|
|
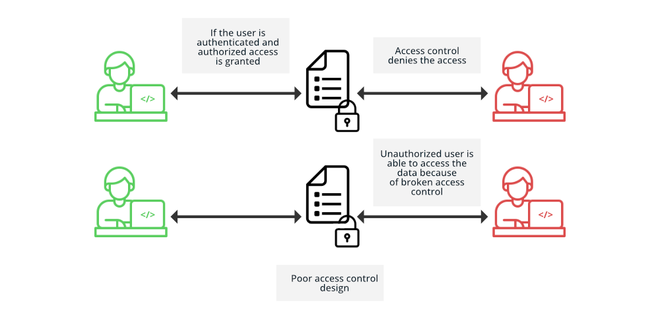
Access control is a security mechanism to put restrictions on the accessibilities of the resources and decide who or what can view or use the resources of a company. This is checked after authentication, and what authorized users are allowed to do. It is not an easy task to do, any failure while checking, can lead to data modification or destruction of data or unauthorized performance of the business functions, etc. Sometimes, developers don’t design access control specifically but simply design them along with the website. As a result that special collection of rules becomes hard to understand. What is Broken Access Control?Poor implementation of access control mechanism leads to flawed access control, which can be easily exploited. This is called broken access control. Because of broken access control, unauthorized users can view content that they are not allowed to view, can perform unauthorized functions, even an attacker can delete the content, or take over site administration.  Broken Access Control Access control vulnerabilitiesWe can split access control vulnerabilities mainly into three categories : 1. Horizontal privilege escalation:When users can access data of other users who have the same level of permissions as them. 2. Vertical privilege escalation:When users can access data of those users who have permissions to perform some actions that normal users don’t, with vertical access controls, different types of users have access to different application functions. 3. Context-dependent privilege escalation:When a user is allowed to perform actions in the wrong order. Impacts of broken access control1. Whenever we make an account on a website, we are given a unique ID. By using that ID, we can access the database where all our sensitive contents are saved. Suppose, you have logged into a website, and your user ID is 986. The URL of your profile page should look something like this: https://brokenaccesscontrol.com/profile?id=986. We have to keep in mind that, like you, everyone else who makes his/her account on that website, is given a unique user ID. So, if you replace your ID with someone else’s user ID, then you can get access to his/her profile. Yes, this can happen if access control is not properly implemented in the server. 2. Hackers can take advantage of access flaws to gain access to the resources and services that should not be accessible to normal users. 3. There are possibilities of Distributed Denial of Service attacks (DDOS). With access to those user accounts, attackers can attempt to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, by deploying bots. This makes it difficult for the server to distinguish legitimate user traffic from attack traffic. How to Prevent Broken Access Control?OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project), an online community that analyzes weaknesses and attacks on web applications, has given a list of the top 10 most dangerous vulnerabilities, and Broken Access Control is one of them. It shows that most web applications have poor security. To prevent broken access control, the security team can adopt the following practices- 1. Continuous Inspection and Testing Access Control:Efficient continuous testing and inspecting the access control mechanism is an effective way to detect the newer vulnerabilities and correct them as soon as possible. 2. Deny Access By Default:Design access control in such a way that not everyone can get access to the resources and functionalities unless it is intended to be publicly accessible. You can apply JIT (Just-in-Time) access, which helps to remove the risks associated with standing privileges. 3. Limiting CORS Usage:CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) protocol provides a controlled way to share cross-origin resources. The implementation of the CORS relies on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) headers used in the communication between the client and the target application. When CORS protocol is misconfigured, it makes it possible for a domain to be controlled by a malicious party to send requests to your domain. 4. Enable Role-based Access Control:This is a widely used access control mechanism. According to this, users are given permissions based on their roles. Instead of identifying each user individually, users are assigned to a group of roles, this way the struggle of IT support and administration can be reduced, and operational efficiency will be maximized. 5. Enable Permission-Based Access Control:This is an access control method, where the authorization layer checks if the user has permission to access particular data or to perform a particular action, typically by checking if the user’s roles have this permission or not. 6. Enable Mandatory access control:It is a security method, that restricts the ability to access resources based on the sensitivity of the information, that the resource contains. This security policy can only be controlled by the administrator, regular users don’t have the ability to change that policy. Because of this centralized administration, it is considered to be very secure. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Computer Networks |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 10 |