|
WebSockets provide a full-duplex communication channel over a single TCP connection, allowing for real-time, bidirectional communication between the client and server. When integrated with a Redux application, WebSockets can enable continuous data updates and improve user experience by providing real-time functionalities.
Prerequisites Benefits of Using WebSocket in a Redux Application - Real-Time Data Updates: WebSockets allow for real-time data transfer, ensuring that the application state is always up-to-date. This is particularly beneficial for applications requiring live data, such as chat apps, stock tickers, or online gaming.
- Reduced Latency: With WebSockets, data can be sent and received instantly, without the need for repeated HTTP requests. This reduces latency and improves the responsiveness of the application.
- Efficient Resource Usage: WebSockets maintain a single connection open for the duration of the session, reducing the overhead associated with opening and closing multiple connections.
- Bidirectional Communication: Both the client and server can send messages independently, enabling more interactive and dynamic applications.
Challenges of Using WebSockets in a Redux Application - Complexity in State Management: Managing real-time data updates and ensuring that the Redux state remains consistent can be challenging, particularly in larger applications.
- Error Handling: Handling errors and connection issues gracefully requires additional effort and can complicate the application logic.
- Scalability: While WebSockets are efficient, managing a large number of concurrent WebSocket connections can be challenging and may require additional infrastructure or optimizations.
- Security Considerations: WebSockets are susceptible to certain security issues, such as man-in-the-middle attacks. Ensuring secure connections (using wss://) and implementing proper authentication and authorization mechanisms are crucial.
Features - Real-Time Communication: WebSockets enable instant data transmission between the server and client, providing real-time updates.
- Full-Duplex Communication: Both client and server can send and receive messages simultaneously.
- Efficient Resource Usage: WebSockets use a single connection, reducing the overhead associated with establishing multiple connections.
- Scalability: Suitable for applications requiring frequent updates, such as chat applications, live sports scores, or financial tickers.
Steps to Create a Redux Application with WebSockets Step 1: Create a new React project
npx create-react-app websocket-redux-app
cd websocket-redux-app Step 2: Install Redux and related dependencies:
npm install redux
npm install react-redux
npm install redux-thunk Step 3: Install a WebSocket library:
npm install ws socket.io-client Step 4: Create reducers:
mkdir src/reducers - Create a file websocketReducer.js inside src/reducers
Step 5: Create actions:
- Create a folder actions inside src:
mkdir src/actions - Create a file websocketActions.js inside src/actions
Updated Dependencies dependencies: {
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.17.0",
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
"react": "^18.3.1",
"react-dom": "^18.3.1",
"react-redux": "^9.1.2",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
"redux": "^5.0.1",
"redux-thunk": "^3.1.0",
"socket.io-client": "^4.7.5",
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4",
"ws": "^8.18.0"
}Creating the WebSocket ServerStep 1: Create a WebSocket server:
- Create a new folder websocket inside your project root
mkdir websocket
cd websocket Step 2: Initialize a new Node.js project inside the websocket folder
npm init -y Step 3: Install the ws library
npm install ws Install express and socket.io:
npm install express
npm install socket.io Step 4: Updated dependencies (in websocket folder) :
dependencies: {
"express": "^4.19.2",
"socket.io": "^4.7.5",
"ws": "^8.18.0"
}Project structure: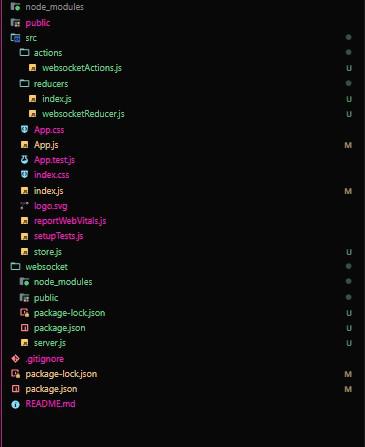 Follow this project structure Step 5: Setting Up Redux and Connecting to WebSocket in a Component.
Example: This Illustrates creation of redux, reducers, actions, websocket reducers, connecting websockets in a component.
JavaScript
// src/index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import store from './store';
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
// src/store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import { thunk } from 'redux-thunk';
import rootReducer from './reducers';
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
export default store;
// src/reducers/index.js
import { combineReducers } from 'redux';
import websocketReducer from './websocketReducer';
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
websocket: websocketReducer,
});
export default rootReducer;
// src/actions/websocketActions.js
export const connectWebSocket = (url) => (dispatch) => {
const socket = new WebSocket(url);
socket.onopen = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'WEBSOCKET_CONNECTED' });
};
socket.onmessage = (message) => {
dispatch({ type: 'WEBSOCKET_MESSAGE', payload: message.data });
};
socket.onclose = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'WEBSOCKET_DISCONNECTED' });
};
};
// src/reducers/websocketReducer.js
const initialState = {
connected: false,
messages: [],
};
const websocketReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'WEBSOCKET_CONNECTED':
return { ...state, connected: true };
case 'WEBSOCKET_MESSAGE':
return { ...state, messages: [...state.messages, action.payload] };
case 'WEBSOCKET_DISCONNECTED':
return { ...state, connected: false };
default:
return state;
}
};
export default websocketReducer;
// src/App.js
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';
import { connectWebSocket } from './actions/websocketActions';
const App = () => {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const messages = useSelector((state) => state.websocket.messages);
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(connectWebSocket('ws://localhost:5000'));
}, [dispatch]);
return (
<div>
<h1>WebSocket Messages</h1>
<ul>
{messages.map((message, index) => (
<li key={index}>{message}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
// websocket/server.js
const WebSocket = require("ws");
const server = new WebSocket.Server({port : 5000});
server.on("connection", (ws) => {
console.log("Client connected");
ws.send("Welcome to the WebSocket server!");
// Send messages periodically
setInterval(() => {
ws.send(`Server message
at ${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}`);
}, 5000);
ws.on("message", (message) => {
console.log(`Received message: ${message}`);
ws.send(`Echo: ${message}`);
});
ws.on("close",
() => { console.log("Client disconnected"); });
});
console.log('WebSocket server
is running on ws://localhost:5000');
Running the ProjectStep 1: Start the WebSocket server
cd websocket
node server.js Step 2: Start the React application
cd websocket-redux-app
npm start Output: After setting up the application, running the React app should display incoming WebSocket messages in real-time. Each message from the server will be appended to the list in the component.
-(1).gif) Output
|


-(1).gif)