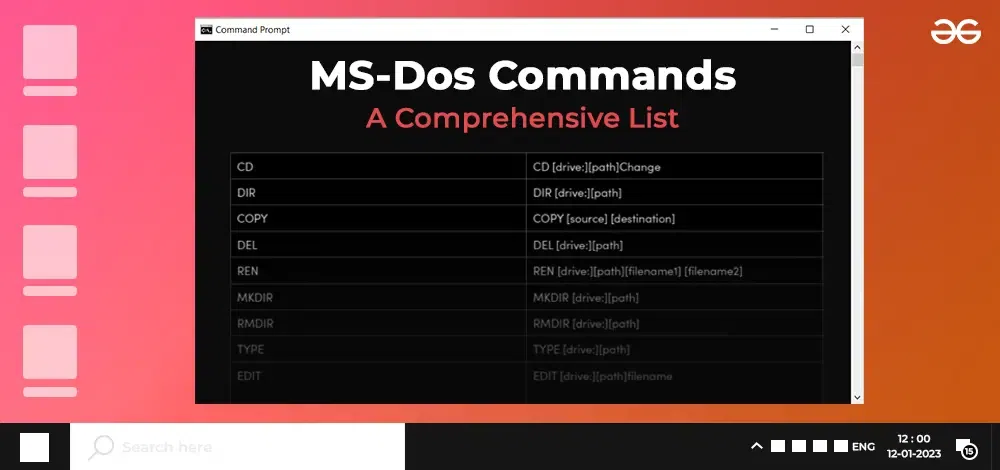
|
CD
|
CD [drive:][path]Change
|
ges the current directory to the specified folder.
|
|
DIR
|
DIR [drive:][path]
|
Displays a list of files and subdirectories in a directory.
|
|
COPY
|
COPY [destination]
|
Copies files from one location to another.
|
|
DEL
|
DEL [drive:][path]
|
Deletes one or more files.
|
|
REN
|
REN [drive:][path][filename1] [filename2]
|
Renames a file or directory.
|
|
MKDIR
|
MKDIR [drive:][path]
|
Creates a new directory.
|
|
RMDIR
|
RMDIR [drive:][path]
|
Removes an existing directory.
|
|
TYPE
|
TYPE [drive:][path]
|
filename Displays the contents of a text file.
|
|
EDIT
|
EDIT [drive:][path]filename
|
Opens the MS-DOS text editor for editing a specified file.
|
|
CHKDSK
|
CHKDSK [volume:][[path]filename] [/F] [/V] [/R] [/X] [/I] [/C] [/L[:size]] [/B]
|
Scans and fixes errors on a disk.
|
|
FORMAT
|
FORMAT volume [/FS:file-system] [/V:label] [/Q] [/L[:size]] [/A:size] [/C] [/X]
|
Prepares a storage medium for data storage.
|
|
XCOPY
|
XCOPY [destination] [/E] [/C] [/H] [/R] [/Y]
|
Copies files and directories, including subdirectories.
|
|
TREE
|
TREE [drive:][path]
|
Graphically displays the folder structure of a drive or path.
|
|
DATE
|
DATE [MM-DD-YYYY]
|
Displays or sets the system date.
|
|
TIME
|
TIME [HH: MM: SS]
|
Displays or sets the system time.
|
|
HELP
|
HELP [command]
|
Provides help information for MS-DOS commands.
|
|
EXIT
|
EXIT
|
Exits the MS-DOS command prompt or a batch file.
|
|
ATTRIB
|
ATTRIB [+ R|-R] [+A|-A] [+ H|-H] [+ S|-S] [d:][path]filename [/S]
|
Sets or clears file attributes (Read-Only, Archive, System, Hidden), managing file visibility and access in MS-DOS.
|
|
MODE
|
MODE [device] [BAUD=b] [PARITY=p] [DATA=d] [STOP=s]
|
Configures system devices.
|
|
DISKCOPY
|
DISKCOPY [drive1:][path1][filename1] [drive2:][path2][filename2]
|
Copies the contents of one disk to another.
|
|
MEM
|
MEM[/program|/debug|/classify|/free|/module(name)] [/page]
|
Displays the amount of used and free memory in the system.
|
|
SCANDISK
|
SCANDISK [/SURFACE] [/AUTOFIX] [/CHECKONLY]
|
Scans and fixes disk errors.
|
|
UNDELETE
|
UNDELETE [drive:][path][filename]
|
Restores a deleted file.
|
|
ASSIGN
|
ASSIGN [drive1:=[drive2:]]
|
Redirects requests for drive letters to a different drive.
|
|
FDISK
|
FDISK
|
Manages disk partitions.
|
|
BACKUP
|
BACKUP [destination] [/S]
|
Backs up files and directories.
|
|
RESTORE
|
RESTORE [destination] [/S]
|
Restores files and directories from a backup.
|
|
MSCDEX
|
MSCDEX [/D: driver /L:drive] [/M:bufsize] [/E /S /V]
|
Provides CD-ROM access.
|
|
SYS
|
SYS [drive1:][path]
|
Transfers system files to a disk.
|
|
SHARE
|
SHARE [/F:(space)] [/L:(locks)]
|
Installs file-sharing and locking capabilities.
|
|
SMARTDRV
|
SMARTDRV [size] [/E /V] [/C] [/L:size]
|
Disk caching utility.
|
|
SETVER
|
SETVER [drive:][path]filename [/B:bytes]
|
Sets the MS-DOS version number for a program.
|
|
ASSIGN
|
ASSIGN [/D]
|
Disables automatic drive-letter assignments.
|
|
FASTHELP
|
FASTHELP [command] [command] /?
|
Provides a quick overview of MS-DOS commands.
|
|
FC
|
FC [/A] [/C] [/L] [/LBn] [/N] [/OFF[LINE]] [/T]
|
Compares two files or sets of files and displays the differences between them.
|
|
FIND
|
FIND [/V] [/C] [/N] [/I] [/OFF[LINE]] “string” [[drive:][path]filename[ …]]
|
Searches for a text string in files.
|
|
MORE
|
MORE [filename]
|
Display the content of a text file one screen at a time
|
|
ECHO
|
ECHO [on/off]
|
This command can either show or hide the text of the commands you type. Command echoing is on by default
|
|
ECHO
|
ECHO [<message>]
|
Specifies the text to display on the screen.
|
|
PATH
|
PATH [[drive:][path] [;…]]
|
Displays or sets a search path for executable files.
|
|
SET
|
SET [variable=[string]]
|
Sets or displays environment variables.
|
|
VOL
|
VOL [drive:]
|
Displays a disk label and serial number.
|
|
SUBST
|
SUBST [drive1: [drive2:]path]
|
Associates a path with a drive letter.
|
|
EDLIN
|
EDLIN [drive:][path][filename]
|
Edits text files.
|
|
DEBUG
|
DEBUG [drive:][path][filename]
|
Starts the Debug program for testing and debugging assembly-language programs.
|
|
HIMEM.SYS
|
HIMEM.SYS [/TESTMEM:off] [/HMAMIN=amount]
|
Provides upper memory block (UMB) and high memory area (HMA) support.
|
|
UNFORMAT
|
UNFORMAT [drive:][path]
|
Restores a formatted disk.
|
|
GRAPHICS
|
GRAPHICS [type] [[drive:][path]filename] [/R] [/B] [/LCD][/PRINTBOX:STD|/PRINTBOX:LCD]
|
Enables output of graphical screen content to print
|
|
QBASIC
|
QBASIC [drive:][path]
|
Starts the MS-DOS-based application for creating and running BASIC programs.
|
|
KEYB
|
KEYB [/CODEPAGE=page[,country]] [/E]
|
Configures a keyboard for a specific language.
|
|
CHOICE
|
CHOICE [/C:choices] [/N] [/S] [/T:c,nn]
|
Provides a prompt with a list of choices.
|
|
DISKCOMP
|
DISKCOMP [drive1:][drive2:]
|
Compares the contents of two floppy disks.
|
|
PRINT
|
PRINT [/D:device] [filename]
|
Sends a text file to a printer.
|
|
SORT
|
SORT [drive:][path][filename]
|
Sorts the contents of a text file.
|
|
APPEND
|
APPEND [[drive:]path[;…]]
|
Sets or displays the search path for data files.
|
|
ASSOC
|
ASSOC [.ext[=[fileType]]]
|
Associates file extension with a file type.
|
|
LABEL
|
LABEL [drive:][label]
|
Creates, changes, or deletes the volume label of a disk.
|
|
RECOVER
|
RECOVER [drive:][path][filename]
|
Recovers readable information from a bad or defective disk.
|
|
FASTOPEN
|
FASTOPEN [/X] [drive:] [path] [/R]
|
Speeds up the opening of files.
|
|
GOTO
|
GOTO <label>
|
Directs the command interpreter to a labeled line in a batch program.
|
|
SHIFT
|
SHIFT [/n <N>]
|
Shifts the position of batch parameters in a batch file.
|
|
JOIN
|
JOIN path [drive:]
|
Joins a drive letter and directory path.
|
|
SMARTDRV
|
SMARTDRV [size] [buffers] [doublebuffer] [/E] [/C] [/L] [/V] [/B]
|
Manages and optimizes disk caching.
|
|
BATCH
|
BATCH [filename]
|
Executes the commands specified in a batch file.
|
|
CALL
|
CALL [drive:][path]filename [batch-parameters]
|
Calls one batch program from another.
|