
|
|
In this article we will learn about test suites and how can we build them using Java and TestNG. TestNG is a modern testing framework that is used very widely used today. It has a broad base of features that allow us to write unit tests and club them together in groups. Table of Content TestNG is used in combination with Selenium to implement browser automation and therefore used for regression testing. By the end of this article, you will be successfully creating and running your own test suites. What is a Test Suite?A test suite is a collection of test cases. There are various ways to create test these. You could either choose to group these tests by functionality or you could simply club your test classes together to form a test suite. In TestNG, the test suite is written in the form of a xml document. This allows you as a tester to have a fine grained control over what tests you want to run and create groups or suites according to the very specific requirements of your project. Steps to Create Test Suite in TestNGStep 1. Setting Up TestNG Environment TestNG does not require any special kind of setup incase of IntelliJ Idea, both enterprise and community edition. Incase you choose to follow this tutorial on eclipse IDE, then you need to setup the TestNG environment before you can start using it in your application. To learn how to install and configure the plugin in the Eclipse IDE, please visit this page. To Create a new TestNG project regardless of the IDE you choose to use, simply – Create a new Maven project and add the TestNG dependencies to it. Maven automatically provides us with a default project structure with a separate place to our unit tests in. Step 2. Create a new Maven Project To learn how to create a new maven project, visit this page. Step 3. Add The following Dependencies to Your pom.xml file Step 4. Creating Test Classes Explanation of test classes in TestNG:
Step 5. For this tutorial, we will create two test classes called TestClassA and TestClassB inside the java folder in the test directory. TestClassA TestClassB Leave these classes as they are for now, we will right tests in them in the next section. Step 6. Writing simple test methods with @Test annotation
Step 7. Open the test classes you created earlier and add the unit tests to it. TestClassA TestClassB Our Test Classes and unit tests are complete as of now. We will now proceed to organizing packages. Step 8. Organizing test classes into packages Create a folder with the inverse domain as com.horje.browsertests. Move the test classes you created earlier inside this folder. This allows the test classes to be detected automatically by the testng environment. The final organization of files should match the following:
This completes the part concerning the test classes and unit tests for this tutorial. Now, we see how we can create test suites. Understanding TestNG XML ConfigurationIntroduction to TestNG XML configuration fileThe testNG XML configuration is defined in the file called as testng.xml in the root directory of your project. It defines how your tests should be run and allows you to have fine-grained control of the unit testing processes. The name should not be modified otherwise you will not be able to run your tests. Instead of running your tests one class at a time, this file allows you to run all your tests inside all your test classes at once. Structure of TestNG XML file (test suite, test, classes, methods)The elements that are added to the file in the form of xml tags have a pre-defined hierarchy that should not be altered. The main elements we use in this file are: suite, test, classes, include and exclude tags. A typical structure of testng.xml file is as follows: Defining test suite, test, and test classes in XML file
We will understand these concepts in more detail in the next section. Creating Test Suites Using TestNG XMLGuide to creating a basic test suite in TestNG XMLTo create a test suite using testng.xml file, we first write the <suite></suite> tag. This is the root element of the test suite document and consists of all the tests that we want to run. The ‘suite’ element contains a name parameter that tells what the name of the test suite is. In the example above, this feature is implemented as:
Inside the suite tag, we can have more than one test tags, each for a set of test cases to be executed. Building up from the previous example as:
Please use readable and appropriate names for the suite tag and the test tags to improve code readability. Including and excluding test classes and methods in the suiteIn the example testng.xml we have taken above, the test tag named functionality test we have the classes tag. Each test tag can have only one classes tag. The classes we have included in this test are LoginTest and SearchTest in the Regression Test and ScrollTest and NightModeTest for the UI Testing. This is the following part in the code above:
Within the class tag, we have an optional methods tag. If we choose to omit it, then by default all the tests in class are run. Otherwise, we can choose to include or exclude the methods as we want. This can be seen from the following example:
We have a class called Search Test and inside that class, we choose to include the method searchByProduct in execution and exclude the method searchByCategory from execution. Parameterizing test suite configurationTest parameterization in test suite is the key to test methods with different datasets. To learn deeply about parameterizing test suite configuration, please visit this page. So, now let us define the contents of our testng.xml file: Our project is complete. We will now look at ways to run it. Running Test SuitesRunning Test Suites From IDETo run the test suite from your IDE, right click on the testng.xml file in the side navigation bar. Then click on the option ‘Run testng.xml’ to run your suite:
Running test suites from command lineTo run test suites from command line, navigate to the root directory of your project in the terminal and type:
This will automatically compile tests as: 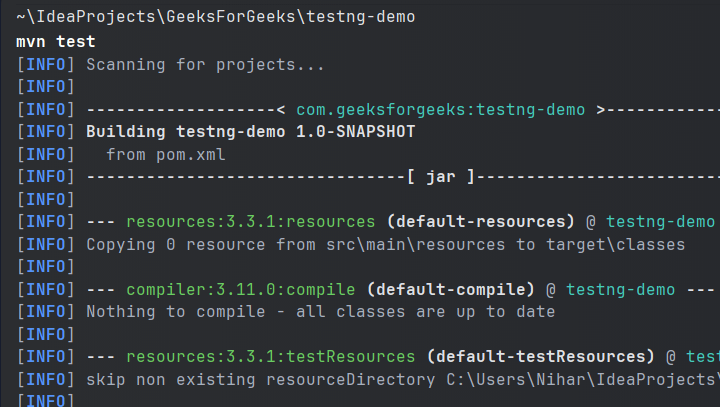 Test Compilation Then the testng.xml file will be automatically run as: 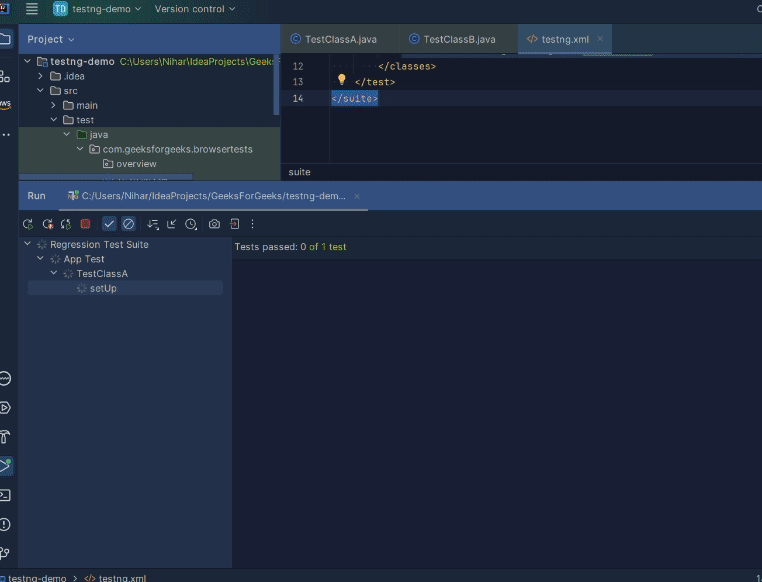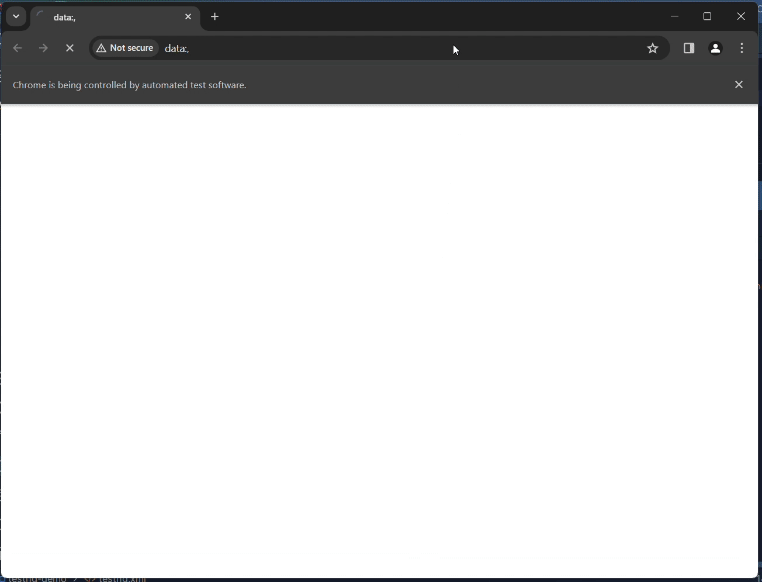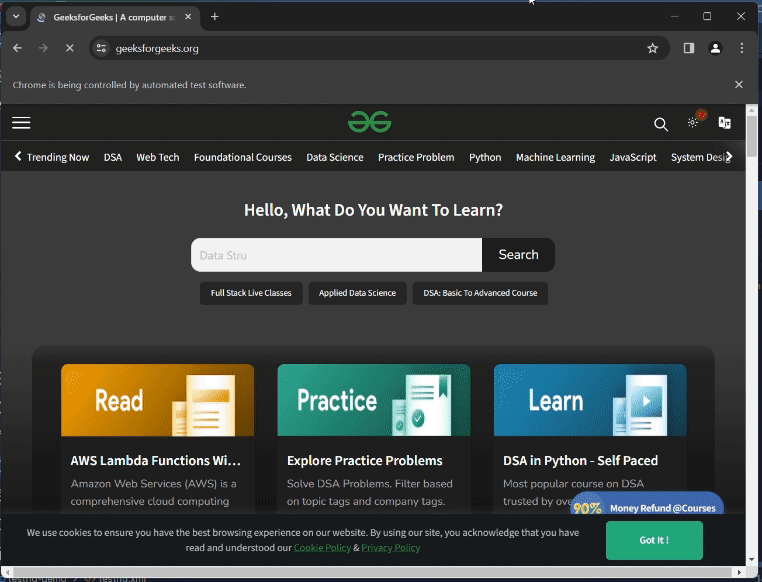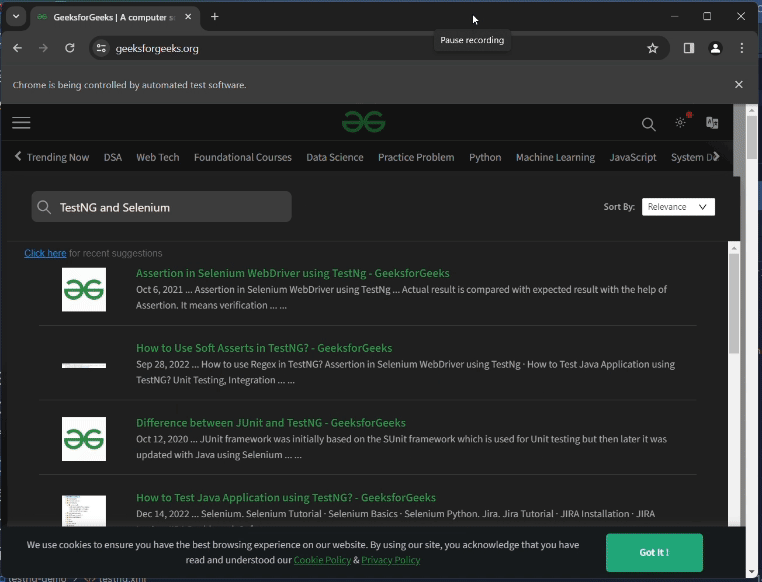 Automation by Test Class A 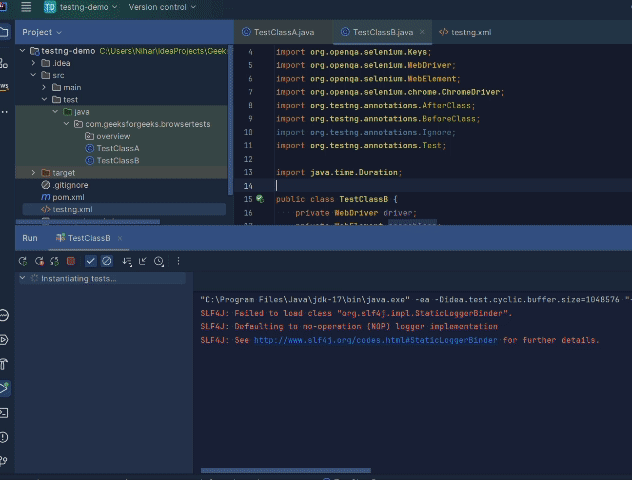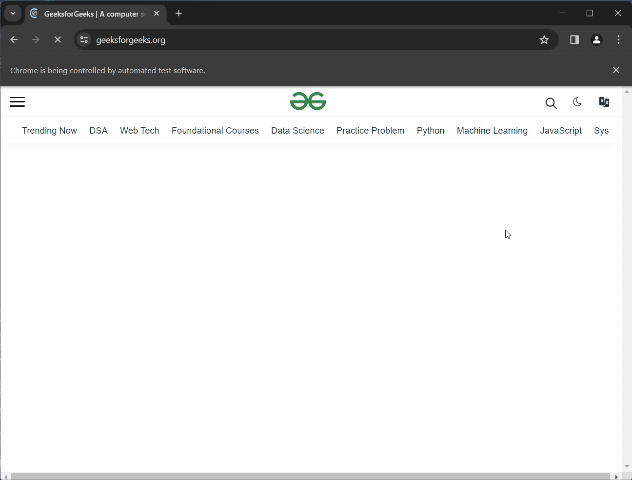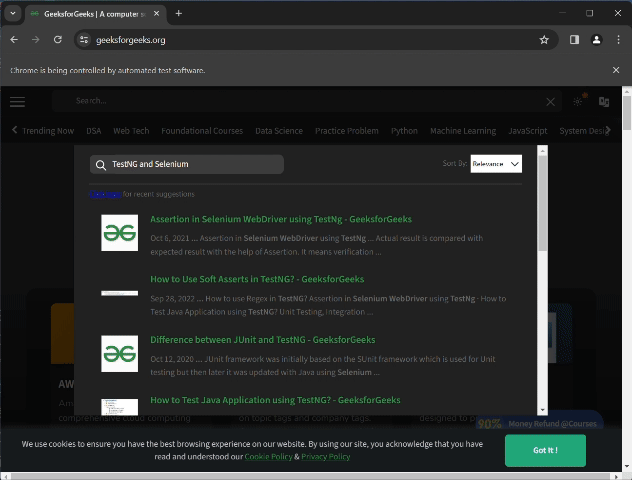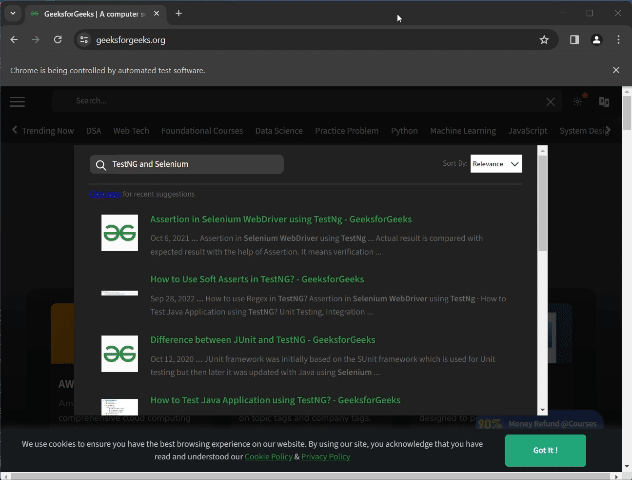 Automation by Test class B Finally you will see the following result logged on the console as: 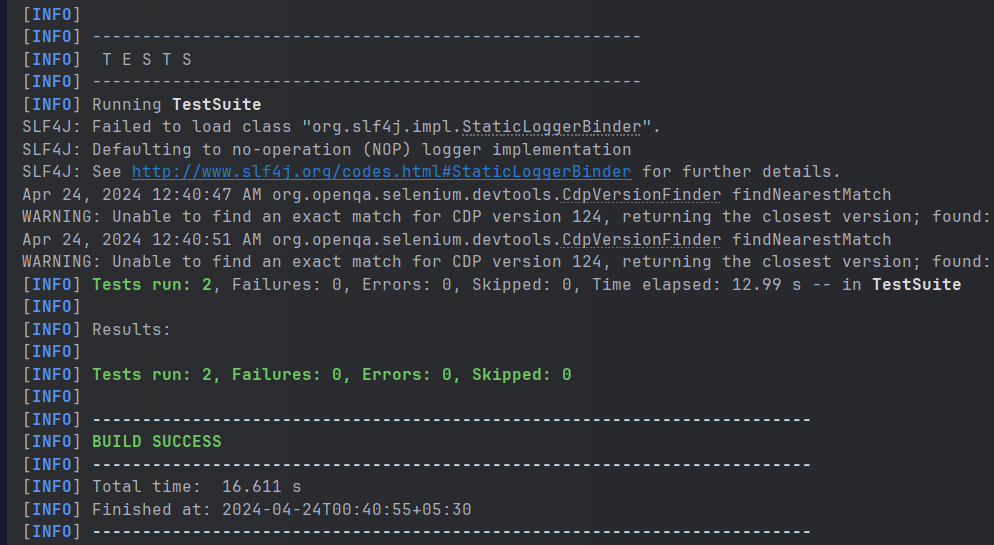 Running testng.xml through command line Configuring test suite execution options1. Thread Count TestNG provides you with the option to define the number of threads you want to use to run your test suite. This can be simply achieved as: You have to assign an integer value to the attribute ‘thread-count’ and you are done. 2. Parallel Execution You can also configure your test suite to allow your tests to run in parallel. To know more on how to parallelize your tests, click here. ConclusionIn this article we looked at what test suites are and how we can create them using TestNG in java. We looked at two approaches to clubbing tests, through groups and through classes. Hope you learnt something useful. If you want to discuss something, please feel free to leave comments below. FAQ’s on How to Create Test Suite in TestNGWhere can I use the <groups>…</groups> tag inside testng.xml?
Can I rename the testng.xml file to anything else?
Can I place the testng.xml file anywhere I want?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Software Testing |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |
