
|
|
The Session and Token-based Authentication methods are used to make a server trust any request sent by an authenticated user over the internet. In this way, a user can interact with their account without continually specifying their credentials. These methods are usually used for different purposes. For example, sessions are commonly used in websites applications while tokens are preferred in server-to-server connections.  Authentication Session AuthenticationA session is a small file, most likely in JSON format, that stores information about the user, such as a unique ID, time of login and expirations, and so on. It is generated and stored on the server so that the server can keep track of the user requests. The user receives some of these details, especially the ID, as cookies that will be sent with every new request, so that the server can recognize the ID and authorize the user’s requests. Working
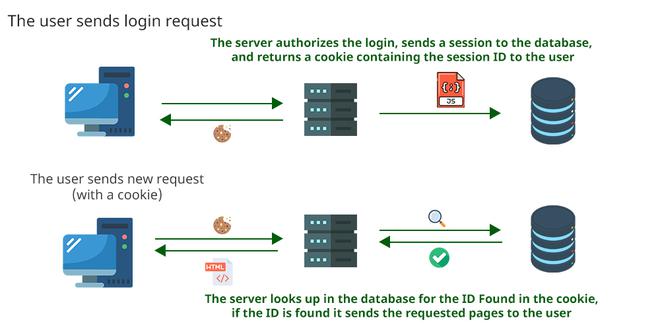 Session Authentication Pros/ConsSince sessions are stored on the server, its administrators are in power over them. For example, if a security team suspects an account is compromised, they can immediately invalidate the session ID, so that the user is immediately logged out. On the other hand, since a session is stored on the server, the server is in charge of looking up the session ID that the user sends. This can cause scalability problems. Cookies may be exposed to cross-site request forgery attacks. The attacker may mislead the user to a hostile website, where some JS scripts may exploit cookies to send malicious requests to the server. Another vulnerability regards the chances of a man-in-the-middle attack, where an attacker can intercept the session ID and perform harmful requests to the server. Token-Based AuthenticationA token is an authorization file that cannot be tampered with. It is generated by the server using a secret key, sent to and stored by the user in their local storage. Like in the case of cookies, the user sends this token to the server with every new request, so that the server can verify its signature and authorize the requests. Working
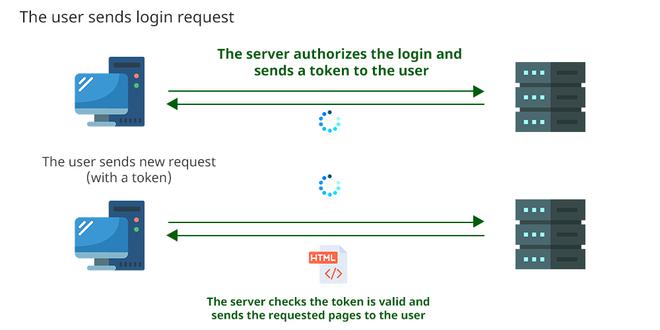 Token Authentication Note- Those are not authentication files, they are authorization ones. While receiving a token, the server does not look up who the user is, it simply authorizes the user’s requests relying on the validity of the token. Pros/ConsTokens can be useful when the user wants to reduce the number of times they must send their credential. In the case of server-to-server connections, using credentials becomes difficult, and tokens overcome this problem. Moreover, servers that use tokens can improve their performances, because they do not need to continuously look through all the session details to authorize the user’s requests. However, the authentication details are stored on the client, so the server cannot perform certain security operations as in the session method. As written above, the server does not authenticate the user, so linking a token to its user can be more difficult. If a hypothetical attacker manages to get a valid token, they may have unlimited access to the server databases. If the server generates keys using older algorithms, these keys can be breached. Differences Between Session and Token-Based Authentication Methods
Conclusion
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Computer Networks |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |