|
|
Spring Boot Data provides support to transparently keep track of who created an entity or changed an entity and when these things happened. All records are maintained clearly. For example, if one user comes into the site and logs in to the site. Then those times are maintained in the database and also when another time the user logs in to the site, those records are also maintained in the database that’s things, we can say auditing. In this article, we will be implementing the configuration of the AuditListener in the Spring Boot Application. Step-By-Step Implementation to Configure AuditListener in Spring Boot ApplicationBelow are the steps to Configure AuditListener in a simple Spring Boot application. Step 1: First, we will create a User Class. User.java Java
This class is user class to maintain the user details and save these data into the database. Step 2: Now Implement service class. Java
The above code is for the service layer, where we write all the business logic to save user data into database. Step 3: Now we will create the Endpiont UserController.java Java
This code is the Endpoint and RestController class to call API and our user save into database. Now we need to save our user with auditing means we are tracking information when our user has saved when they update, so automatically they update time and data of the system. Step 4: Now, create the Auditable class, that continuously monitor the application. Java
This Entitylistner continuously monitor our user when they come into the system. Step 5: Now, implement the AuditAware Interface (in-built interface). Java
The AuditorAware interface is in-built interface they monitor whom want to modify the system data and save whatever name your provided. Step 6: Now, set the Spring Boot Main Application. Java
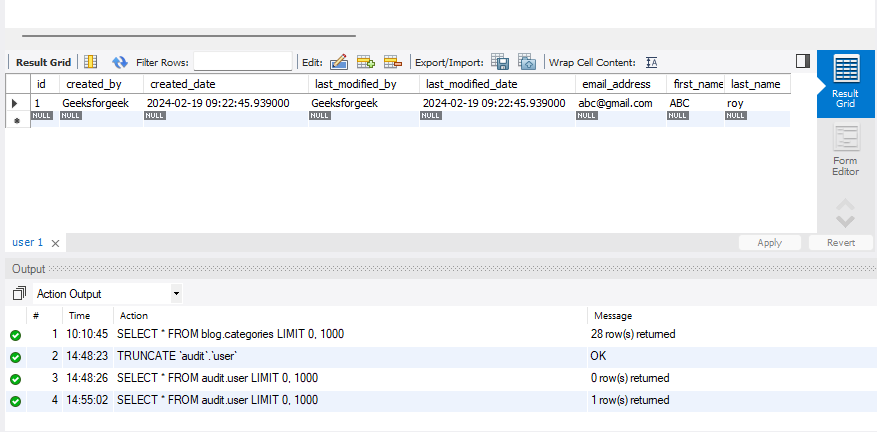
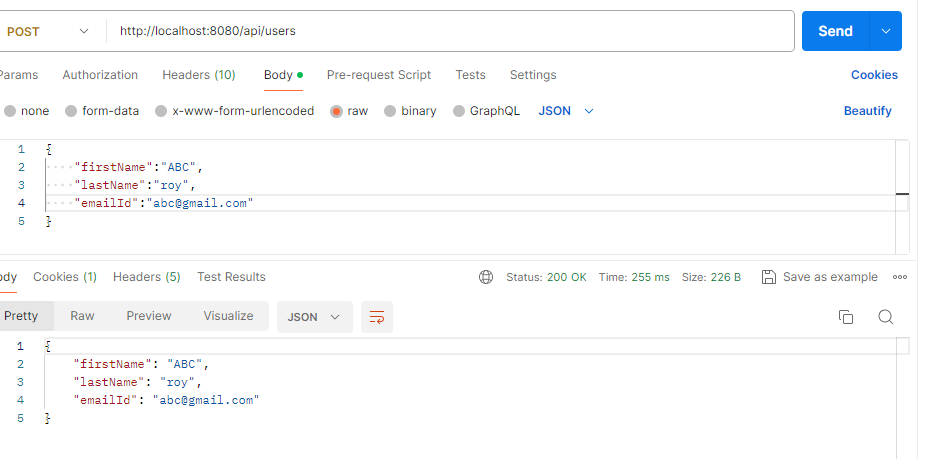
In the main application, we need to make a bean like the above. Through this thing, all application in auditing will be saved and also the updates will be saved. Now, if we run this application, automatically createdBy, createdOn, updatedBy, updatedOn this field fill according to our System Time. Call the Rest API
Now, in MySQL Database we can see createdBy, createdOn, updatedBy and updatedOn included.
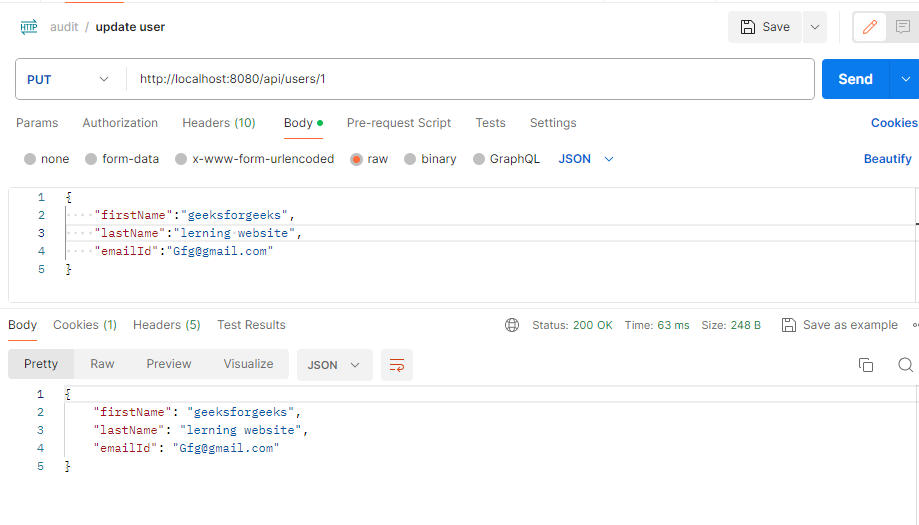
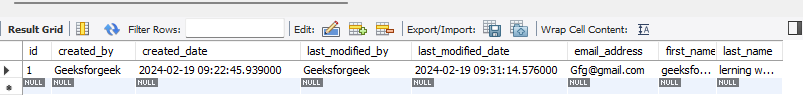
If any user tries to update their data, the lastUpdatedTime will get change. This way we can Audit anything here.
Now, we are updating the user, so automatically lastModified time also updated.
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Advance Java |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |