|
Given an undirected Graph consisting of N nodes in the form of an adjacency matrix graph[][] of size N*N, the task is to print all Hamiltonian cycles possible in the given undirected Graph (taking starting vertex as ‘0’).
A Hamiltonian cycle (or Hamiltonian circuit) is a Hamiltonian Path such that there is an edge (in the graph) from the last vertex to the first vertex of the Hamiltonian Path.
Examples:
Input: graph[][] = {{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}}
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 0
0 1 5 4 3 2 0
0 2 3 4 1 5 0
0 2 3 4 5 1 0
0 5 1 4 3 2 0
0 5 4 3 2 1 0
Explanation:
All Possible Hamiltonian Cycles for the following graph (with the starting vertex as 0) are
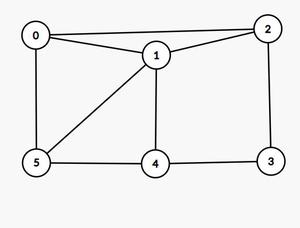
- {0 ? 1 ? 2 ? 3 ? 4 ? 5 ? 0}
- {0 ? 1 ? 5 ? 4 ? 3 ? 2 ? 0}
- {0 ? 2 ? 3 ? 4 ? 1 ? 5 ? 0}
- {0 ? 2 ? 3 ? 4 ? 5 ? 1 ? 0}
- {0 ? 5 ? 1 ? 4 ? 3 ? 2 ? 0}
- {0 ? 5 ? 4 ? 3 ? 2 ? 1 ? 0}
Input: graph[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}}
Output: No Hamiltonian Cycle possible
Explanation:
For the given graph, no Hamiltonian Cycle is possible:
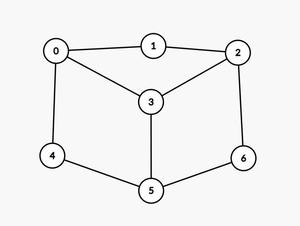
Approach: The given problem can be solved by using Backtracking to generate all possible Hamiltonian Cycles. Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create an auxiliary array, say path[] to store the order of traversal of nodes and a boolean array visited[] to keep track of vertices included in the current path.
- Initially, add the source vertex (in this case ‘0’) to the path.
- Now, recursively add vertices to path one by one to find the cycle.
- Before adding a vertex to path, check whether the vertex being considered is adjacent to the previously added vertex or not and is not already in path. If such a vertex is found, then add it to the path and mark its value as true in the visited[] array.
- If the length of path becomes equal to N, and there is an edge from the last vertex in path to 0, then print the path array.
- After completing the above steps, if there exists no such path, then print No Hamiltonian Cycle possible.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool hasCycle;
bool isSafe(int v, int graph[][6], vector<int> path, int pos)
{
if (graph[path[pos - 1]][v] == 0)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)
if (path[i] == v)
return false;
return true;
}
void FindHamCycle(int graph[][6], int pos, vector<int> path, bool visited[], int N)
{
if (pos == N) {
if (graph[path[path.size() - 1]][path[0]] != 0) {
path.push_back(0);
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
cout << path[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
path.pop_back();
hasCycle = true;
}
return;
}
for (int v = 0; v < N; v++) {
if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos) && !visited[v]) {
path.push_back(v);
visited[v] = true;
FindHamCycle(graph, pos + 1, path, visited, N);
visited[v] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
void hamCycle(int graph[][6], int N)
{
hasCycle = false;
vector<int> path;
path.push_back(0);
bool visited[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
visited[i] = false;
visited[0] = true;
FindHamCycle(graph, 1, path, visited, N);
if (!hasCycle) {
cout << "No Hamiltonian Cycle" << "possible " << endl;
return;
}
}
int main()
{
int graph[][6] = {
{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
};
hamCycle(graph, 6);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
class GFG {
boolean isSafe(int v, int graph[][],
ArrayList<Integer> path,
int pos)
{
if (graph[path.get(pos - 1)][v]
== 0)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)
if (path.get(i) == v)
return false;
return true;
}
boolean hasCycle;
void hamCycle(int graph[][])
{
hasCycle = false;
ArrayList<Integer> path
= new ArrayList<>();
path.add(0);
boolean[] visited
= new boolean[graph.length];
for (int i = 0;
i < visited.length; i++)
visited[i] = false;
visited[0] = true;
FindHamCycle(graph, 1, path,
visited);
if (!hasCycle) {
System.out.println(
"No Hamiltonian Cycle"
+ "possible ");
return;
}
}
void FindHamCycle(int graph[][], int pos,
ArrayList<Integer> path,
boolean[] visited)
{
if (pos == graph.length) {
if (graph[path.get(path.size() - 1)]
[path.get(0)]
!= 0) {
path.add(0);
for (int i = 0;
i < path.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(
path.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
hasCycle = true;
}
return;
}
for (int v = 0;
v < graph.length; v++) {
if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)
&& !visited[v]) {
path.add(v);
visited[v] = true;
FindHamCycle(
graph, pos + 1,
path, visited);
visited[v] = false;
path.remove(
path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
GFG hamiltonian = new GFG();
int[][] graph = {
{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
};
hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph);
}
}
|
Python3
def isSafe(v, graph, path, pos):
if graph[path[pos - 1]][v] == 0:
return False
for i in range(pos):
if path[i] == v:
return False
return True
hasCycle = False
def hamCycle(graph):
global hasCycle
hasCycle = False
path = []
path.append(0)
visited = [False]*(len(graph))
for i in range(len(visited)):
visited[i] = False
visited[0] = True
FindHamCycle(graph, 1, path, visited)
if hasCycle:
print("No Hamiltonian Cycle" + "possible ")
return
def FindHamCycle(graph, pos, path, visited):
if pos == len(graph):
if graph[path[-1]][path[0]] != 0:
path.append(0)
for i in range(len(path)):
print(path[i], end = " ")
print()
path.pop()
hasCycle = True
return
for v in range(len(graph)):
if isSafe(v, graph, path, pos) and not visited[v]:
path.append(v)
visited[v] = True
FindHamCycle(graph, pos + 1, path, visited)
visited[v] = False
path.pop()
graph = [
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 ],
]
hamCycle(graph)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static bool isSafe(int v, int[,] graph, List<int> path, int pos)
{
if (graph[path[pos - 1],v] == 0)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)
if (path[i] == v)
return false;
return true;
}
static bool hasCycle;
static void hamCycle(int[,] graph)
{
hasCycle = false;
List<int> path = new List<int>();
path.Add(0);
bool[] visited = new bool[graph.GetLength(0)];
for (int i = 0; i < visited.Length; i++)
visited[i] = false;
visited[0] = true;
FindHamCycle(graph, 1, path, visited);
if (!hasCycle) {
Console.WriteLine("No Hamiltonian Cycle" + "possible ");
return;
}
}
static void FindHamCycle(int[,] graph, int pos, List<int> path, bool[] visited)
{
if (pos == graph.GetLength(0)) {
if (graph[path[path.Count - 1], path[0]] != 0) {
path.Add(0);
for (int i = 0; i < path.Count; i++) {
Console.Write(path[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
hasCycle = true;
}
return;
}
for (int v = 0; v < graph.GetLength(0); v++) {
if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos) && !visited[v]) {
path.Add(v);
visited[v] = true;
FindHamCycle(graph, pos + 1, path, visited);
visited[v] = false;
path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
}
}
}
static void Main() {
int[,] graph = {
{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
};
hamCycle(graph);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)
{
if (graph[path[pos - 1]][v] == 0)
return false;
for (let i = 0; i < pos; i++)
if (path[i] == v)
return false;
return true;
}
let hasCycle;
function hamCycle(graph)
{
hasCycle = false;
let path = [];
path.push(0);
let visited = new Array(graph.length);
for (let i = 0; i < visited.length; i++)
visited[i] = false;
visited[0] = true;
FindHamCycle(graph, 1, path, visited);
if (!hasCycle) {
document.write("No Hamiltonian Cycle" + "possible ");
return;
}
}
function FindHamCycle(graph, pos, path, visited)
{
if (pos == graph.length) {
if (graph[path[path.length - 1]][path[0]] != 0) {
path.push(0);
for (let i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
document.write(path[i] + " ");
}
document.write("</br>");
path.pop();
hasCycle = true;
}
return;
}
for (let v = 0; v < graph.length; v++) {
if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos) && !visited[v]) {
path.push(v);
visited[v] = true;
FindHamCycle(graph, pos + 1, path, visited);
visited[v] = false;
path.pop();
}
}
}
let graph = [
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 ],
];
hamCycle(graph);
</script>
|
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 0
0 1 5 4 3 2 0
0 2 3 4 1 5 0
0 2 3 4 5 1 0
0 5 1 4 3 2 0
0 5 4 3 2 1 0
Time Complexity: O(N!)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
|

