|
|
In database management selecting random records from a table can be a useful operation for various applications such as sampling data, generating random samples for testing or selecting winners in a lottery. In this article, we will explore different methods to select random records from a table in PL/SQL, Oracle’s procedural language extension for SQL. By the end of this article, you will understand how to use different approaches to achieve this task effectively. How to Select Random Record from Table?When working with large datasets, selecting random records can be challenging due to the need for efficient and reliable methods. We will select random records from the table in PL/SQL using the below method are as follow:
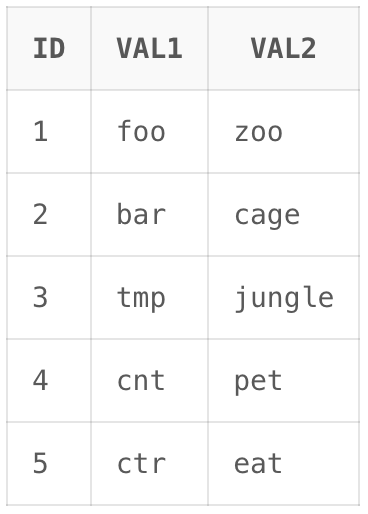
Let’s set an environment for Select Random Record To understand How to select random records from a table in PL/SQL we need a table on which we will perform various operations and queries. Here we will consider a table called test which contains id, val1 and val2 as Columns. Query: CREATE TABLE test Output:  test table Explanation: Our table has been created. 1. Using DBMS_RANDOM PackageThe DBMS_RANDOM package provides random generation capabilities. It has several functions but we are going to make use of the RANDOM function from the package. The RANDOM function generates integers in the range [-2^31, 2^^31). Syntax: DBMS_RANDOM.RANDOM
Example: The following query uses the RANDOM function Query: SELECT DBMS_RANDOM.RANDOM FROM DUAL;
Output:  Random value Explanation: In this above query, We can use the DBMS_RANDOM.RANDOM function to select a random record from the table. We will make use of the function in the ORDER BY clause and then use row_number to filter the records. The following query implements the above logic. Query: SELECT * FROM ( Output:  Output Explanation: In the above query, we have selects a single random record from the 2. Using SAMPLE ClauseThe SELECT statement includes a Sample clause which can be used to sample a particular percentage of data from the table. Syntax: SELECT cols FROM table SAMPLE(percentage) Explanation:
Example: The following query samples 50% record from the table Query: SELECT * FROM test SAMPLE(50);
Output:  Sampled data Explanation: In the above query, we selects approximately 50% of the rows from the “test” table using the We can make use of the sample clause to first sample some amount of data from the table and then later use the row_number to filter out just the specified number of records as we did in method 1. Query: SELECT * FROM test SAMPLE(40) Output: 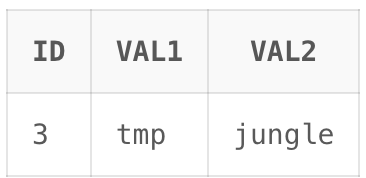 Output Explanation: In the above query, first samples approximately 40% of the rows from the “test” table using the More Technical ExampleLet’s create the table and insert some data inside it. The following query creates a lottery table and inserts three records in it. Query: CREATE TABLE lottery( Output:  Initial lottery data Explanation: Our table has been created. Now suppose that we now need to select two lottery winners. We can implement some complex logic for this or we could just simply select two records at random from the table. We will look at both the methods to implement this just for completion sense. Query: SELECT * FROM ( Output:  Output Explanation: In the above query, we selects two random records from the “lottery” table. It first orders the table randomly using Query: SELECT * FROM lottery SAMPLE(50) Output:  Output Explanation: In the above query, it selects a random 50% sample of records from the “lottery” table and then limits the output to the first two rows using ConclusionOverall, After reading this article now you have good understanding of How to select random record from table in PL/SQL. In this article, we saw two different methods to randomly select records from a table. First we saw DBMS_RANDOM.RANDOM function and then later made use of SAMPLE clause of SELECT statement to select random records. Finally, we went through a technical example to solidify our understanding of the concepts. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |