![How to Flush DNS Cache? [Windows, Mac, and Linux]](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/20240404020147/How-to-Flush-DNS-Cache-[Mac-Windows-and-Linux].webp)
|
|
Flushing the DNS cache is a crucial step in troubleshooting and maintaining optimal internet connectivity. The DNS cache stores information about previous DNS lookups, which can sometimes become outdated or corrupted, leading to issues accessing websites. Whether you are using Windows, Mac, or Linux, knowing how to flush the DNS cache can help ensure your system is using the most current DNS information.
This guide will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to flush the DNS cache on all three operating systems, helping you resolve connectivity issues and maintain a smooth browsing experience. What are the Signs You Should Flush Your DNS Cache?Although the DNS cache is generally good, sometimes it may be worthwhile to flush the DNS cache to fix browsing issues. Some of the indicators of such situations are as follows:
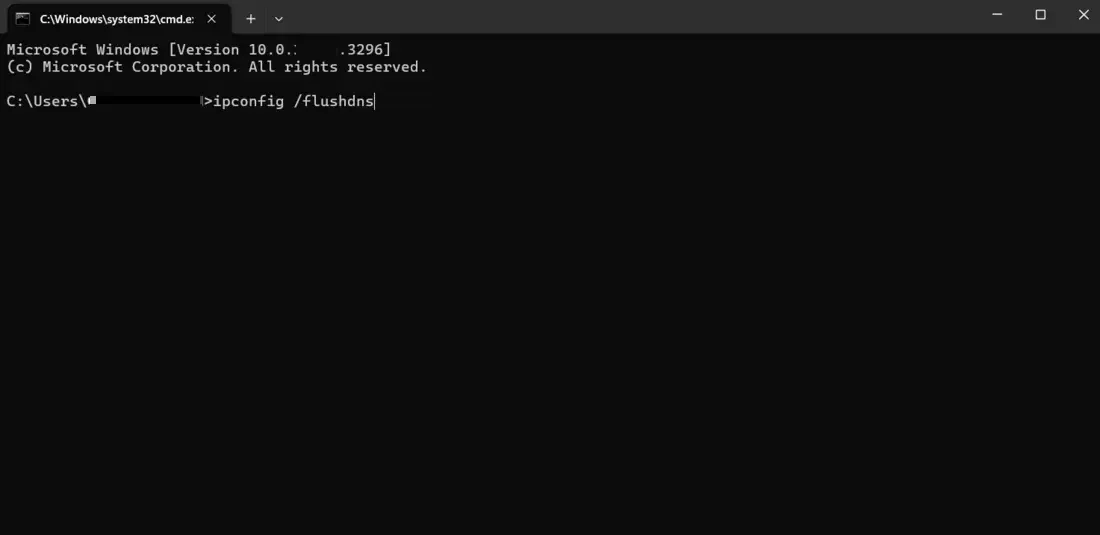
How to Flush DNS Cache?However, clearing your DNS cache is simple but will differ depending on your operating system (OS) and whether you are doing it from your computer or browser. In the following sections, we shall detail how to clear the DNS cache for macOS, Windows, and Linux. 1. Flushing the DNS Cache on WindowsFlushing the DNS cache on Windows involves using the Command Prompt:
ipconfig /flushdns
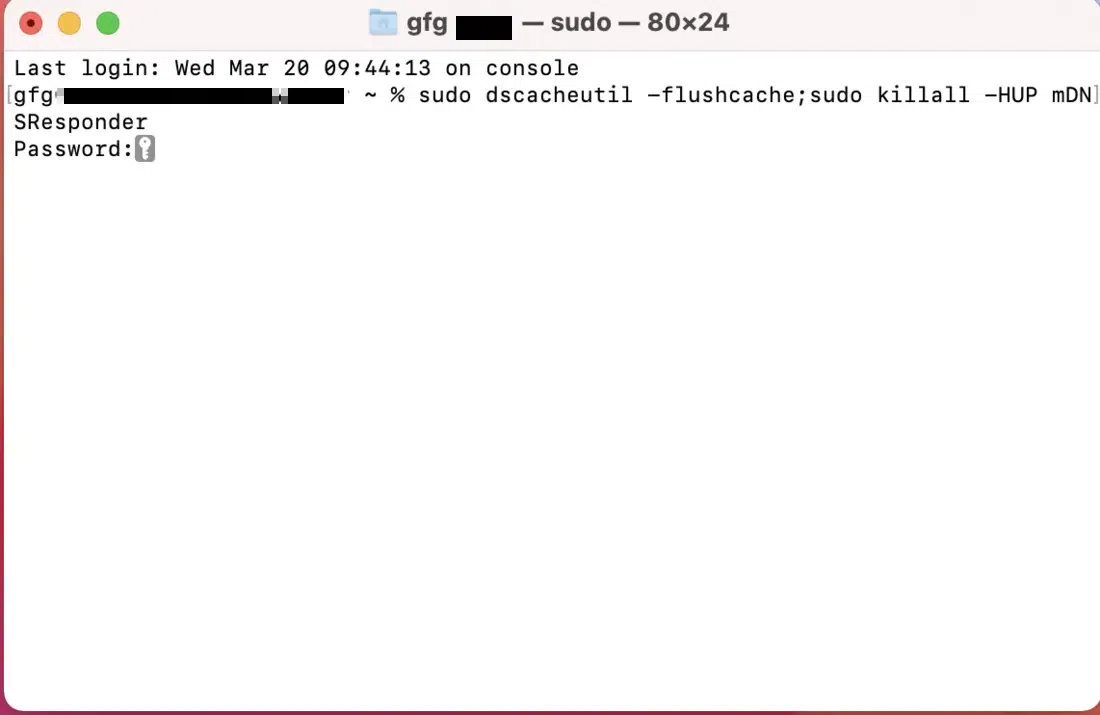
2. Flushing the DNS Cache on MacHere’s how to flush the DNS cache on your Mac:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
3. Flushing the DNS Cache on LinuxThe specific commands for flushing the DNS cache on Linux can vary depending on your distribution. Here are some common methods: For Ubuntu and Debian
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches
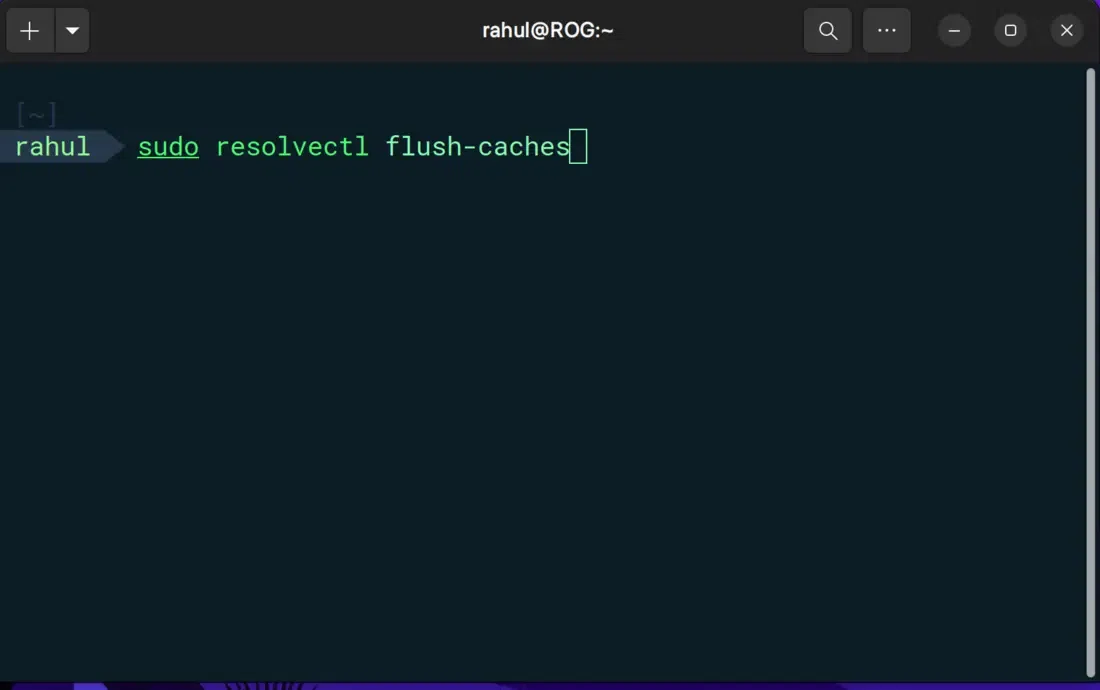
For newer versions of UbuntuYou may need to use this command instead:
sudo resolvectl flush-caches
If successful, you won’t see any confirmation message, but your DNS cache will be flushed.
Other DistributionHere are some examples of other Linux distributions:
sudo service nscd restart
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches
Important Note: The above examples are just a few of many possible “sudo systemd-resolve –flush-caches,” and yours might differ. For more accurate instructions, consult your distribution’s documentation. Once you clear the DNS cache, there may be some slight latency when first visiting web pages. This is because your device has to obtain fresh IP addresses from the DNS server. This delay should be minimal, and subsequent visits to the same website should load at the usual speed. When Flushing the DNS Cache Might Not HelpThis DNS (Domain Name System) cache flushing is not a magic bullet for all internet connectivity problems that affect your computer. Here are some scenarios where it might not be the solution:
ConclusionRegularly flushing the DNS cache can prevent and resolve many common internet connectivity issues across different operating systems. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your Windows, Mac, or Linux system is using the latest DNS information, leading to a more stable and efficient browsing experience. Keep this guide handy to quickly address any DNS-related issues that may arise in the future.
How to Flush DNS Cache? [Windows, Mac, and Linux] – FAQsWhat is the DNS cache, and why should I flush it?
How often should I flush my DNS cache?
Will flushing the DNS cache erase my browsing history?
Is flushing the DNS cache safe?
How do I flush the DNS cache on Windows?
How do I flush the DNS cache on a MacOS?
How do I flush the DNS cache on Linux?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| TechTips |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 15 |