|
|
The at command in Linux is used to schedule one-time tasks to be executed at a specified time in the future. It allows users to submit a command or script for execution at a later time, offering a convenient way to automate tasks without the need for complex cron jobs. The scheduled jobs are managed by the atd (at daemon) service, which runs in the background and executes the queued tasks at the specified times. In this article, we will explore the at command and the atd service used by the at command in Linux. at command in LinuxThe at command in Linux is used for scheduling one-time tasks to be executed at a specified time. Users can submit commands or scripts, and the atd daemon manages the execution of these scheduled jobs. It provides a simple way to automate future tasks without the need for complex cron expressions. Syntax:The basic syntax of the at command is as follows: at [-q queue] [-f file] [-mldv] TIME
How to Schedule Tasks Using at Command in LinuxExample 1: Scheduling a command to run at a specific time:at 2:30 PM This example schedules the echo command to write “Hello, World!” to a file at 2:30 PM.
Example 2: Using a file to specify commands:$ echo "ls -l" > myscript In this example, a script file (myscript) containing the ls -l command is scheduled to run at 10:00 PM.
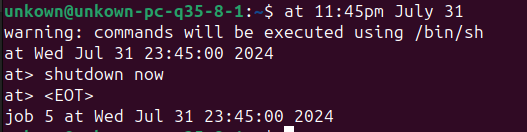
Example 3:System Shutdown at Specific Date:at 11:45pm July 31 In this example , the computer will shutdown on a specific date
Example 4 : Delete a file on a specific Time:at 11:45pm In this example the hello.txt file will be removed at 11:45PM today
Which service is used by at command in Linux?The at command in Linux is used to schedule one-time tasks to be executed at a specified time in the future. It utilizes the atd (at daemon) service, which runs in the background and manages the execution of these scheduled jobs. Users can use the at command to submit commands or scripts along with the desired execution time, and atd ensures their execution at the specified time. How atd service manages at command in Linux?The atd (at daemon) in Linux manages the execution of commands scheduled using the at command. When a user submits a job using the at command, the job details are stored in the /var/spool/at directory. atd periodically checks this directory for pending jobs and, when the scheduled time arrives, it executes the jobs on behalf of the user. atd ensures the proper handling of scheduled tasks, managing their execution without requiring continuous user involvement, making it an efficient solution for one-time job scheduling in Linux systems. Components of atd service:
Frequently Asked Questions on Service Used by at command in Linux -FAQsHow does the
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Linux Unix |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 15 |