|
|
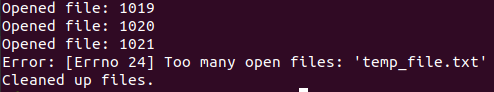
Encountering the “Too Many Open Files” error in Linux can be frustrating, especially when it disrupts your workflow or server operations. This error typically occurs when a process or system reaches its limit for open file descriptors, which are references to open files or resources such as sockets, pipes, or device files. Fortunately, resolving this issue involves understanding the underlying causes and applying appropriate solutions. In this article, we will explore the common causes of this error and provide practical solutions with examples and code executions.  too many opne file error in Linux Understanding the ErrorBefore delving into solutions, it’s essential to understand why this error occurs. Linux systems impose limits on the number of file descriptors that a process can open simultaneously. When a process exceeds this limit, the system throws the “Too Many Open Files” error. This limit is controlled by the ulimit command and can be adjusted both globally and per user. Identifying the CauseSeveral factors can contribute to the “Too Many Open Files” error:
Solutions1. Adjusting System LimitsTo address the issue of system limits, you can increase the maximum number of file descriptors allowed per process. Follow these steps: Step 1: Check the current limits using the ulimit command: ulimit -n current limit to open files Step 2: To temporarily increase the limit, use the ulimit command with the -n flag followed by the desired value: ulimit -n 2000
changing limit temporarily Step 3: To make the change permanent, edit the limits.conf file located in the /etc/security/ directory. Add or modify the following lines: * soft nofile 65536 Replace 65536 with the desired maximum number of file descriptors. 2. Closing Unused File DescriptorsEnsure that your application or script properly closes file descriptors after use. Failure to do so can result in resource leakage. Here’s a Python example demonstrating proper file descriptor management: file = open('example.txt', 'r') 3. Debugging and MonitoringUse tools like lsof (list open files) and strace (trace system calls) to identify processes with a high number of open file descriptors and trace their behavior. For example: lsof -u <username>
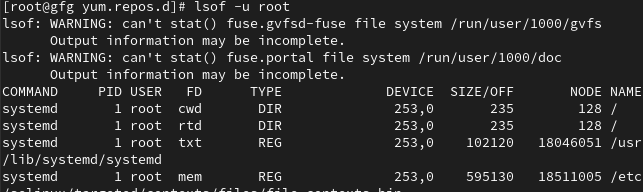 To view list of open files in particular user Replace <username> with the username of the affected user. How to Fix the “Too Many Open Files” Error in Linux – FAQsWhat does the “Too Many Open Files” error mean in Linux?
What causes the “Too Many Open Files” error?
How can I check the current limit for open files in my Linux system?
How do I fix the “Too Many Open Files” error in Linux?
Are there any tools or commands to help diagnose and troubleshoot the “Too Many Open Files” error?
ConclusionThe “Too Many Open Files” error in Linux can be mitigated by adjusting system limits, closing unused file descriptors, and debugging resource-intensive processes. By understanding the causes and applying appropriate solutions, you can ensure smoother operation of your Linux system and applications. Remember to monitor system resources regularly to detect and address potential issues proactively. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Linux Unix |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |