
|
|
In the data managing systems, MariaDB stands as a robust and adaptable MariaDB stands as a robust and adaptable choice in data managing systems. It’s known for efficiently retrieving data with lots of tools and instructions. We’re looking at the SELECT TOP clause, a key part of fetching data from MariaDB tables. The SELECT TOP in MariaDB limits the number of rows as queried results. we can MariaDB stands as a robust and adaptable choice in the data managing systems for the top N rows, by a set order criteria. How to Select Top RowsIn the MariaDB to select TOP N rows and TOP 10 rows firstly we have to use the LIMIT clause with the SELECT query, and how the select query, Order By Clause works. We will understand through various examples. Syntax: SELECT column1, column2, ... Explanation:
Examples of How to Select the Top 10 Rows From TableFor better understanding we will create an table called salaries to perform various queries and operations. Query: CREATE TABLE salaries Output:  salaries table Example 1: Let’s Fetch Only Top 10 Records From the SalariesSuppose we want to fetch all columns from the “salaries” table and limits the result set to the first 10 rows. Query: SELECT * FROM salaries LIMIT 10;
Output: 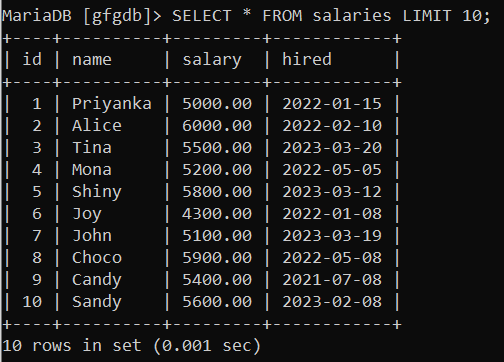 only 10 records Explanation: In this query, We have limited the output to the top 10 records only. Example 2: Let’s Fetch TOP 10 Highest(maximum) SalariesSuppose we want to fetch all columns from the “salaries” table, orders the result set in descending order based on the “salary” column, and then limits the output to the first 10 rows. Query: SELECT * FROM salaries ORDER by salary DESC LIMIT 10;
Output: 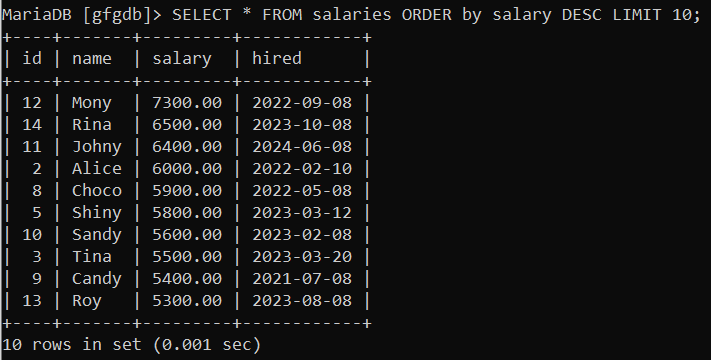 max 10 salaries Explanation: In this query, We are fetching top 10 salary records by sorting(ordering descending) by salary. Example 3: Let’s Fetch TOP 10 Salary Records for Employees Who Hired in the Year 2023Suppose we want to fetch the “name” and “salary” columns from the “salaries” table for employees hired in the year 2023 and limits the output to the first 10 rows. Query: SELECT name, salary FROM salaries Output:  year 2023 salary Explanation: In this query, we are retrieving the name and salary of TOP 10 who hired in 2023. Example 3: Suppose We to need to Retrieve the Name and Salary of the Top 10 Employees Who were Hired Before ‘2023-01-01’ and have a salary More Than the Average Salary.Suppose we want to fetch the “name” and “salary” columns from the “salaries” table for employees hired before January 1, 2023, with a salary greater than the average salary of all employees. The result set is ordered by salary in descending order, and the output is limited to the first 10 rows. Query: SELECT name, salary Output:  top 10 have more than average salary Explanation: In this query we have fetched top 10 records which were hired before ‘2023-01-01‘ and having salary more than the average salary. Example 4: Let’s Retrieve the Name, Salary, and the Difference Between the SalarySuppose we want to fetch the “name,” “salary,” and calculates the “salary_difference” by subtracting the average salary of all employees in the “salaries” table. The below query focuses on employees hired in the year 2022, orders the result set by the salary difference in descending order, and limits the output to the first 10 rows. Query: SELECT name, salary, Output:  output Explanation: In the above Query, We are fetching the name and salary of 2022 hired in this query. we are also showing how their salaries compare to the average. It’s ranked from highest to lowest difference.we are limiting it to the top 10. ConclusionIn the MariaDb slecting top N rows from a table is easy using with the LIMIT clause. This clause helps manage in the big datasets. It sets a limit on the number of rows a query returns. This helps us to improve speed and the use of resources. It could be taking the top N records using some conditions or clauses. The LIMIT clause in MariaDB gives flexibility and control in handling data. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 10 |