|
|
Data is everywhere, and managing data is a challenge. Most web websites and applications, businesses, and organizations use databases to store their data. while everything is moving online in a rapid manner managing databases becomes a challenge for organizations. Google Cloud Platform solves all major Relational database problems by introducing their Cloud SQL. Cloud SQL supports all major RDBMS and provides migration from offline databases. In this article, we will learn how businesses can use Cloud SQL to create databases and manage Relational Databases and use their most of time on business logic rather than investing in managing Databases. What is SQL Database?Relational databases are referred to as SQL databases. SQL is a structured query language used for programming and managing Relational Databases. A relational database is a database where data are stored in the form of tables and tables share a relationship among themselves. In these types of Databases, each row reflects a data entity, and every column defines a specific information field. SQL provides all major operations like create, read, update, and delete for a Relational Database or SQL Database. What is Cloud SQL?Cloud SQL is a fully-managed relational database service provided by Google Cloud Platform. Cloud SQL manages your databases so you don’t have to, so your business can run without disruption. From automatic backups to high availability, this service of database management, allowing organizations to focus on business logic while leaving the headache of database administration to Cloud SQL. Cloud SQL supports a variety of popular relational database management systems (RDBMS) including: MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server. Learn more on Cloud SQL by visiting google-cloud-sql. Benefits of Cloud SQL
Setting Up a SQL Database- ProcessStep 1: Create InstanceVisit console.cloud.google.com and Log in with your valid credentials. Then on the left sidebar select SQL.
On the next page click on create instance.
Step 2: Choose Database EngineWhen creating a Cloud SQL instance on Google Cloud Platform (GCP), you have the flexibility to choose from several database engines based on your specific requirements. Select the database engine that suites your requirement (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server).
Step 3: Configure Database InstanceAn instance refers to a single, isolated database running on a cloud server. It includes the database engine, storage, and configuration settings.
Give your instance a name and set a secure password to prevent un-authorized access. Select Database version as MySQL 8.0.
Set Availability Zone as your nearest and explore other configurations, you can change accordingly or left unchanged. For further more customization scroll down to customize your instance and explore other customization options like Machine configuration, Storage, etc.
Once done, click on create. Step 4: Check Database InstanceWait for sometime, until the instance is created. You will notice a tick mark before your instance name, once it is created.
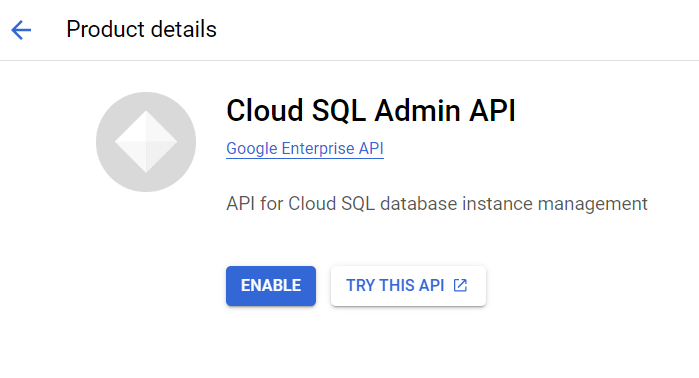
Now you have successfully created a Relational Database using Cloud SQL on GCP. Enabling SQL Admin APISQL Admin API in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) allows you to programmatically manage your Cloud SQL databases using API requests. Cloud SQL provides a REST API for administering your instances programmatically. The SQL Admin API provides a set of methods for tasks such as creating and managing database instances, configuring user accounts, and handling backups. Search for “APIs & Services” on the search-bar available in the Google Cloud console or on the left sidebar look for APIs and Services and then click on “Enable APIs & Services”.
This will move you to GCP API Library, search for SQL Admin API there and click on it and then click on Enable API.
Creating DatabaseOnce our SQL instance is ready, let’s create a Database. Navigate to all instances and then select the database instance you have created and scroll down to find Open Cloud Shell.
Wait for few seconds until the terminal opens up. You will find a pre-written command is there for you to connect your database to the Cloud shell. Press ENTER and give your instance’s password.
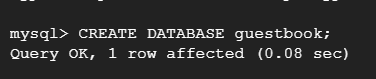
After sometime MySQL prompt will open and you can execute MySQL quires. To learn about MySQL Quires check this article on mysql-common-mysql-queries. To create a new Database in MySQL execute the following query CREATE DATABASE guestbook;
This will create a new database named “guestbook” in cloud sql.
Now using the same database create a new table and insert two rows of data. Let’s name our table as “entries” and columns as “guestName”, “content”, and “entryID”. We will make “entryID” as the primary key for the table. /* Using the guestbook database*/
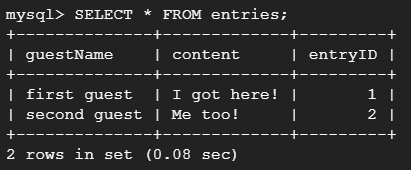
Let’s check the table we have just created. Execute the following query to see the table. SELECT * FROM entries;
As you can see 2 rows are there in the table with the data we have inserted. Managing Relational Database using Cloud SQLGoogle Cloud platform provides plenty of features to manage relational databases. You can use charts to observe your instance behavior. Create your databases using GUI or using cloud shell. Cloud SQL provides option for replication and high availability. You can always opt for better performance and storage by upgrading your plans and services so that you don’t feel problems operating your database services running on Cloud SQL. If you are migrating from an existing database, use tools like mysqldump or pg_dump to import data into your Cloud SQL instance.
Access the sidebar on left side to view all services provided for efficient management of your Relational Database.
On Configuration section you can see all the configurations made to your RDBMS. This include Database edition, Database version, Backup Settings, etc. You can see that there is an option given for upgrade so you can opt for update anytime.
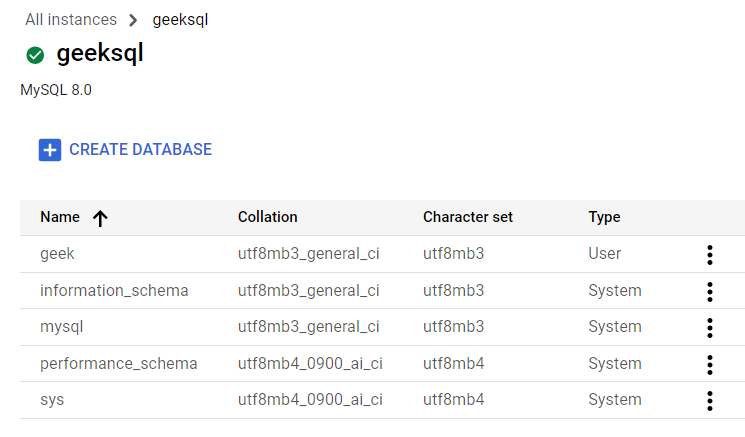
On Database section you will be able to see all your existing databases and create an delete databases. More more efficient management of Relational Database, you can use cloud shell and execute your queries. Check the article on Cloud SQL to learn how queries are executed.
To check about resource usage visit System insights and you will be able to see all usages.
ConclusionCloud SQL provides user the priviledge to create and manage Relational Databases effortlessly. Automatic frequent tasks and backup processes Cloud SQL helps reducing down-time and Integration with google services is one of the major feature of Cloud SQL. Through this article we have discussed creation and management of Google Cloud’s Cloud SQL. You can explore more on Google Cloud domain by visiting the article on FAQs on Cloud SQL to Create and Manage Relational DatabasesWhich Relational Database Engines Are Supported By Cloud SQL?
How Do I Create a New Cloud SQL Instance In Google Cloud Platform?
Is It Free To Create Cloud SQL On Google Cloud Platform?
How Can I Migrate An Existing Relational Database To Cloud SQL?
How Can I Secure Data During The Migration Process To Cloud SQL?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Android |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |