|
|
M (MongoDB) E (Express.js) R (React.js) N (Node.js) stack is a popular JavaScript language-based stack for building full-stack applications, MongoDB, ExpressJs, and NodeJs being responsible for server building and React for client-side development. This article is going to be your guide if you want to get started with the MERN stack development. Table of Content
1. Setting Up Node.Js EnvironmentNode.Js is a Javascript runtime environment that allows you to run javascript code outside the browser console. To install Node.Js, you need to visit the Node.Js website and download the installer. In this article, we are going with the Windows Installer package.  node.js installer Proceed with the default installation. Once the installation is complete, close the installer and verify the node.js installation by writing the following command in the terminal. node --version  node –version 2. Starting a Node.Js Project and Installing DependenciesCreate a directory and enter into it to initialize a new Node.js Project. Further install the necessary dependecies for the MERN app (mongoose, express, cors, nodemon) using `npm` (node package manager). Here are the step by step explanation of how to do that. Step 1: Create a new directory and enter into it by running the following commands. mkdir mern-app-backend Step 2: Intialize a new node.js project by running the following command. npm init -y
Note: The above command will ask you for some basic details about the project. Fill them accordingly. It will also highlight the starting point of the project. You can give it any name. Here will will name it as `index.js` Step 3: Install the required dependencies by running the following command. npm install express mongoose cors
3. Create a basic server with Express.JsExpress.js is an application framework that simplies the creation of web servers and handling HTTP requests. We can create a we server by importing express, creating an app out of it, defining a port where the server will hold, and writing the basic `app.listen()` function. Node
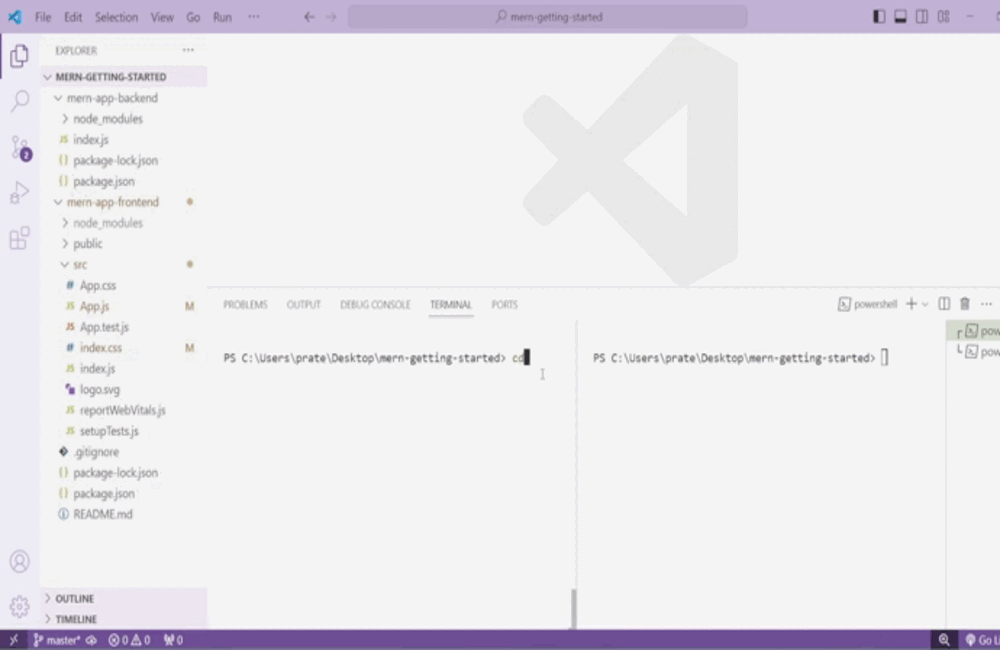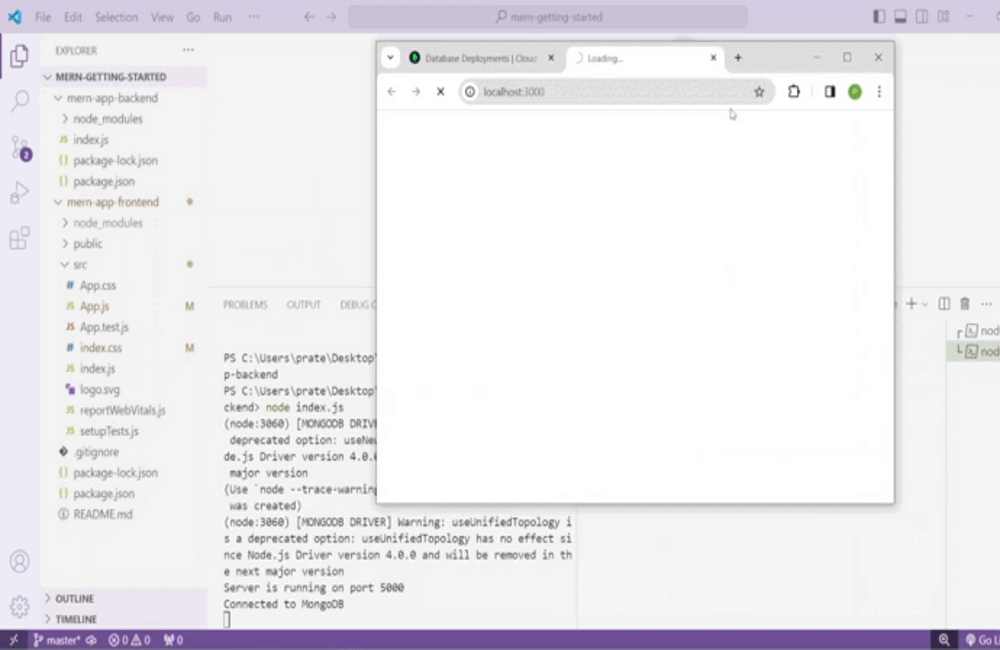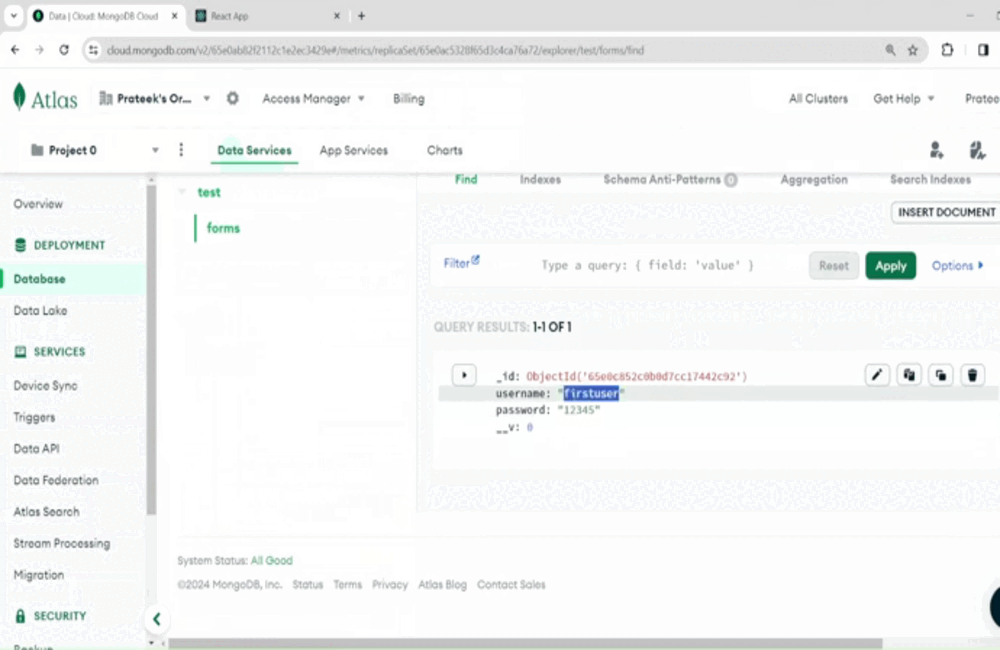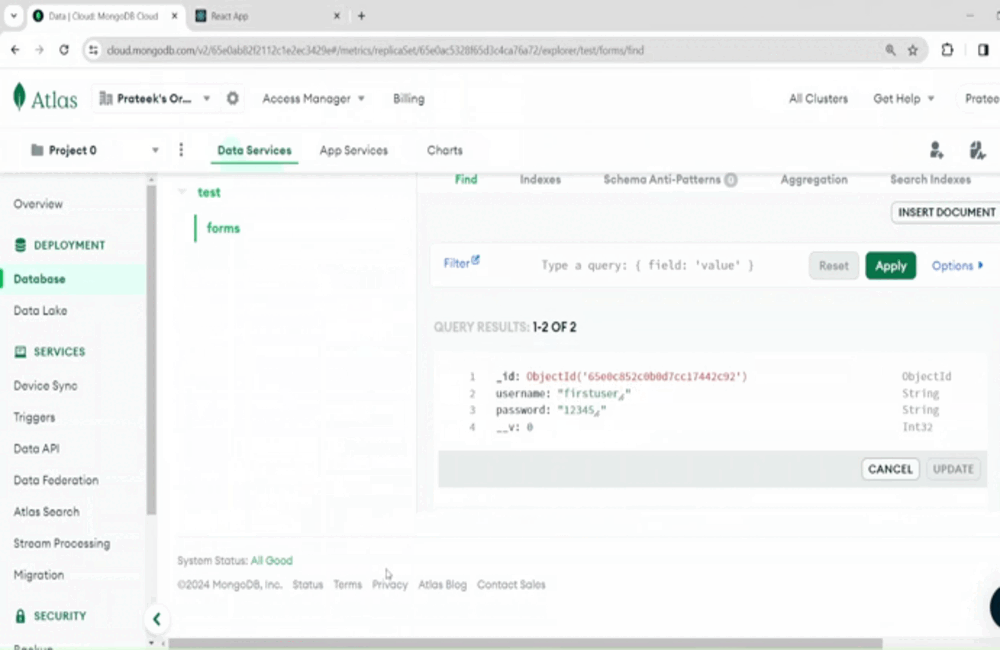
6. Defining a Route and Query in a DatabaseThe route functions (get, post, put, delete) receives a callback function. That callback function receives two parameters (request and response) when someone access the route parameter. Request holds the information about incoming request while response is used to send a response back to the client. Each route combined with the port addess serves as an endpoint through which, the frontend can communicate to the backend server, send request and receive response. Provided below is the syntax through which we can create a route to submit the form data received from the frontend. Node
9. Combining Everything to Make a MERN ApplicationTo summarize, we successfully installed Node.js, Express.js, created a database in mongoDB, and also create a react app to submit the data into the database. Provide below are the project structure and the code structures. Backend (mern-app-backend)Project Structure: 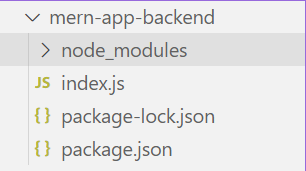 backend-project-structure Dependencies List: "dependencies": { Code Example: Node
Javascript
To start the frontend run the following command on frontend path npm start
To start the backend run the following command on backend path node index.js
Output:
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| MERN Stack |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 15 |