|
In Vue.js, we can watch the nested data to properly control the changes within the nested properties. In this article, we will explore both of the approaches with the practical implementation of these approaches in terms of examples and outputs.
We can watch this by using two different approaches:
Approach 1: Using deep: true Option
In this approach, we are using the deep: true option in the watcher to properly watch changes within the nested Data Structures. This makes sure that the changes to the deeply nested properties like user.name, trigger the handler function.
Syntax:
new Vue({
watch: {
'nestedDataProperty': {
handler: function(newValue, oldValue) {
// Tasks
},
deep: true
}
}
});
Example: Below is the implementation of the above-discussed approach.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<title>Example 1</title>
<script src=
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 style="color:green">
GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h3>Approach 1: Using deep:true Option</h3>
<p>Name: {{ user.name }}</p>
<p>Age: {{ user.age }}</p>
<input v-model="newName"
placeholder="Enter new name">
<button @click="changeName">Update Name</button>
<p v-if="dataChanged" style="color: green;">
Data has changed!
</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
user: {
name: 'GFG USER',
age: 23
},
newName: '',
dataChanged: false
},
watch: {
user: {
handler: function (newValue, oldValue) {
console.log('User data is changed!', newValue);
this.dataChanged = true;
},
deep: true
}
},
methods: {
changeName: function () {
this.user.name = this.newName;
this.newName = '';
this.dataChanged = false;
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
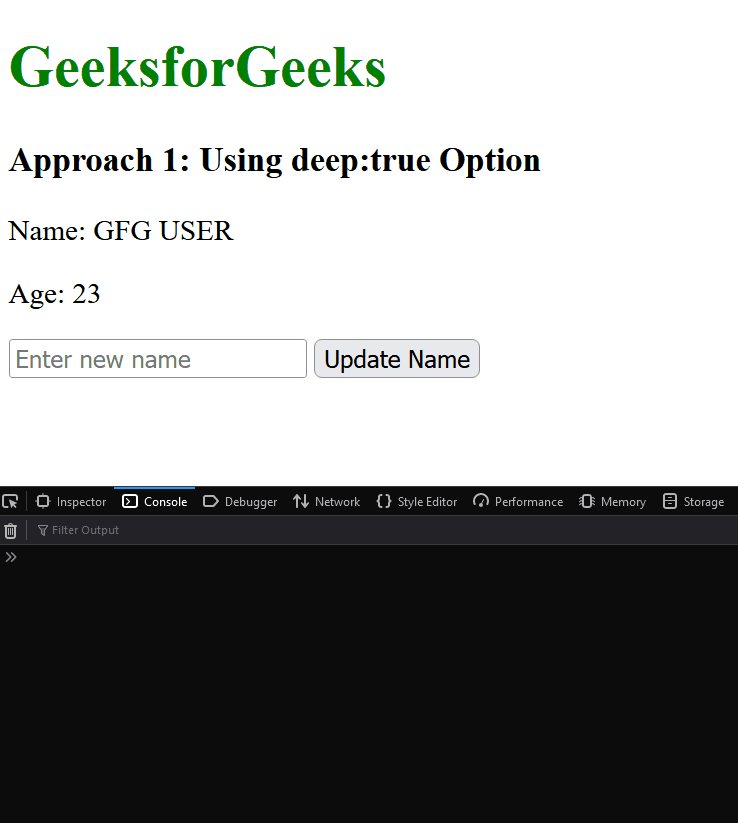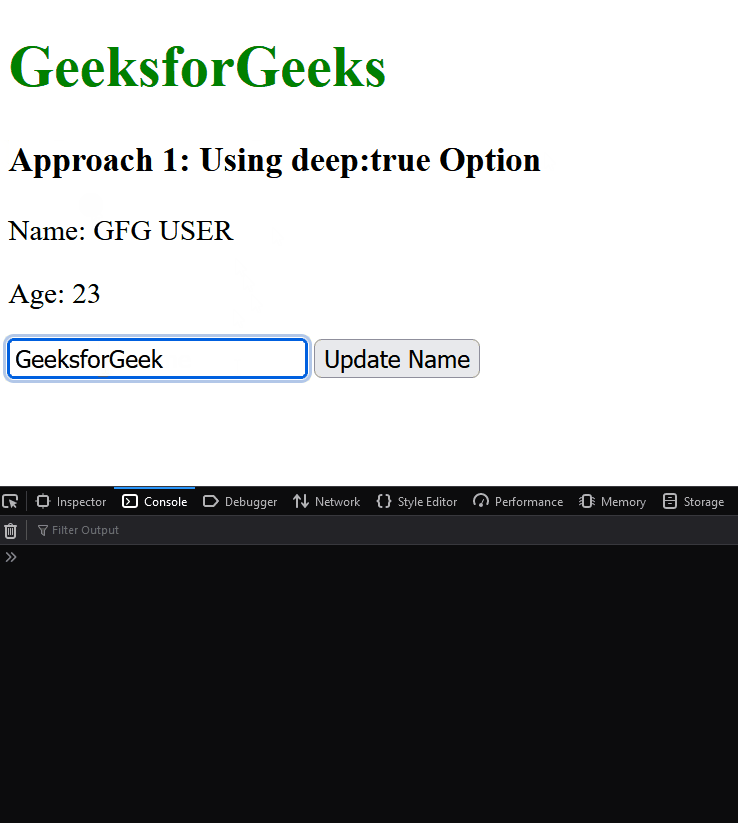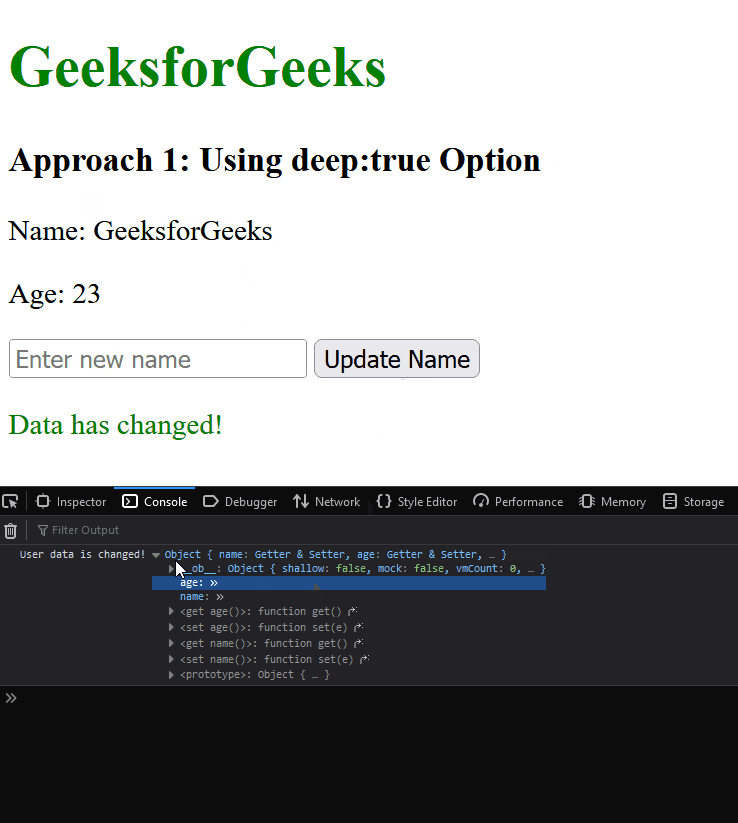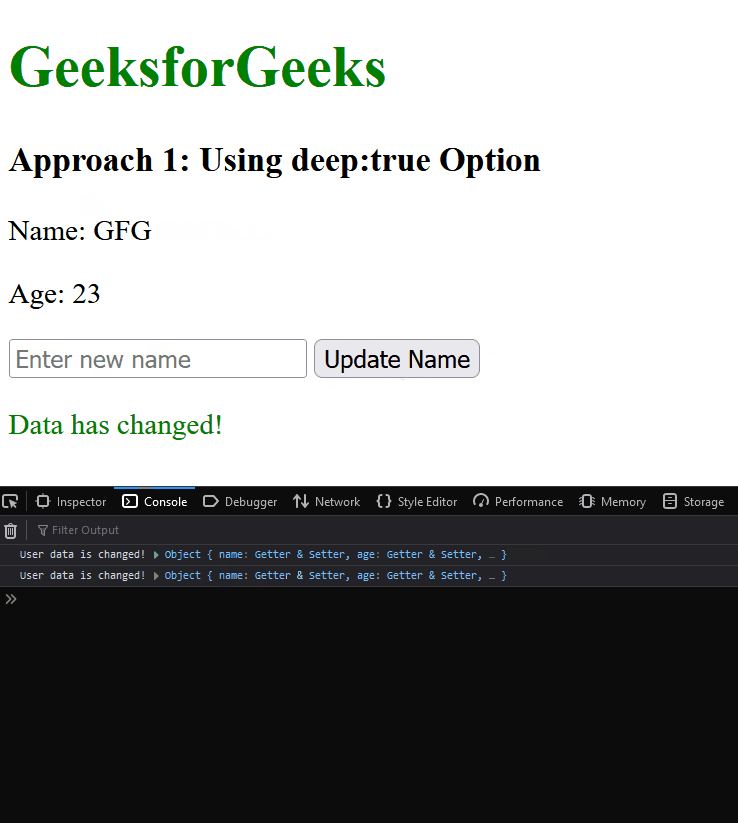
Approach 2: Using Computed Property
In this apporach, we are using the computed property to watch the nested data. We have the personName and personage computed properties which allows the 2 directional binding, this enabes the reactivity to changes in the nested objects like name and age properies by providing the clear separation.
Syntax:
new Vue({
data: {
nestedData: {
property1: 'value1',
property2: 'value2'
}
},
computed: {
computedProperty: {
get: function() {
// getter logic
},
set: function(newValue) {
// setter logic,
}
}
}
});
Example: Below is the implementation of the above-discussed approach.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<title>Example 2</title>
<script src=
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 style="color: green">GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h3>Approach 2: Using Computed Property</h3>
<p>Geek Name: {{ personName }}</p>
<p>Geek Age: {{ personAge }}</p>
<input v-model="person.name"
placeholder="Enter the name">
<input v-model="person.age"
placeholder="Enter the age" type="number">
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
person: {
name: '',
age: null
}
},
computed: {
personName: {
get: function () {
return this.person.name;
},
set: function (newName) {
this.person.name = newName;
console.log('Name changed:', newName);
}
},
personAge: {
get: function () {
return this.person.age;
},
set: function (newAge) {
this.person.age = newAge;
console.log('Age changed:', newAge);
}
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

|

