|
|
Exporting SQL Server data to a text file is a common task that is used in data migration, data sharing, etc. SQL Server provides several methods to export data to a text file format, including using the SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), the SQL Server Command Line Tool (sqlcmd), and the SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS). In this article, we will see how to export SQL Server data to a text file using these three techniques. Before we proceed, let’s set up our database and table. Query: CREATE DATABASE geeks; The table will created, and now we will export this table into text file. How to Export Table Data to a Text File in SQL Server?There are three methods to export the table data from SQL Server into a text file:
Let’s understand each of these methods in detail. We will cover each method and learn how to export table data to a text file in SQL Server with examples and step-by-step process. Method 1: Saving Result to File via SSMSSaving result to file via SSMS is a simple way to export table data to a text file in SQL Server. This method involves selecting the query results and then saving them to a file. Let’s look at the steps for this method. Step 1: First, let’s have a look at our brand’s table. Query: SELECT * FROM brands;
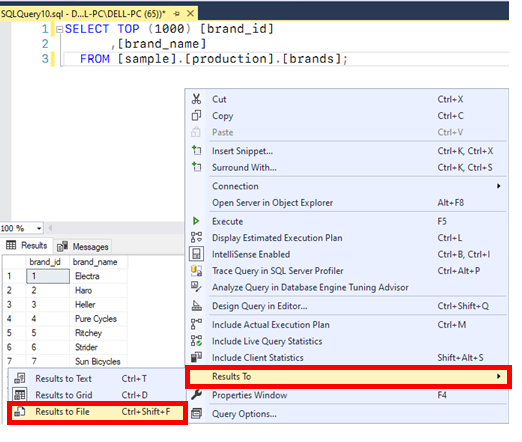
Step 2: Write down the query onto the editor whose output needs to be saved. If you want to save the results in a flat file, you can do this in SSMS. Right Click on Editor > Results to > Results to File: Query: SELECT TOP (1000)
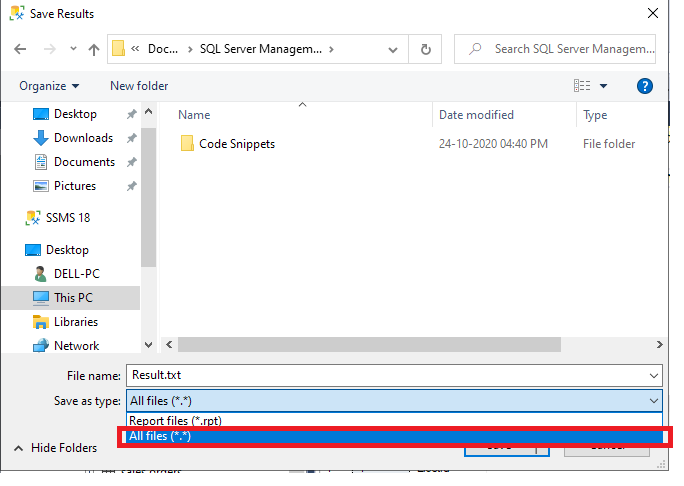
Step 3: Execute the query. An option to specify the name and path will be displayed. Change the type to All Files and Save it with the .txt extension:
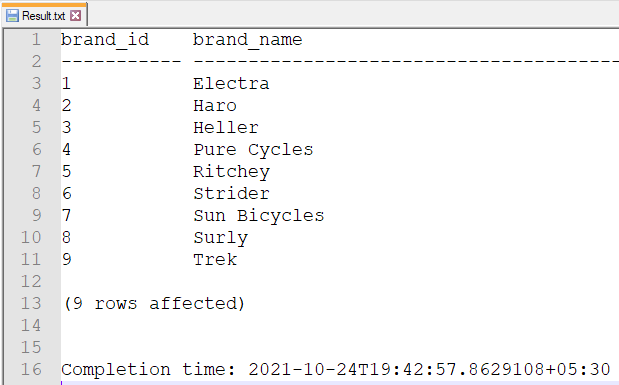
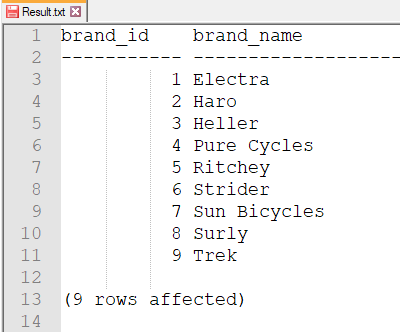
Step 4: Result.txt file looks like this:
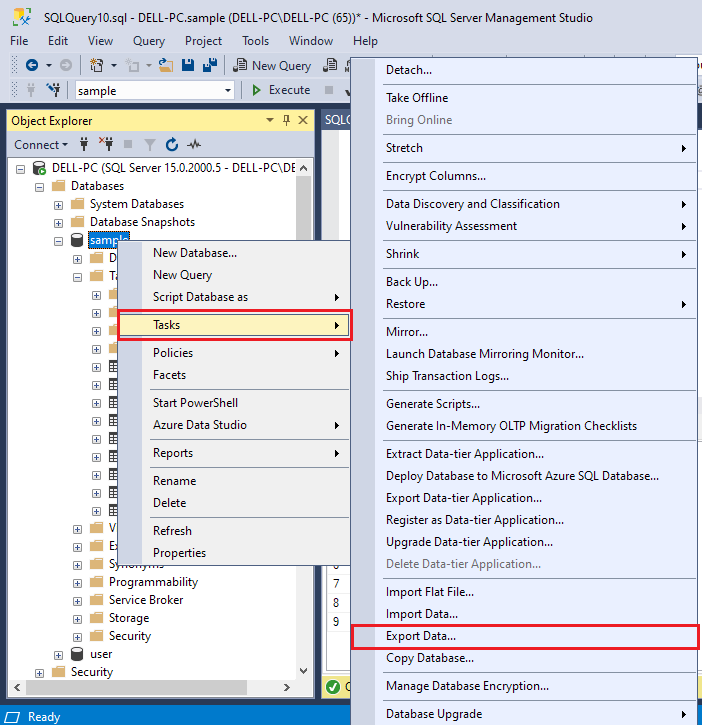
Method 2: Using Import/Export Wizard in SSMSThe SQL Server Import and Export Wizard is a tool in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) that allows users to copy data from one location to another. Using this tool, we can export the data to text file and save it for later use. Let’s look at the steps to perform this method. Step 1: When we right-click a database in SSMS. It is possible to import or export data. Navigate to Tasks>Export Data:
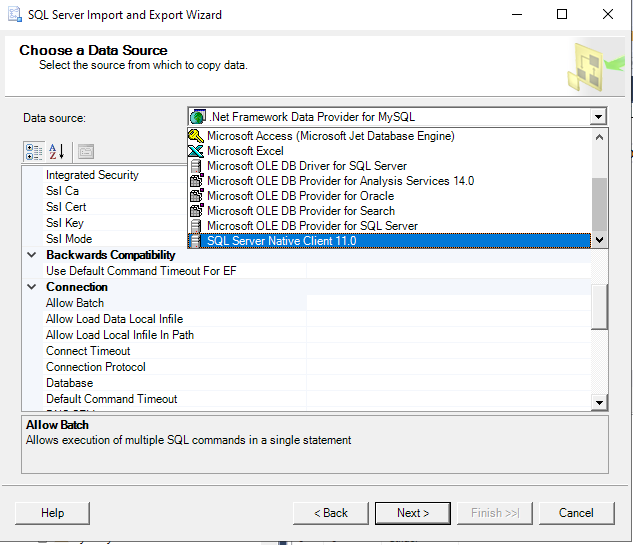
Step 2: The SQL Server Import and Export wizard will be launched. We will export from SQL Server to a Flat file. Select the SQL Server Native Client 11.0 as the Data Source:
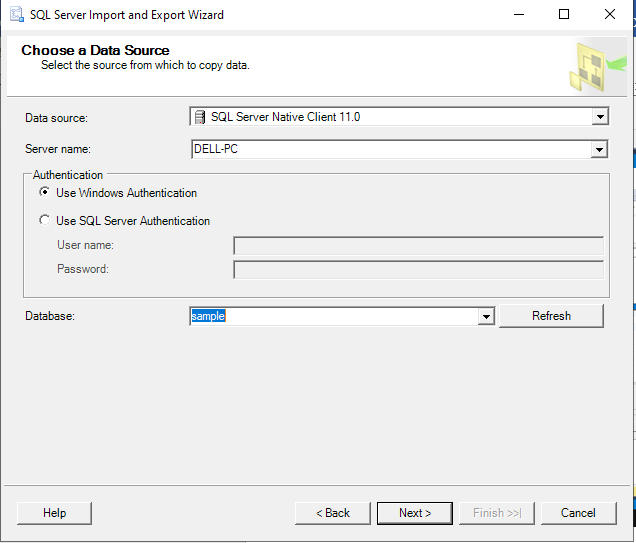
If necessary, specify the Server name and connection information:
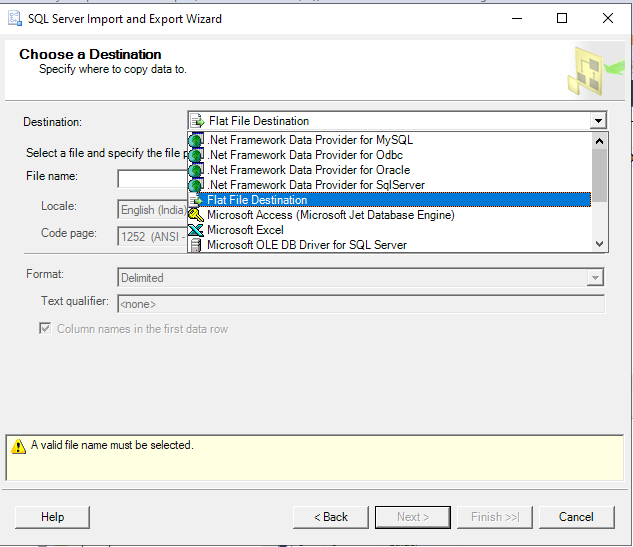
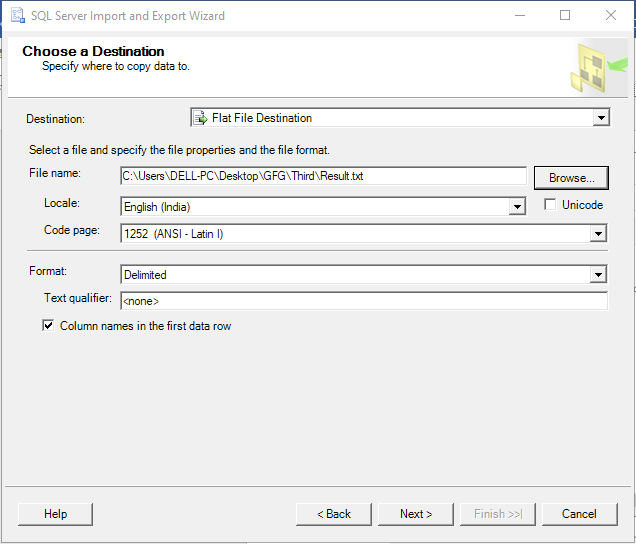
Step 3: Select Flat File Destination from the destination drop-down menu and hit Browse to set the file name and path:
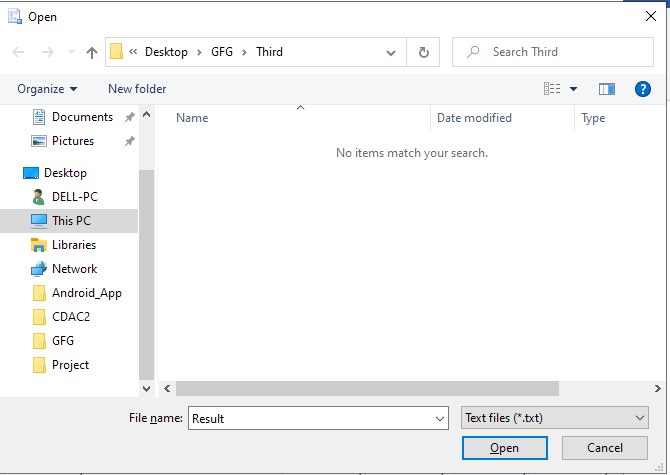
Step 4: The flat file name in our case would be Result.txt:
Step 5: Once we have determined the file name and path, proceed as follows:
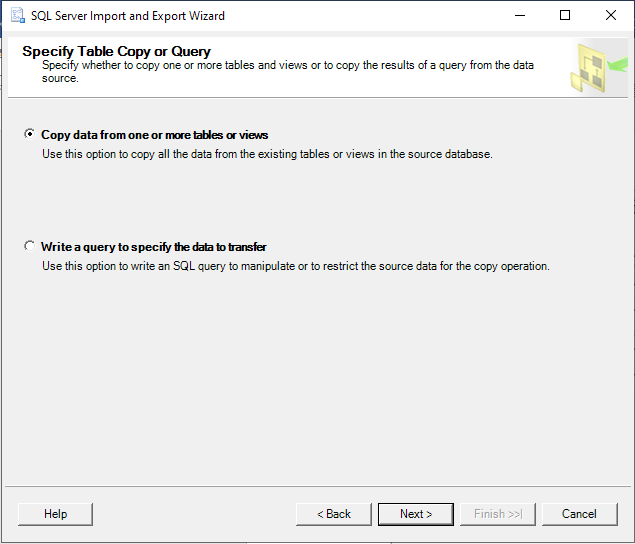
Step 6: Choose “Copy data from one or more table or views” or select second option to specify our own query:
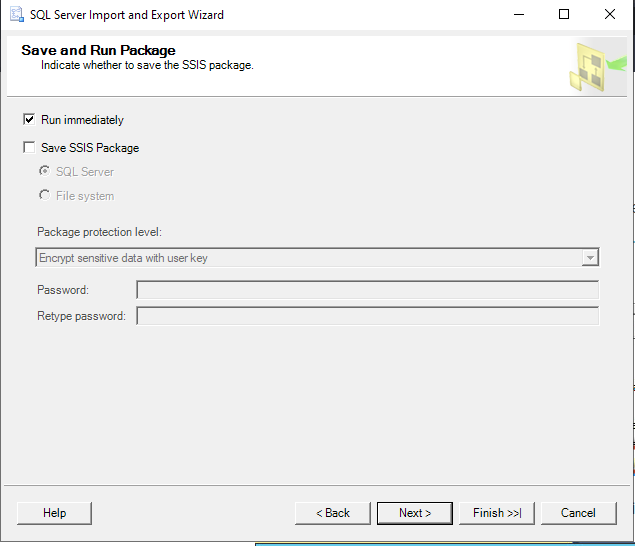
Step 7: To export the data instantly, choose Run immediately:
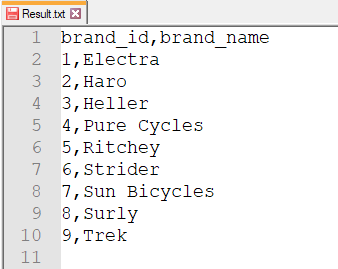
Step 8: The Result.txt file will contain the output:
Method 3: SQLCMD UtilityThe SQL Server Command Line tool is SQLCMD. This tool allows you to store the results in a file. When utilizing batch files to automate processes, this option comes in handy. Let’s check the steps to use this method. Step 1: Here’s how our SaveOutputToText.sql file look’s like: Query: SELECT TOP (1000) Step 2: Use the following command on your terminal to save the results of any query onto file: Query: sqlcmd -i SaveOutputToText.sql -o Result.txt
Step 3: The Result.txt file contains the output:
These were the best three methods to export data to text format in SQL Server. You can use any of the three methods provided as all of them are easy and effective. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |