
|
|
In this article, we will learn about what are Host objects and Native objects, and their differences. JavaScript objects are broadly classified into 2 categories – native javascript objects and host javascript objects. Native objects: Native javascript objects are standard javascript objects which are provided by javascript itself. They are also known as built-in objects, pre-defined objects, or global objects. These objects work in the same fashion and are available to all users, irrespective of the machine and the environment. Their functionalities do not change with the change in the machine or environment and can be used as both, constructors (like String(), Array(), Object()) and primitive values (like true, 999). For example:
Example: Javascript
Output: 
Host objects: Host javascript objects are environment-specific javascript objects, and may vary as per the environment of the machine in which the javascript is being used. Objects provided by one environment, may or may not be present in another environment. For example, most browsers provide window objects or navigator objects, but these objects are not present in the server running node.js. However, some objects like consoles are provided by both, the browsers and the node.js servers. Therefore, we can say that the host objects are host specific and may differ from one host (environment) to other. For example:
Example: Javascript
Output: 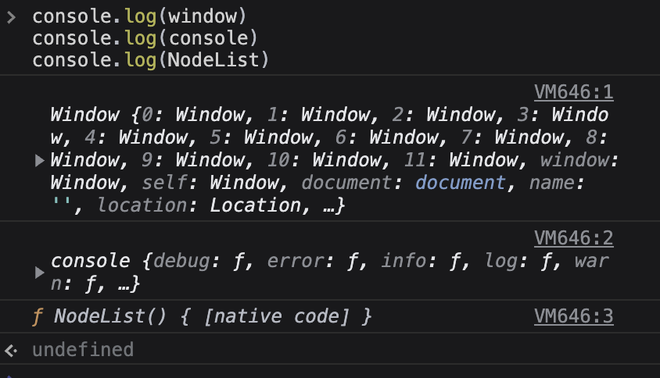
Difference between Native objects and Host objects:
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| JavaScript |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 11 |