
|
|
Views in MariaDB are powerful tools that allow us to create virtual tables based on the result set of a SELECT query. They provide a way to simplify complex queries, improve security by limiting access to certain columns,, and enhance performance by precomputing expensive operations. In this article, we will explore how to create views in MariaDB along with multiple examples. How to Create View in MariaDB?Creating views in MariaDB involves defining a query that selects data from one or more tables and then saving this query as a view. Views can be used to simplify complex queries, provide a layer of abstraction over the underlying tables, and improve performance by storing the results of frequently used queries. The CREATE VIEW statement is used to create or replace an existing view by providing the view name and column names which is optional. We can create a view with the help of WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, and ORDER BY. We will understand the below examples to get a better understanding as follows.
Syntax of Create View: CREATE [OR REPLACE] VIEW [IF NOT EXISTS] view_name [column1,column2, ...] Let’s set up an environment to CREATE View in MariaDB To understand How to Create a View in MariaDB we need a table on which we will perform various operations and queries. Here we will consider two table called Departments which contain id and name as Columns. Also, The following query creates the table departments. CREATE TABLE departments Output:  Creation of Departments Table The following query creates the table Jobs which consists of id, title as Columns. CREATE TABLE jobs ( Output:  Creation of Jobs Table The following query creates the table employees which consists of id, name, department_id, job_id as Columns. Here The CREATE TABLE employees ( Output:  Creation of Employees Table After Inserting Some data into the departments table. The Table looks:  Insertion in Departments Table Insertion in Jobs Table After Inserting Some data into the Jobs table. The Table looks:  Insertion in Jobs Table Insertion in Employees Table After Inserting Some data into the employees table. The Table looks: Output: 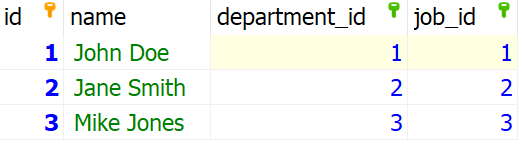 Insertion in Employees Table Creating a View Based on Multiple TablesThe following view is created to display the employees name along with their department and job title with respect to their id. The INNER JOIN keyword is used to match the id of employees, departments and jobs table to provide the respective result. CREATE VIEW employee_details AS Output: Explanation: In the above query, we have creates a virtual table named Creating a View Based on Another ViewThe following view is created to count the employees based on the job title from the employee_details view. We use the COUNT( ) to get the number of employees which we group by job title. CREATE VIEW employee_count_by_job_title AS Output:  Creating a view based on another view Explanation: In the above query, we have creates a virtual table named Creating a View Based on The Summary Data of other TablesThe following view is used to get the count of the employees based on the department. We use the COUNT( ) to get the number of employees which we group by department name. To join the employees and department table we use the INNER JOIN keyword to display result by matching the employees id to the respective department. CREATE VIEW employee_count_by_department AS Output: 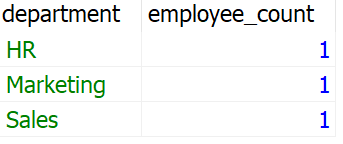 Creating a view based on the summary data of other tables Explanation: In the above query, we have creates a virtual table named ConclusionMariaDB CREATE VIEW statement is a very useful and time saving features as we can save the SELECT statements which is frequently being queried. It can also be used to simplify complex queries and manipulate them and you can also use it to replace an existing query without any deletion. Knowing when to use the statement is a deciding factor for efficient data monitoring and management. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |
