|
|
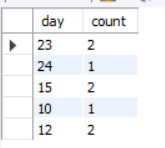
GROUP BY clause is an essential feature for data analysis. It enables users to aggregate information based on specific criteria. To group records based on day, month, and year, we can use DAY(), MONTH(), and YEAR() functions respectively. In this article, we will look at how to use MySQL’s GROUP BY clause to organize data based on the DAY, MONTH, and YEAR components of date data. We will start by creating a database and a table and populate it with the sample data. Then, we will use the three methods of GROUP BY: GROUP BY DAY(), GROUP BY MONTH (), and GROUP BY YEAR (). What is the GROUP BY clause?GROUP BY is a special command in SQL that allows you to group rows of data together based on similar values in one or more columns. Imagine you have a list of items where some items share the same characteristics, like color or type. GROUP BY helps you gather all items with the same characteristics into separate groups. After grouping, you can perform calculations on each group, like counting how many items are in each group, finding the total sum, calculating the average, or identifying the highest and lowest values within each group. This is really useful when you want to summarize data and get insights into how different groups compare or behave in a dataset. Demo MySQL DatabaseIn this tutorial, we will learn how to group data based on day, month, and year. Let’s create a sample table, on which we will use the MySQL queries to group by day, month, and Year. CREATE DATABASE gfg; Group by Day ExampleSELECT DAY(date_column) AS day, COUNT(*) AS count Output:  Group by day Explanation: This MySQL query extracts the day component from the “date_column” in the “date_month_year_table” and counts the occurrences for each unique day. The result is presented with two columns: “day,” representing the day of the month, and “count,” indicating the frequency of records for each specific day. This query is part of a broader exploration of MySQL’s `GROUP BY` functionality, allowing for the systematic analysis and aggregation of data based on the day component of date values within the specified table. Group By Month ExampleSELECT MONTH(date_column) AS month, COUNT(*) AS count Output: 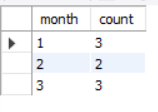 Group by month Explanation: This MySQL query utilizes the `MONTH()` function to extract the month component from the “date_column” in the “date_month_year_table” and counts the occurrences for each unique month. The result is presented with two columns: “month,” representing the numeric month value, and “count,” indicating the frequency of records for each specific month. This query showcases the application of the `GROUP BY` clause in MySQL for aggregating and analyzing data based on the month component of date values within the specified table. Group By Year ExampleSELECT YEAR(date_column) AS year, COUNT(*) AS count Output: 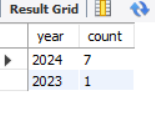 Group by year Explanation: This MySQL query employs the `YEAR()` function to extract the year component from the “date_column” in the “date_month_year_table” and counts the occurrences for each unique year. The result is presented with two columns: “year,” representing the numeric year value, and “count,” indicating the frequency of records for each specific year. This query exemplifies the application of the `GROUP BY` clause in MySQL for systematically aggregating and analyzing data based on the year component of date values within the specified table. ConclusionUsing DATE(), MONTH(), the and YEAR() functions with the GROUP BY clause allows a group of data based on date, month, and year respectively. This is very useful for tasks like trend analysis and reporting, enhancing precision and efficiency in aggregating information. MySQL’s `GROUP BY` feature is a powerful tool for extracting meaningful insights and understanding the patterns within date-related datasets. FAQs on Group by Month and Year in MySQLWhat is the purpose of the GROUP BY clause in MySQL?
How does GROUP BY DAY() work in MySQL?
Can GROUP BY MONTH() aggregate data by month in MySQL?
What is the advantage of using GROUP BY YEAR() in MySQL?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |