion and live in a specific region of the country. Minority religious and linguistic groups can also establish their educational institutions. They will be able to preserve and develop their own culture in this way.
Democracy, as we all know, is the rule of the majority. Minorities, on the other hand, are critical to the organization’s success. As a result, minorities’ languages, cultures, and religions must be protected. This is necessary for minorities to not feel forgotten or undervalued under majority rule. Though individuals are proud of their own culture and language, our constitution provides for a particular right known as the Cultural and Educational Right.
Examples of Cultural and Educational Rights:
- Sikhs are allowed to take sharp objects such as Kirpan (a sharp object) in airports where any other sharp objects such as knives, daggers, etc are banned.
- Anyone in India can freely celebrate any religious or cultural festival unless it is in contradiction with Indian laws.
Right to Freedom of Religion
The Constitution declares India a “secular state” because it is a multi-religious country where Hindus, Christians, Sikhs, and many more communities coexist. It signifies that the Indian state does not have its religion or “national” religion. However, it gives all residents complete freedom to believe in any religion and worship whomever they want. However, this should not interfere with other people’s religious views and/or practices. This liberty is also available to foreigners. No one shall be forced to pay any tax whose earnings are used only to pay for expenses made in the promotion or preservation of any particular religion or religious denomination. Through educational institutions, this article allows the dissemination of religious knowledge.
Examples of Freedom of Religion:
- Any citizen of India can follow or abide by any religion they feel fit to follow at any time they want.
- The Government of India cannot persecute any person just based on religion.
Right to Constitutional Remedies
- Right to Constitutional Remedies: In India, individuals have the right to approach the Supreme Court for the protection of their fundamental rights.
- Articles 32 and 226: These articles of the Constitution safeguard the right for the Supreme Court and the High Court, respectively.
- Scope of the Right: The Supreme Court and high courts can enforce fundamental rights, with local courts also having some authority in this regard.
- Exemption of CourtMartial: Military law governed courtmartials are exempt from this constitutional protection.
- Significance of Article 32: Dr. B. R. Ambedkar referred to Article 32 as the constitution’s soul and heart, essential to its basic structure.
- Appeal Rights: This right ensures that the appeal to the highest court cannot be denied, except by courts established by the Indian constitution.
- Suspension During Emergencies: Under Article 359, this privilege can be suspended during a national emergency.
- Supreme Court’s Role: The Supreme Court acts as a guarantor and defender of fundamental rights under Article 32.
- Direct Appeal to Supreme Court: Individuals can directly approach the Supreme Court for redressal, bypassing the appeals process.
- Invocation During Emergencies: Citizens can invoke this right even during national emergencies.
Examples of constitutional remedies:
- Every Citizen has the right to appeal to the court for remedies to the constitution either by approaching the Courts directly or by submitting a PIL.
Features of Fundamental Rights
Fundamental rights are different from ordinary rights as they are enforced and if legal rights are violated, the aggrieved person cannot directly approached the Supreme Court by passing from the lower courts. He or she has to approach the lower courts.
Some fundamental rights are available for all citizens while rest for all the people.
- Fundamental rights are not absolute rights and have certain restrictions, which are subjected to conditions of state safety, public morality and friendliness with foreign countries.
- They are justifiable by implication and enforceable by court.
- Fundamental rights can be suspended during national emergency and rights under Article 20 and 21 cannot be suspended.
Importance of Fundamental Rights
Here are some of the key reasons why fundamental rights are important
- Protecting Individual Liberties: Fundamental rights provide individuals with protection against the arbitrary exercise of state power. This means that individuals have the right to live, work, and speak freely without fear of government repression or infringement of their personal liberties.
- Promoting Equality: Fundamental rights promote equality by ensuring that everyone is treated fairly and equally before the law, regardless of their race, religion, caste, gender, or social status. They prohibit discrimination and provide a level playing field for all individuals.
- Ensuring Justice: Fundamental rights ensure that justice is accessible to everyone. They guarantee the right to a fair trial, the right to legal representation, and the right to seek redressal for grievances.
- Fostering Democracy: Fundamental rights are a cornerstone of democracy. They empower individuals to participate actively in the democratic process by providing them with the freedom to express their opinions, to vote, and to hold their elected representatives accountable.
- Protecting Human Dignity: Fundamental rights protect the dignity of individuals by ensuring that they are treated with respect and have the right to live their lives with autonomy and self-determination.
Improving the Scope of Rights
- Broader Rights Beyond Fundamental Rights: The Indian Constitution and legislation encompass a wider range of rights than just the Fundamental Rights.
- Expansion of Legal Rights: Occasionally, this leads to the expansion of a citizen’s legal rights.
- Judicial Rulings on Rights Expansion: Courts have made decisions over time to broaden the scope of rights.
- Rights Beyond Fundamental Rights: Includes media freedom, access to information, and the right to education.
- Right to Education: School education is now a right for Indian citizens, with the government ensuring free and compulsory education for all children under 14.
- Right to Information: Enacted by Parliament, this right allows citizens to request information from government departments, stemming from the Fundamental Right to Freedom of Thought and Expression.
- Constitutional Rights Beyond Fundamental Rights: Some rights, like the right to property, are constitutional rights rather than Fundamental Rights.
- Human Rights as a Tool for Growth: These universal moral claims may or may not be recognized by law, but there’s increasing pressure on governments to acknowledge them as democracy spreads.
- Evolving Scope of Rights: Over time, the scope of rights has expanded, leading to the emergence of new rights.
Also Check:
Conclusion: The Cornerstone of Democracy – Fundamental Rights
In conclusion, fundamental rights are the bedrock of a democratic society, ensuring the dignity, liberty, and equality of all citizens. These rights provide a framework for a just and equitable society, safeguarding individuals against any form of discrimination and state excesses. They empower citizens to participate actively in the democratic process, fostering a culture of mutual respect and understanding. By guaranteeing freedoms such as speech, expression, and belief, fundamental rights not only protect individual liberties but also nurture a healthy and vibrant democracy. As democracy evolves, these rights adapt and expand, reflecting the changing needs and values of society, thereby maintaining the dynamic and resilient nature of a democratic system.
FAQs on Fundamental Rights in India
1. What are the Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution?
There are six fundamental rights in India. They are Right to Equality, Right to Freedom, Right against Exploitation, Right to Freedom of Religion, Cultural and Educational Rights, and Right to Constitutional Remedies.
2. Why are Fundamental Rights important in India?
Fundamental Rights are crucial as they ensure the dignity, liberty, and equality of all citizens. They form the cornerstone of a democratic society, protecting individuals from state excesses and discrimination.
3. Can Fundamental Rights be amended or suspended?
Fundamental Rights can be amended, but not in a way that violates the basic structure of the Constitution. During a national emergency, certain rights can be suspended.
4. How do Fundamental Rights protect individual freedoms?
These rights safeguard various individual freedoms, including speech, expression, assembly, movement, and the practice of any profession.
5. Are Fundamental Rights enforceable by law?
Yes, Fundamental Rights are justiciable and enforceable by the courts. If violated, an individual can approach the judiciary for enforcement or remedies.
6. Do Fundamental Rights apply to all citizens of India?
Most Fundamental Rights are available to all citizens of India, but some are also applicable to persons, including non-citizens.
7. What is the Right to Equality?
The Right to Equality ensures equal treatment before the law, prohibiting discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
8. What does the Right against Exploitation entail?
This right prohibits all forms of forced labor, child labor, and human trafficking, ensuring dignity and protection for all individuals, especially the vulnerable.
9. How does the Right to Freedom of Religion protect religious practices?
It allows all citizens to freely profess, practice, and propagate any religion, and also ensures that every religious group can manage its own affairs.
10. What is the significance of Cultural and Educational Rights?
These rights protect the interests of minorities by allowing them to preserve their languages, scripts, and cultures, and establish and administer educational institutions.
|
