
|
|
A FOREIGN KEY is a field/column(or collection of fields) in a table that refers to a PRIMARY KEY in another table. It is used for linking one or more than one table together. FOREIGN KEY is also called referencing key. A Foreign key creates a link (relation) between two tables thus creating referential integrity. In this article, we will learn about how to use foreign keys in MySQL with examples. FOREIGN KEY in MySQLThe FOREIGN KEY creates a relationship between the columns in the current table or let’s say table A (the one with the foreign key) and the referenced table or table B (the one with the unique key). FOREIGN KEY creates a parent-child type of relationship where the table with the FOREIGN KEY in the child table refers to the primary or unique key column in the parent table. How to Define FOREIGN KEY in MySQLThere are 2 ways to create a FOREIGN KEY in MySQL: We can create a FOREIGN KEY while creating the table, or add a FOREIGN KEY after the creation of the table. Using CREATE TABLE Statement to Create FOREIGN KEYCREATE method can be used to define your FOREIGN KEY in MYSQL in the following way: CREATE TABLE child_table ( Parameters:
Creating FOREIGN KEY Using CREATE TABLE ExampleLet us understand the concept of MySQL FOREIGN KEY with an example. We are two tables namely Users and Orders. The Users table will be the parent table, as it contains the PRIMARY KEY (user_ID) and referenced by foreign key (User_ID). And Orders table will be the child table. CREATE TABLE users ( Output: users Table: orders Table: Explanation: We have created two table users and orders. orders table has a foreign key on field user_id that references the primary key user_id of users table. Using ALTER TABLE Statement to Add FOREIGN KEYWe can define a foreign key using the ALTER TABLE statement in MySQL. This is the case where you already have a table and need to get a foreign key in it. The foreign key constraint helps maintain referential integrity between the two tables. SyntaxALTER TABLE child_table Let us apply this in an example and understand the working. Adding FOREIGN KEY Using ALTER TABLE ExampleWe will create two tables orders and customers. CREATE TABLE customers ( Now in the orders table, let us add the foreign key using ALTER TABLE. Query: ALTER TABLE orders Table Structure VerificationTable structure verification can be done by using some SQL queries. The following queries can help you inspect the structure of the tables and also confirm if there is a foreign key available: 1. Show tableThis lists all the tables in your database SHOW TABLES;
2. Describe TableThe structure of specific table can be viewed with this query. Query: DESCRIBE <table_name>; 3. Show Foreign KeysNow the foreign keys in a table can be listed using the following query. Query: SELECT Foreign Key Example Using SET NULL ActionThe SET NULL action in a foreign key constraint is used to delete or update row in the parent table while setting the foreign key column in the child table to NULL. [NULL here refers to empty or not known] Let me simplify this with help of an example: We have two tables: employees and departments. Employee table has the information about the employees along with the dept_id (the department to which they belong). The departments table has the department name and its corresponding id, in the dept_id column. (for ex. 101 for HR, 102 for IT…) The employees table has the dept_id as foreign key that refers to the primary key (dept_id) in the departments table. Now in a scenario where the department is deleted, the corresponding dept_id in the employees table will automatically change NULL. So even when a department is deleted, we still have record of the employees that were from that department. This is an important rule that helps us to retain data and avoid errors in the employee table even when something in the departments table is changed or deleted. CREATE TABLE departments ( Output of employees table:  EMPLOYEE TABLE Output of department table: 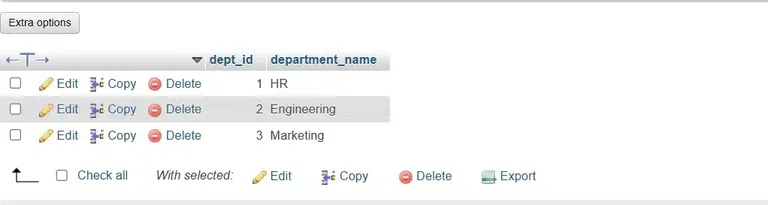 DEPARTMENT TABLE Now let’s update the department_id in the departments table and set it to NULL in employees table UPDATE departments SET dept_id = 4 WHERE dept_id = 2; Output: 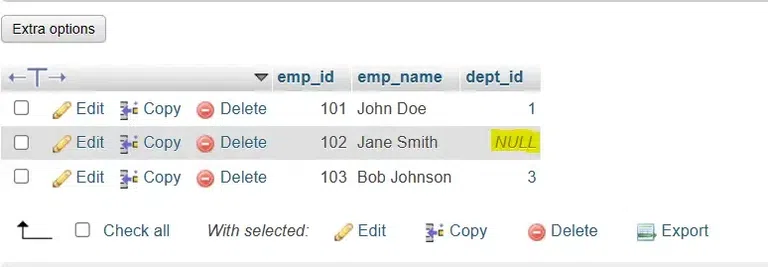 The deleted department was set to NULL Now let’s delete a department and set corresponding dept_id to NULL in employees table DELETE FROM departments WHERE dept_id = 1; Output:
DROP Foreign KeyThe foreign key can be dropped using the DROP FOREIGN KEY clause. Syntax: ALTER TABLE <table_name> Enabling and Disabling Foreign Key ChecksForeign key checks are rulebooks/ mechanisms that ensure the consistency of relationships between tables. These help us maintain referential integrity, preventing actions that could disturb the relationships. Let us understand the concept of foreign key checks. Foreign key checks are in two modes: Enabled or Disabled. 1. To enable foreign key checks:SET foreign_key_checks = 1;
2. To disable foreign key checks:verificationThe foreign key checks help us to make sure that every record has a valid corresponding value in the other table. It's like double-checking to be sure everything is in order. In the most cases it is suggested to keep the checks enabled.
Now when we need to perform some special actions like bulk updation, insertion or deletion we may need to disable these checks temporarily to avoid errors. It’s crucial to re-enable foreign key checks promptly after the bulk update or deletion to ensure that data integrity is restored. ConclusionIn conclusion, effectively utilizing foreign keys in MySQL is important for designing robust and well-structured relational databases. Foreign keys serve as a very helpful tool in maintaining referential integrity, ensuring that relationships between tables are consistent and reliable. FAQs on FOREIGN KEY in MySQLWhat is a FOREIGN KEY in MySQL?
What is the purpose of a FOREIGN KEY?
Can I create multiple FOREIGN KEYs in a single table?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |
