|
|
In this article, we will write data to a table in DynamoDB. DynamoDB is a NoSQL database that supports semi-structured data i.e. key-value and document data structures. A DynamoDB table contains items. An item is a collection of attributes and each item has a primary key that should be not null. Also, each item can have a different number of attributes. See the below examples. Example 1:
{
"ArticleID": 1,
"NameofArticle": "DynamoDb"
}
Example 2:
{
"ArticleID": 1,
"NameofArticle": "DynamoDb"
}
{
"ArticleID": 2,
"NameofArticle": "S3 Bucket",
"WrittenBy": "Rohan Chopra"
}
Approach:
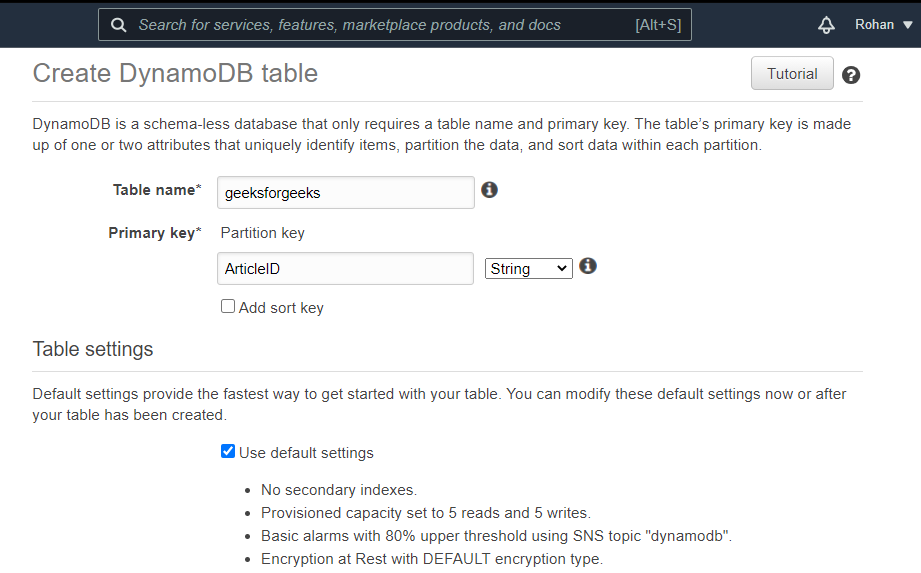
The above approach has been illustrated below with images. Create a table:Navigate to the DynamoDB on AWS Console and click on create a table. There provide the name of the table and specify a primary key that will differentiate one item from another. In our case, the primary key is ArticleID and it is of type Number. Keep the table settings as default and click Create.  Create Table Add items to the table:Once the table is created, we need to add items to write data to a table. Navigate to the Items tab of the table and click, Create item. An article will by default have ArticleID as one attribute because it is the primary key. Click on append to add more attributes. Different items can have different numbers of attributes. See the below images. 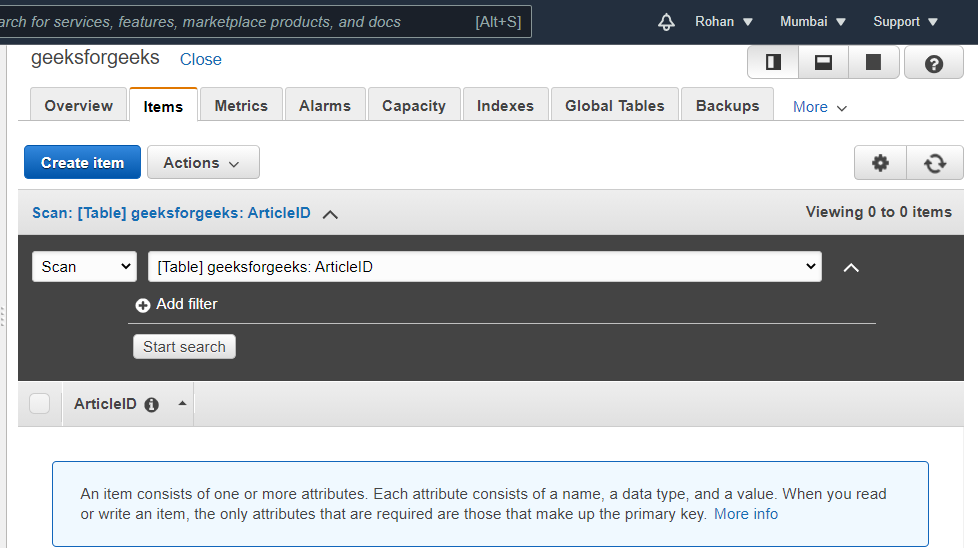 Add items to table 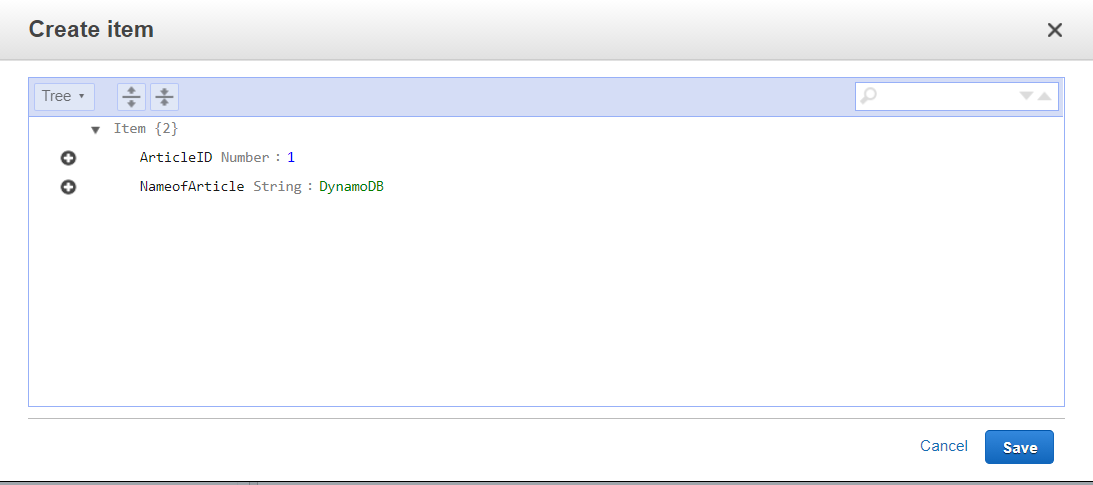 Item 1 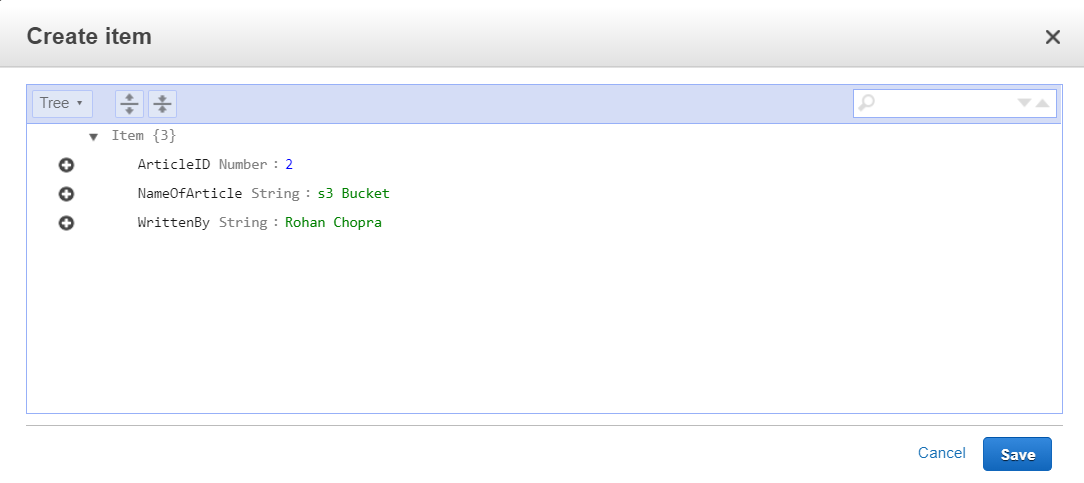 Item 2 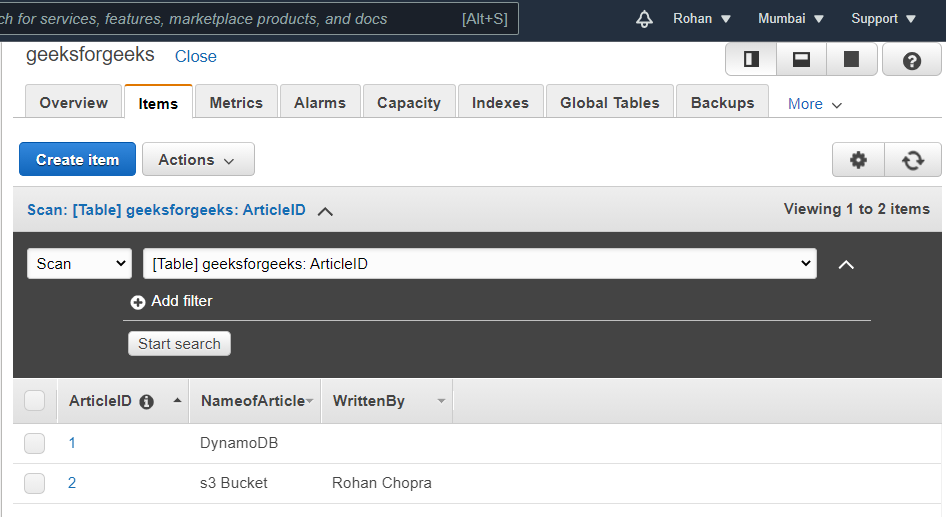 Table with data From the above images, we see that data has been successfully written to the DynamoDB table. We can add as many items as we want to a table. Thus, by adding items, we are writing data to the table. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| DevOps |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |