|
|
Buffer Solution is a special aqueous solution that resists the change in its pH when some quantity of acid and Base is added. Many fluids, such as blood, have specific pH values of 7.14, and variations in these values indicate that the body is malfunctioning. The change in pH of Buffer Solutions on adding a small quantity of acid or bases is very minimal and hence they are used to make solutions that resist the change in pH. Let us learn about Buffer solution, its types, and others in this article. Buffer Solution Definition
Buffer Solution is a water-based solvent-based solution made up of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. They are resistant to changes in pH caused by dilution or the addition of relatively small amounts of acid or alkali. When a small amount of strong acid or strong base is added, the pH of the buffer solution changes very little. As a result, they’re used to maintaining a steady pH. When a tiny amount of strong acid or base is given to it, its pH varies very little, and it is thus used to keep a solution’s pH stable. A buffer solution is one that can maintain its hydrogen ion concentration (pH) with just slight dilution or the addition of a small amount of acid or base. Fermentation, food preservation, medicine administration, electroplating, printing, enzyme activity, and blood oxygen-carrying capability all require particular hydrogen ion concentrations (pH) in buffer solutions. Buffer solutions are made up of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid that can maintain pH. Read More: What is Equilibrium? Types of Buffer SolutionsAcidic and basic buffers are the two types of buffer solutions that are extensively classified. These are discussed in greater depth down below. Acidic Buffers
The pH of an aqueous solution containing an equal amount of acetic acid and sodium acetate is 4.74. Furthermore, the pH of these liquids is less than seven. These solutions are made up of a weak acid and its salt. 
Basic or Alkaline Buffers
An aqueous solution of equal parts of ammonium hydroxide and ammonium chloride has a pH of 9.25. These solutions have a pH of greater than seven. They contain a weak base and a weak base salt. 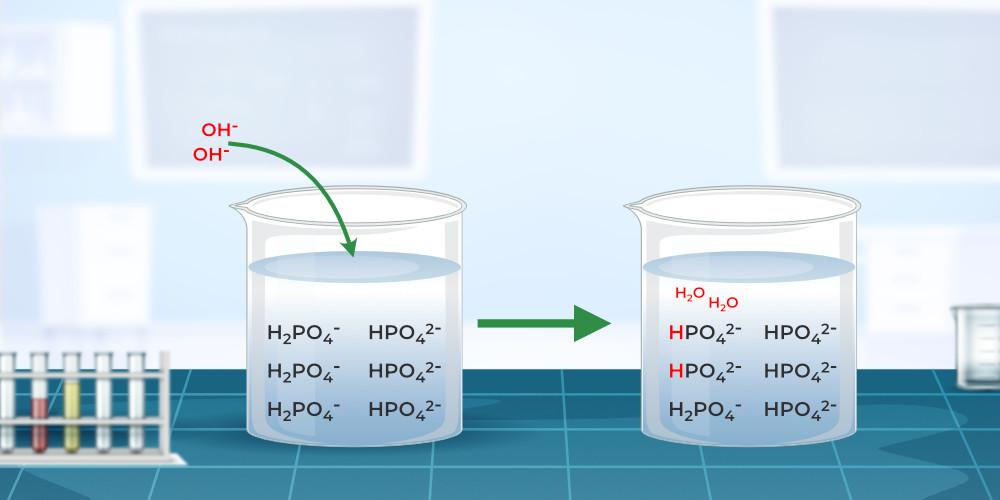
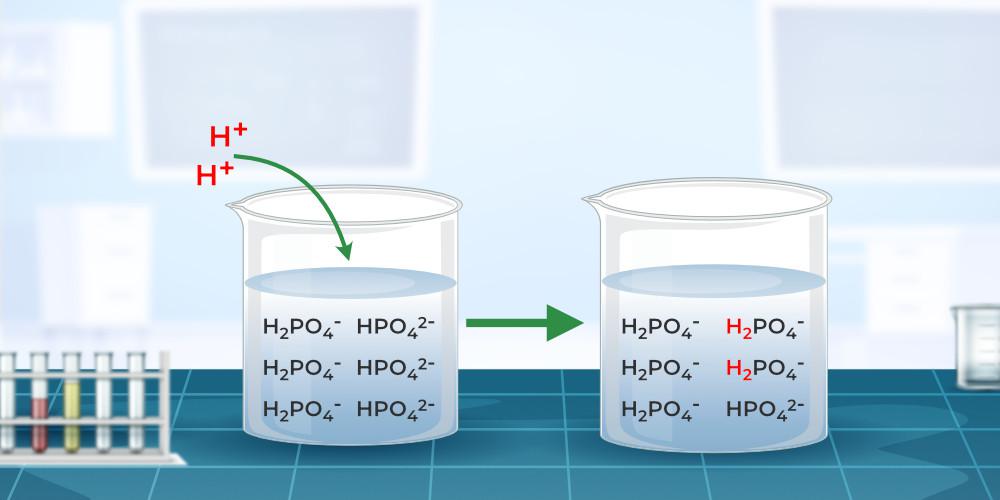
Also Read: Acids, Bases, and Salts Mechanism of Buffering ActionTo understand how a buffer works, think about the example of a buffer solution created by combining sodium acetate and acetic acid. Acetate acid, as implied by its name, is an acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH, whereas sodium acetate dissociates in solution to produce the conjugate base CH3COO– acetate ions. The reaction equation is:
Now, the acetate ion can be neutralized by adding a strong acid to this solution as,
Thus, the original buffer reaction equilibrium changes, and hence, the pH remains constant. Preparation of Buffer SolutionA buffer solution can be made by controlling the salt acid or salt base ratio if the dissociation constants of the acid (pKa) and the base (pKb) are known. Weak bases and their conjugate acids, or weak acids and their respective conjugate bases, are used to make these solutions. The Handerson-Hasselbalch equation and the preparation of acidic buffer and basic buffer. Henderson-Hasselbalch EquationHenderson-Hasselbalch equation is the equation that provides a relationship between the pH of acids and their pKa. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is,
Importance of Henderson EquationThe significance of the Henderson Equation is,
Limitations of Henderson-Hasselbalch EquationThe Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation is not applicable in many cases are:
A buffer solution can easily be prepared using Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation Preparation of Acid BufferIn an acid buffer solution with a strong base (KOH), consider a weak acid (HA) and its salt (KA). The weak acid (HA) ionizes, and the equilibrium is as follows: H2O + HA ⇋ H+ + A– The acid dissociation constant is, Ka = ([H+] [A–])/[HA] RHS and LHS take negative logs: -log Ka = -log [H+] – log ([A–]/[HA]) pKa = pH – log ([salt]/[acid]) pH = pKa + log ([salt]/[acid])
Preparation of Base BufferConsider a basic buffer solution with strong acid, salt (BA), and a weak base (B). As a result, the basic buffer solution will be, pOH = pKb + log ([salt]/[base]) pOH of a basic buffer solution = pKb + log ([salt]/[acid])
Buffering CapacityBuffering Capacity is the property of solutions which is represented by the symbol β. It is defined as the ratio of the moles of acid or base required to change the pH of the solution by 1 and the pH change and the volume of buffers.
Uses of Buffer SolutionsVarious uses of Buffer solution are,
pH MaintenanceHow the pH of any solution is kept constant can easily be explained with the help of the example given below, Take formic acid and sodium formate ions in an aqueous solution they behave as buffer solution and their equilibrium reaction is,
If the strong acids are added to the above buffer solution, the hydrogen ion (H+ ions) combine with the HCOO– ions to give a weakly ionized formic acid, and thus, the pH of the solution is kept constant or slightly changed. If the strong base is added to the above buffer solution, the hydroxide ion (OH– ions) combine with the H+ ions available in the solution to give water molecules, and thus, the pH of the solution is kept constant. The reaction occurring in the process is given below. HCOOH + OH– ⇌ HCOO– + H2O Thus, the pH of the buffer solution is kept constant. Read More, Solved Examples on Buffer SolutionExample 1: What is the pH of a buffered solution of 1.5 M NH3 and 2.5 M NH4Cl when 0.5 M HCl is added to the solution? Solution:
Example 2: How many moles of sodium formate and formic acid are required to prepare 1.00 L of a 0.25 mol/L buffer solution with pH 4.00? (given pKa of Sodium formate is 3.86) Solution:
FAQs on Buffer SolutionQuestion 1: What is a buffer solution?Answer:
Question 2: What is buffering capacity?Answer:
Question 3: What is a buffer action?Answer:
Question 4: What are the advantages of buffer solutions?Answer:
Question 5: What is the pH range of an Acidic Solution?Answer:
Question 6: What is the pH range of the Basic Solution?Answer:
Question 7: What is the pH of the Neutral Solution?Answer:
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| School Chemistry |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |