|
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to find the sum of leaf nodes at every level of the given tree.
Examples:
Input:
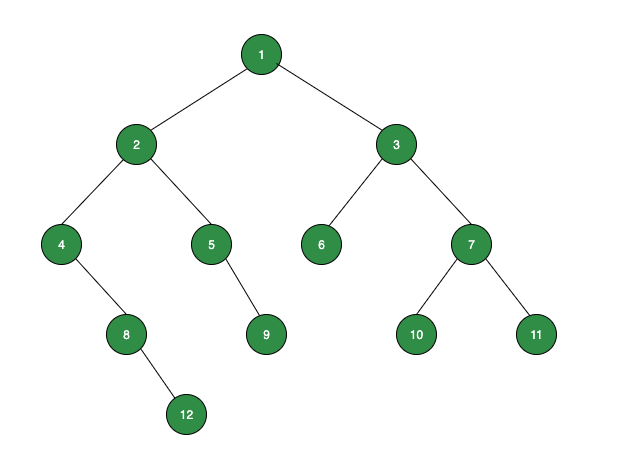
Output:
0
0
6
30
12
Explanation:
Level 1: No leaf node, so sum = 0
Level 2: No leaf node, so sum = 0
Level 3: One leaf node: 6, so sum = 6
Level 4: Three leaf nodes: 9, 10, 11, so sum = 30
Level 5: One leaf node: 12, so sum = 12
Input:

Output:
0
0
6
28
Approach: The given problem can be solved by using the Level Order Traversal. Follow the steps below to solve the given problem:
- Create a queue qu, to store the node alongside its level. Also, create a map to store the sum of each level.
- Perform the level order traversal from the root node and store each node with its level in the queue, and also check the current node for the leaf node. If it’s a leaf node then add its value in the map corresponding to its level.
- After completing the above steps, print the values in the map as the sum of each level of the given tree.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
void printLevelSum(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL) {
cout << "No nodes present\n";
return;
}
map<int, int> mp;
queue<pair<Node*, int> > q;
q.push({ root, 1 });
pair<Node*, int> p;
while (!q.empty()) {
p = q.front();
q.pop();
if (mp.find(p.second) == mp.end()) {
mp[p.second] = 0;
}
if (p.first->left == NULL
&& p.first->right == NULL) {
mp[p.second] += p.first->data;
}
if (p.first->left)
q.push({ p.first->left, p.second + 1 });
if (p.first->right)
q.push({ p.first->right, p.second + 1 });
}
for (auto i : mp) {
cout << i.second << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
root->left->left->right = new Node(8);
root->left->right->right = new Node(9);
root->right->right->left = new Node(10);
root->right->right->right = new Node(11);
root->left->left->right->right = new Node(12);
printLevelSum(root);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Print_Level_Sum_Btree {
static class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
static class Pair{
Node n;
int i;
Pair(Node n, int i){
this.n = n;
this.i = i;
}
}
static void printLevelSum(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
System.out.println("No nodes present");
return;
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<Pair>();
q.add(new Pair(root, 1));
Pair p;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
p = q.peek();
q.remove();
if (!map.containsKey(p.i))
map.put(p.i, 0);
if (p.n.left == null && p.n.right == null)
{
map.put(p.i, map.get(p.i) + p.n.data);
}
if (p.n.left != null)
q.add(new Pair(p.n.left, p.i + 1));
if (p.n.right != null)
q.add(new Pair(p.n.right, p.i + 1));
}
for (Map.Entry mapElement : map.entrySet()) {
int value = ((int)mapElement.getValue());
System.out.println(value);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = null;
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.left.left.right = new Node(8);
root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
root.right.right.left = new Node(10);
root.right.right.right = new Node(11);
root.left.left.right.right = new Node(12);
printLevelSum(root);
}
}
|
Python3
class newNode:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
def printLevelSum(root):
if (not root):
print("No nodes present")
return
dict = {}
q = []
q.append([root, 1])
p = []
while (len(q)):
p=q[0]
q.pop(0)
if (p[1] not in dict.keys()):
dict[p[1]] = 0
if (not p[0].left and not p[0].right):
dict[p[1]] = p[0].data + dict.get(p[1])
if (p[0].left):
q.append([p[0].left, p[1] + 1])
if (p[0].right):
q.append([p[0].right, p[1] + 1])
for sum in dict.values():
print(sum)
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
root.right.left = newNode(6)
root.right.right = newNode(7)
root.left.left.right = newNode(8)
root.left.right.right = newNode(9)
root.right.right.left = newNode(10)
root.right.right.right = newNode(11)
root.left.left.right.right = newNode(12)
printLevelSum(root)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Print_Level_Sum_Btree {
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
public class Pair{
public Node n;
public int i;
public Pair(Node n, int i){
this.n = n;
this.i = i;
}
}
static void printLevelSum(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("No nodes present");
return;
}
Dictionary<int, int> map = new Dictionary<int,int>();
Queue<Pair> q = new Queue<Pair>();
q.Enqueue(new Pair(root, 1));
Pair p;
while (q.Count!=0) {
p = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
if (!map.ContainsKey(p.i))
map.Add(p.i, 0);
if (p.n.left == null && p.n.right == null)
{
map[p.i]= map[p.i] + p.n.data;
}
if (p.n.left != null)
q.Enqueue(new Pair(p.n.left, p.i + 1));
if (p.n.right != null)
q.Enqueue(new Pair(p.n.right, p.i + 1));
}
foreach(KeyValuePair<int, int> entry in map){
int value = (entry.Value);
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = null;
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.left.left.right = new Node(8);
root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
root.right.right.left = new Node(10);
root.right.right.right = new Node(11);
root.left.left.right.right = new Node(12);
printLevelSum(root);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
function printLevelSum(root) {
if (root == null) {
document.write("No nodes present\n");
return;
}
let mp = new Map();
let q = [];
q.push([root, 1]);
let p = [];
while (q.length) {
p = q[q.length - 1];
q.pop();
if (!mp.has(p[1])) {
mp.set(p[1], 0);
}
if (p[0].left == null && p[0].right == null) {
mp.set(p[1], mp.get(p[1]) + p[0].data);
}
if (p[0].left) q.push([p[0].left, p[1] + 1]);
if (p[0].right) q.push([p[0].right, p[1] + 1]);
}
for (let i of mp) {
document.write(i[1] + "<bR>");
}
}
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.left.left.right = new Node(8);
root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
root.right.right.left = new Node(10);
root.right.right.right = new Node(11);
root.left.left.right.right = new Node(12);
printLevelSum(root);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Another Approach(Recursive):
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
1). In this method we will traverse the each node of binary tree recursively and keep track of level with each node.
2). If the current node is leaf node then we will store the node value in vector otherwise if the node is not leaf node then we will add the sum in 0 so it will not effects out answer.
3). Finally print the array of answers.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int data){
this->data = data;
this->left = NULL;
this->right = NULL;
}
};
int height(Node* root){
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int l = height(root->left);
int r = height(root->right);
return max(l,r)+1;
}
void printLevelSum(Node* root, vector<int> &ans, int level){
if(root == NULL) return;
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL){
ans[level] += root->data;
}else{
ans[level] += 0;
}
printLevelSum(root->left, ans, level+1);
printLevelSum(root->right, ans, level+1);
}
int main(){
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
root->left->left->right = new Node(8);
root->left->right->right = new Node(9);
root->right->right->left = new Node(10);
root->right->right->right = new Node(11);
root->left->left->right->right = new Node(12);
vector<int> ans(height(root), 0);
printLevelSum(root, ans, 0);
for(int i : ans)
cout<<i<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
int height(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return 0;
int lheight = height(node.left);
int rheight = height(node.right);
return Math.max(lheight, rheight) + 1;
}
void printLevelSum(Node node, int[] ans, int level) {
if (node == null)
return;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
ans[level] += node.data;
} else {
ans[level] += 0;
}
printLevelSum(node.left, ans, level + 1);
printLevelSum(node.right, ans, level + 1);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.left.right = new Node(8);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(10);
tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11);
tree.root.left.left.right.right = new Node(12);
int[] ans = new int[tree.height(tree.root)];
tree.printLevelSum(tree.root, ans, 0);
for (int i : ans) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
|
Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def height(root):
if root is None:
return 0
l = height(root.left)
r = height(root.right)
return max(l, r) + 1
def printLevelSum(root, ans, level):
if root is None:
return
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
ans[level] += root.data
else:
ans[level] += 0
printLevelSum(root.left, ans, level+1)
printLevelSum(root.right, ans, level+1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
root.left.left.right = Node(8)
root.left.right.right = Node(9)
root.right.right.left = Node(10)
root.right.right.right = Node(11)
root.left.left.right.right = Node(12)
ans = [0] * height(root)
printLevelSum(root, ans, 0)
for i in ans:
print(i)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
public int height(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
int lheight = height(node.left);
int rheight = height(node.right);
return Math.Max(lheight, rheight) + 1;
}
public void printLevelSum(Node node, int[] ans, int level)
{
if (node == null)
return;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
{
ans[level] += node.data;
}
else
{
ans[level] += 0;
}
printLevelSum(node.left, ans, level + 1);
printLevelSum(node.right, ans, level + 1);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.left.right = new Node(8);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(10);
tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11);
tree.root.left.left.right.right = new Node(12);
int[] ans = new int[tree.height(tree.root)];
tree.printLevelSum(tree.root, ans, 0);
foreach (int i in ans)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function height(root){
if(root == null) return 0;
let l = height(root.left);
let r = height(root.right);
return Math.max(l,r)+1;
}
let ans;
function printLevelSum(root, level){
if(root == null) return;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
ans[level] += root.data;
}else{
ans[level] += 0;
}
printLevelSum(root.left, level+1);
printLevelSum(root.right, level+1);
}
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.left.left.right = new Node(8);
root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
root.right.right.left = new Node(10);
root.right.right.right = new Node(11);
root.left.left.right.right = new Node(12);
ans = new Array(height(root)).fill(0);
printLevelSum(root, 0);
for(let i = 0; i<ans.length; i++){
console.log(ans[i]);
}
|
Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the number of nodes in given binary tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(h) where h is the height of binary tree due to recursion.
|

